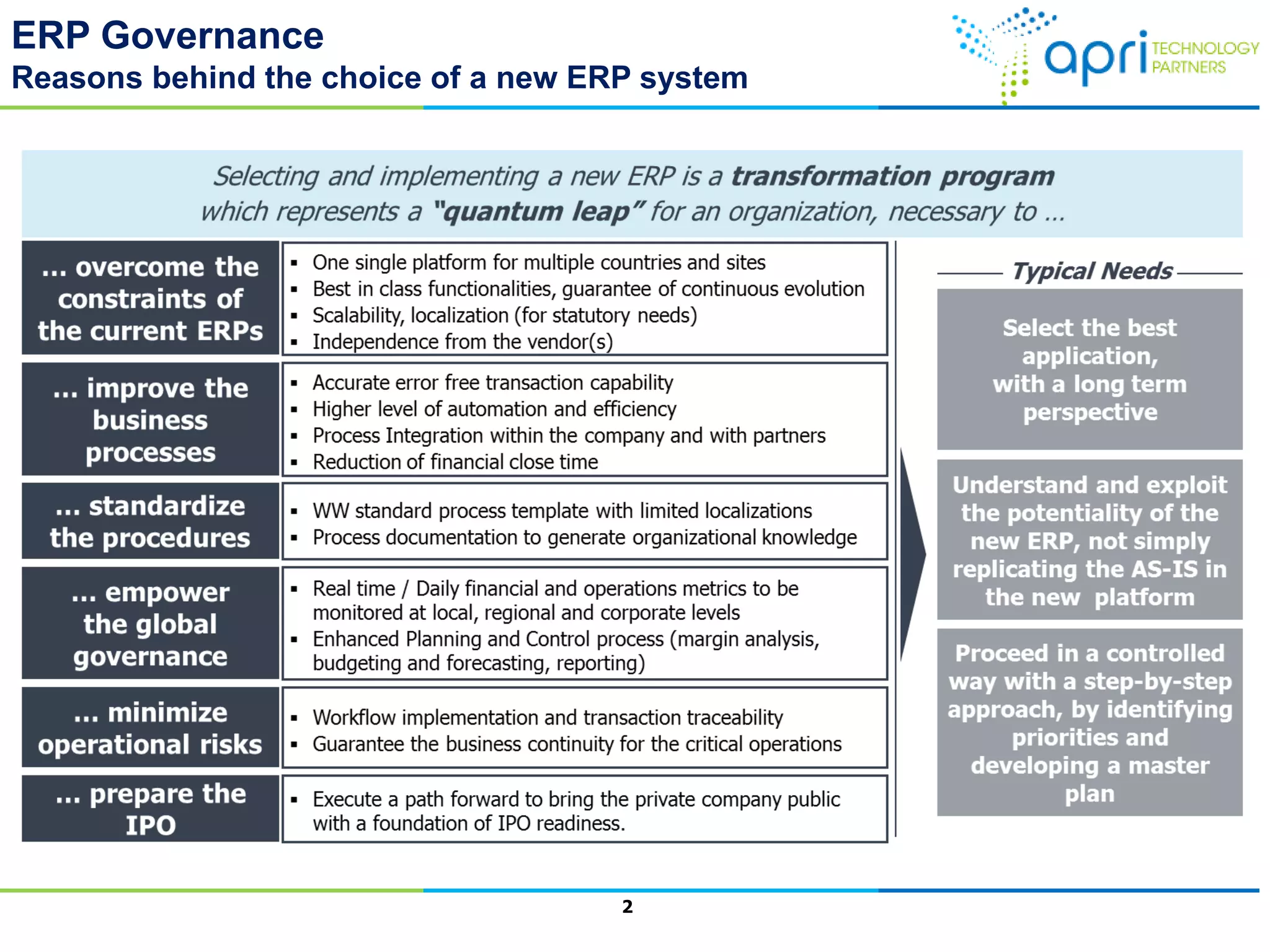
