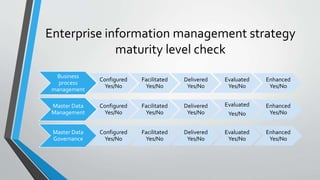
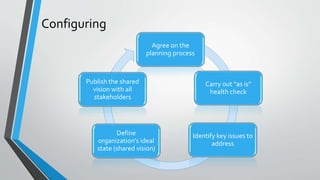
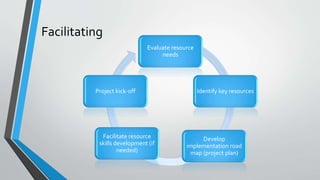
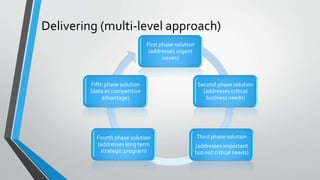
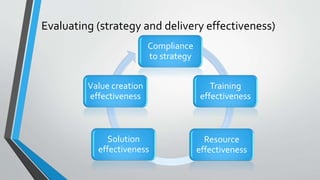
The document discusses the importance of aligning master data management, master data governance, and business process management for effective enterprise information management and decision making. It states that bad data costs businesses 10-20% of annual revenue. The document provides a framework for assessing the maturity of these initiatives and advancing them in a synchronized manner from the initial configuration stage through facilitating, delivering, evaluating, and changing stages. It identifies key factors for evaluating solutions for master data management, governance, and business process management.