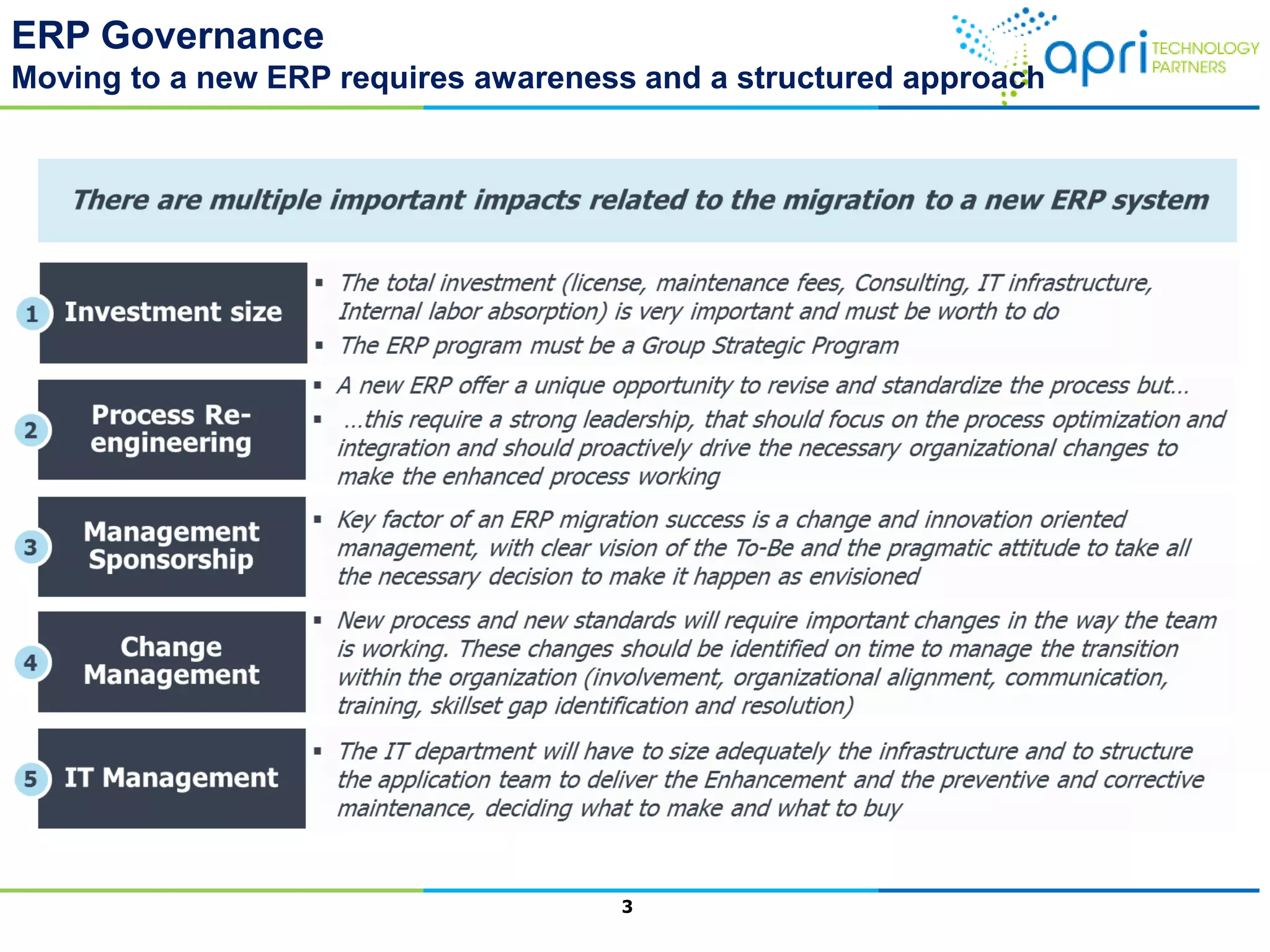
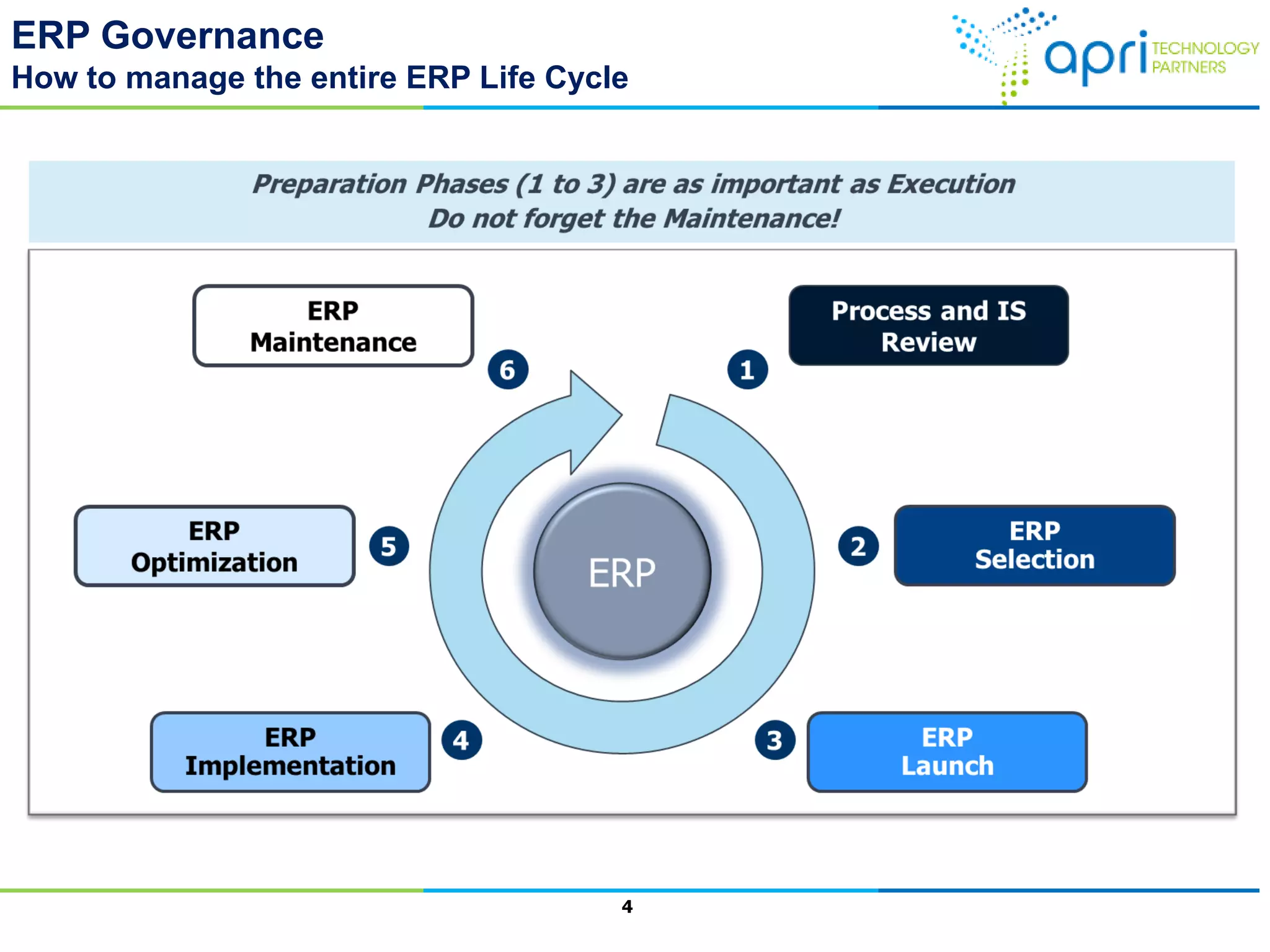
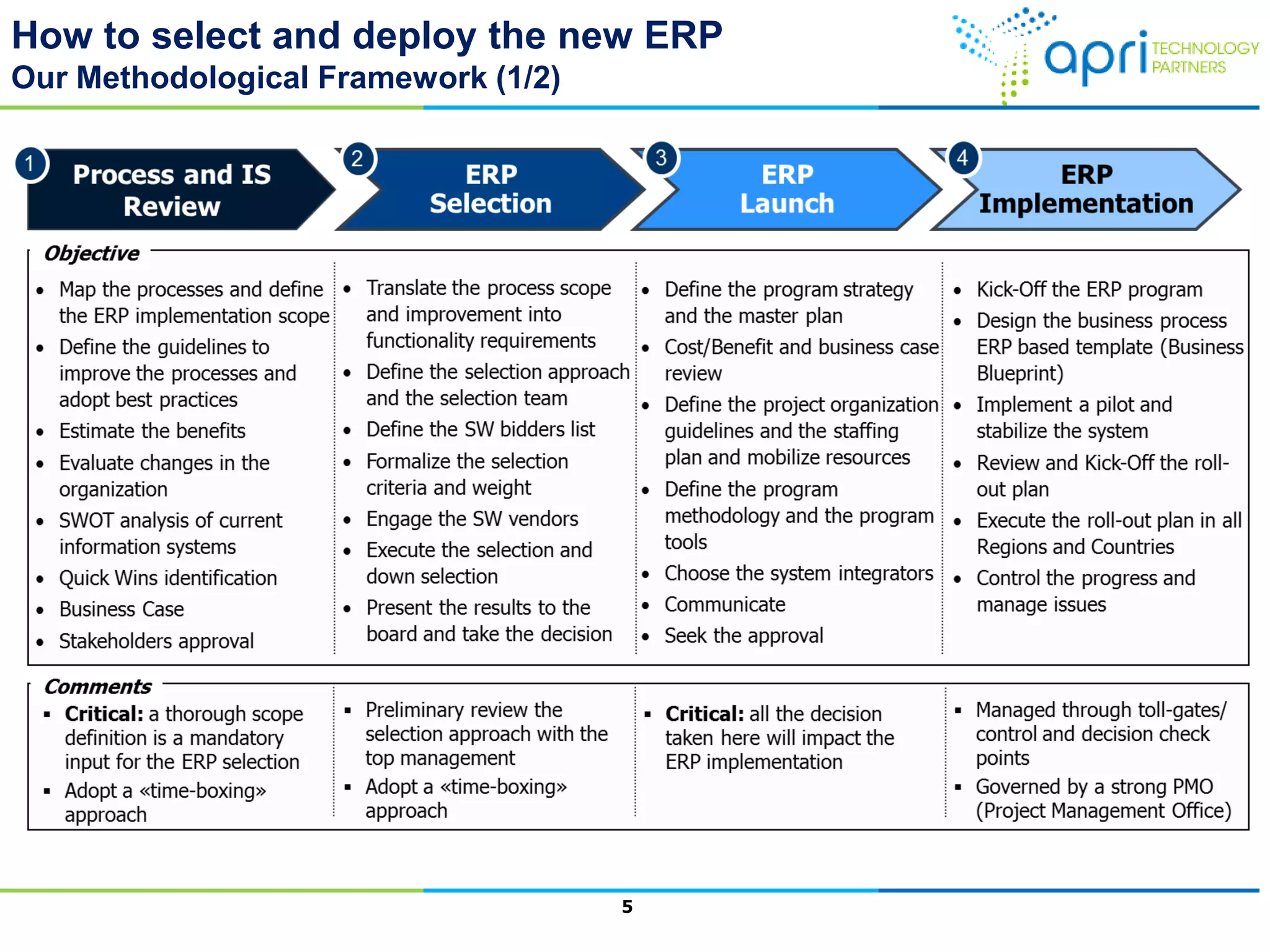
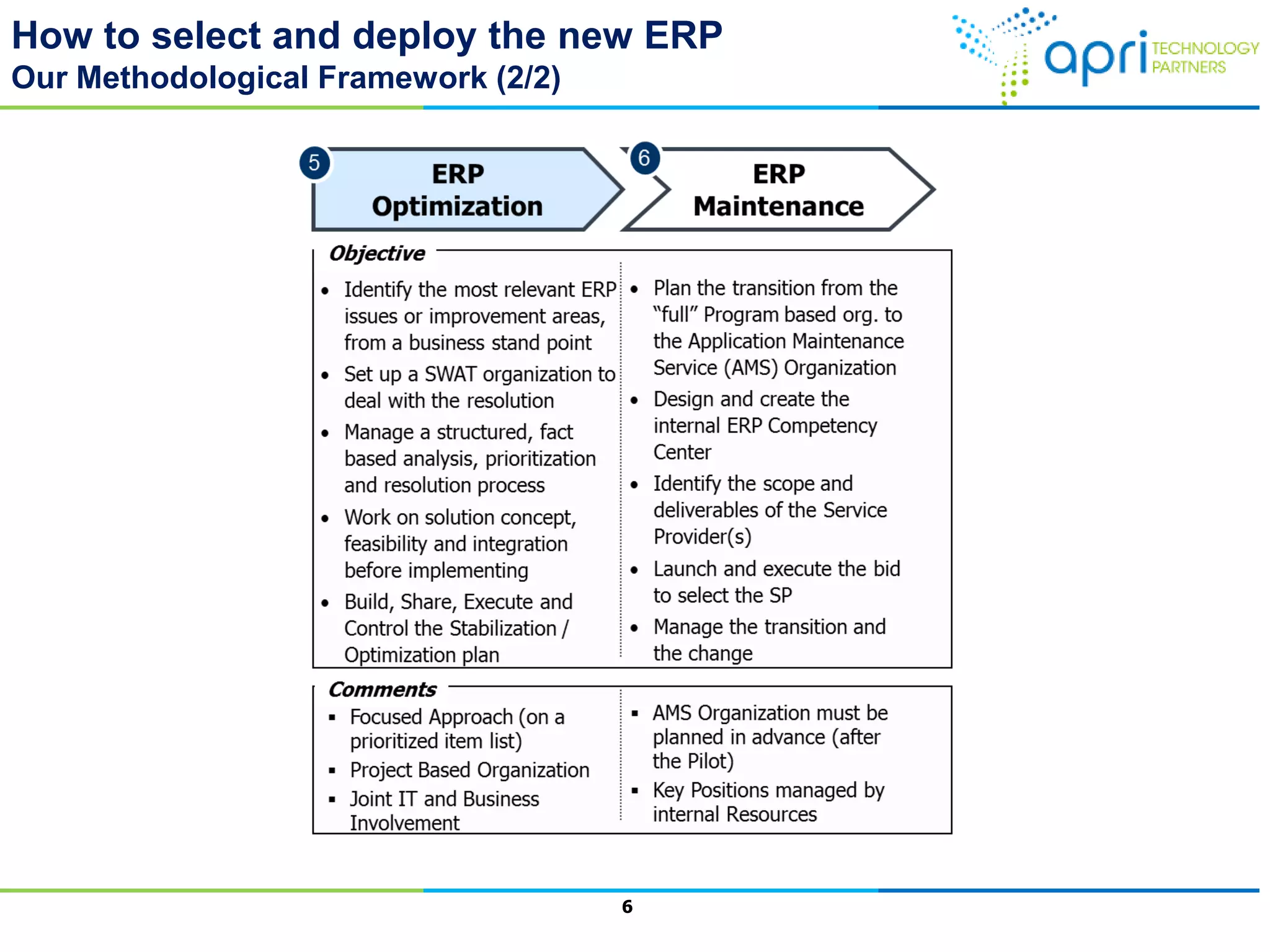
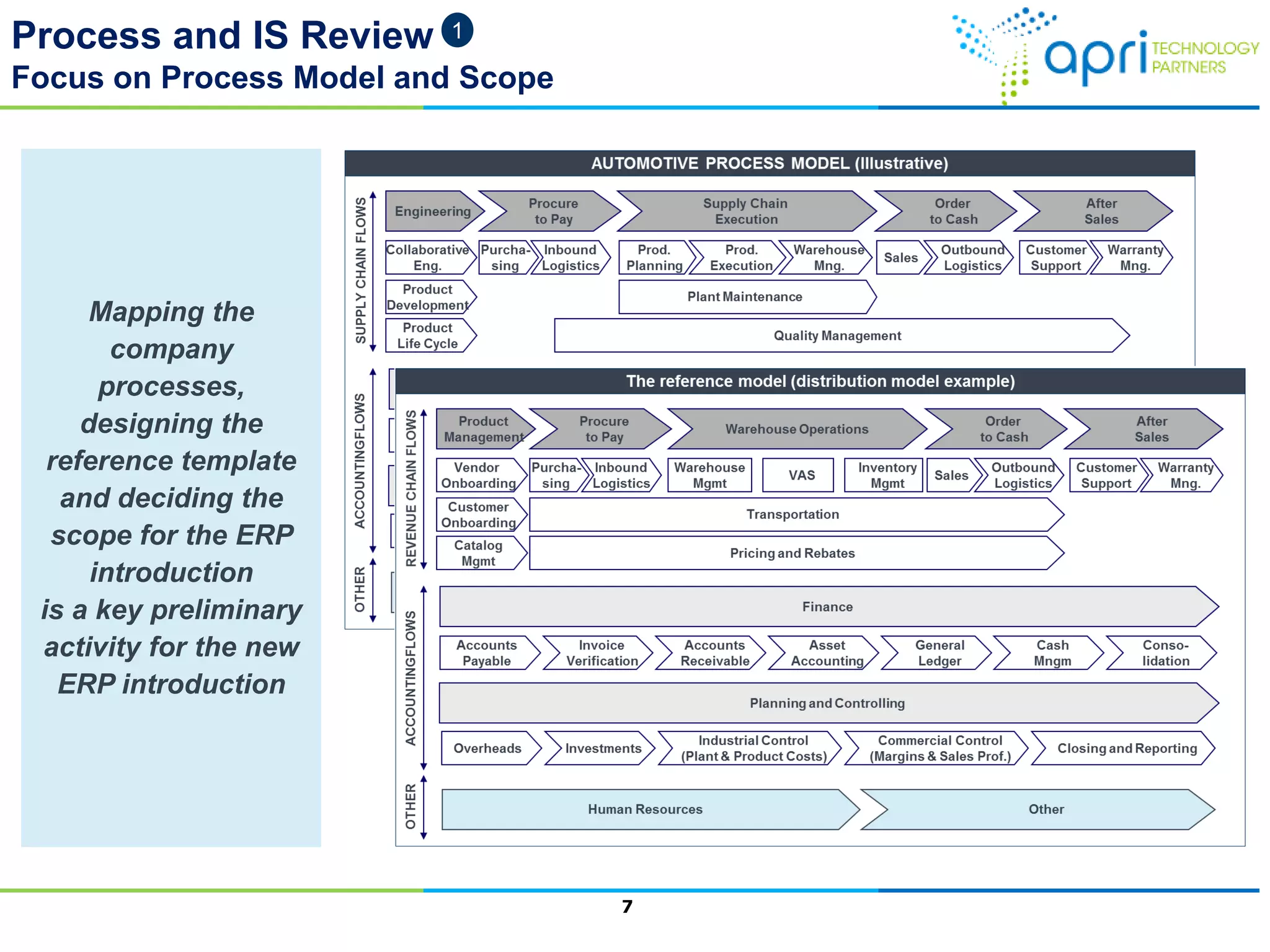
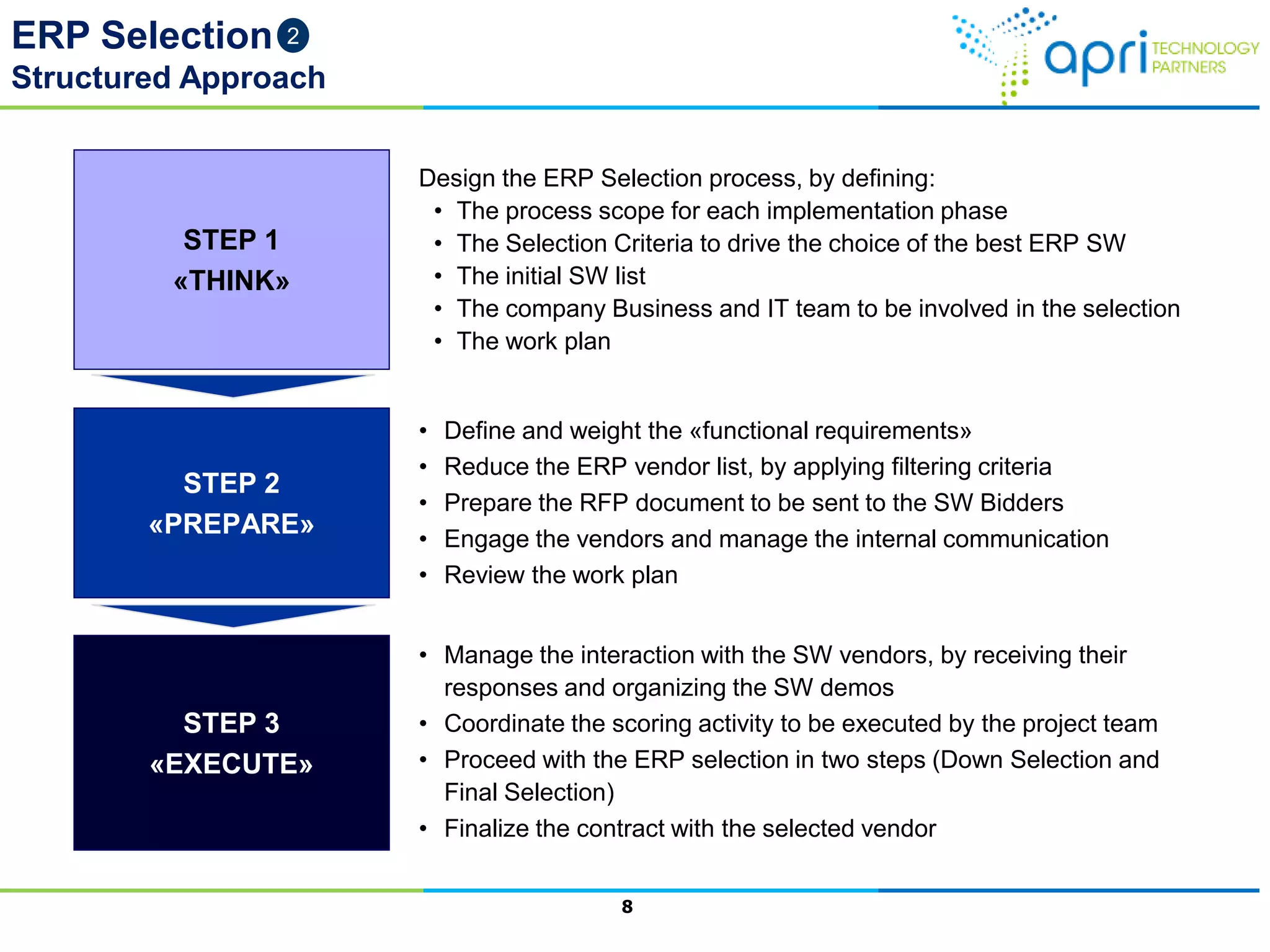
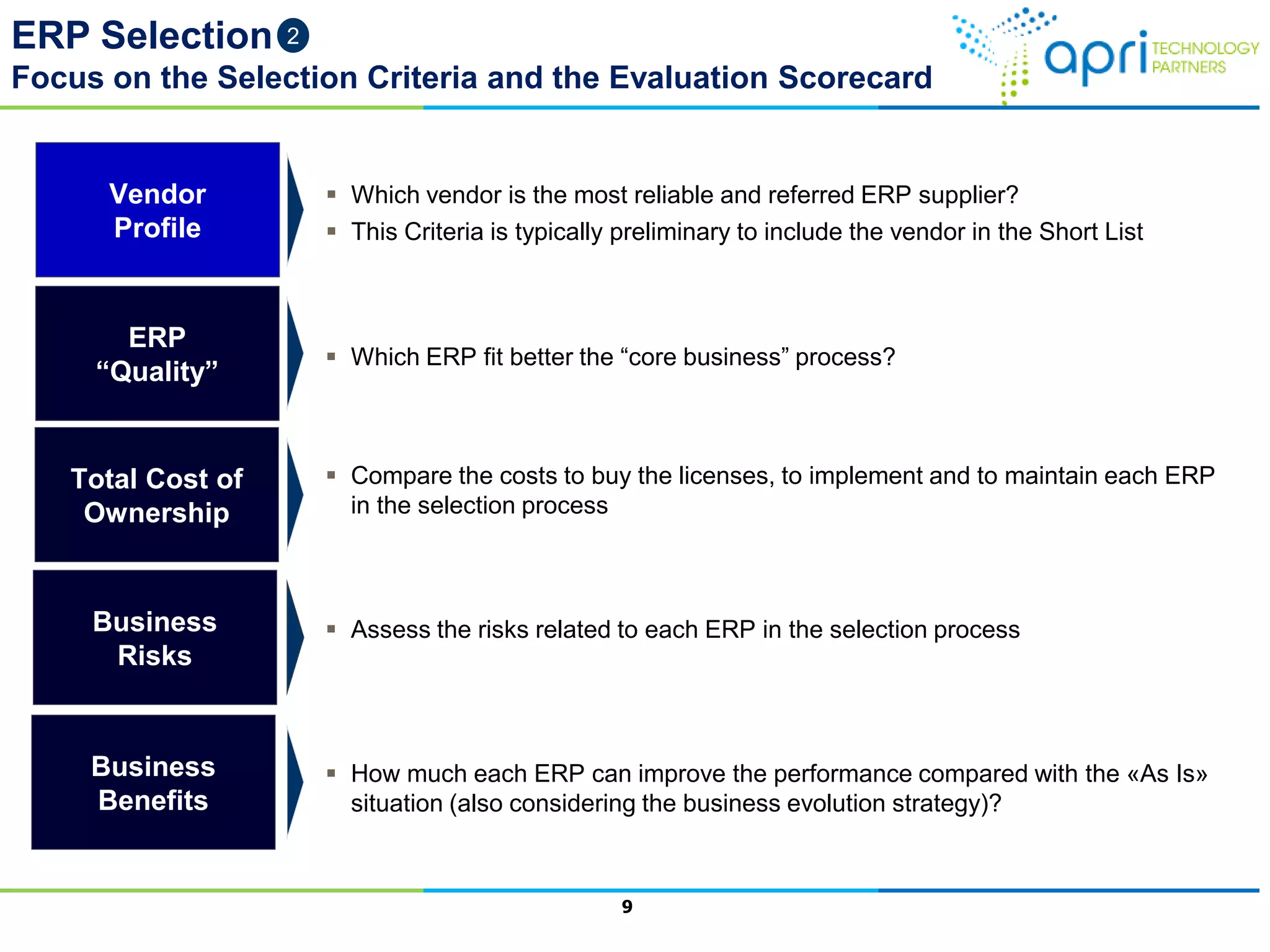
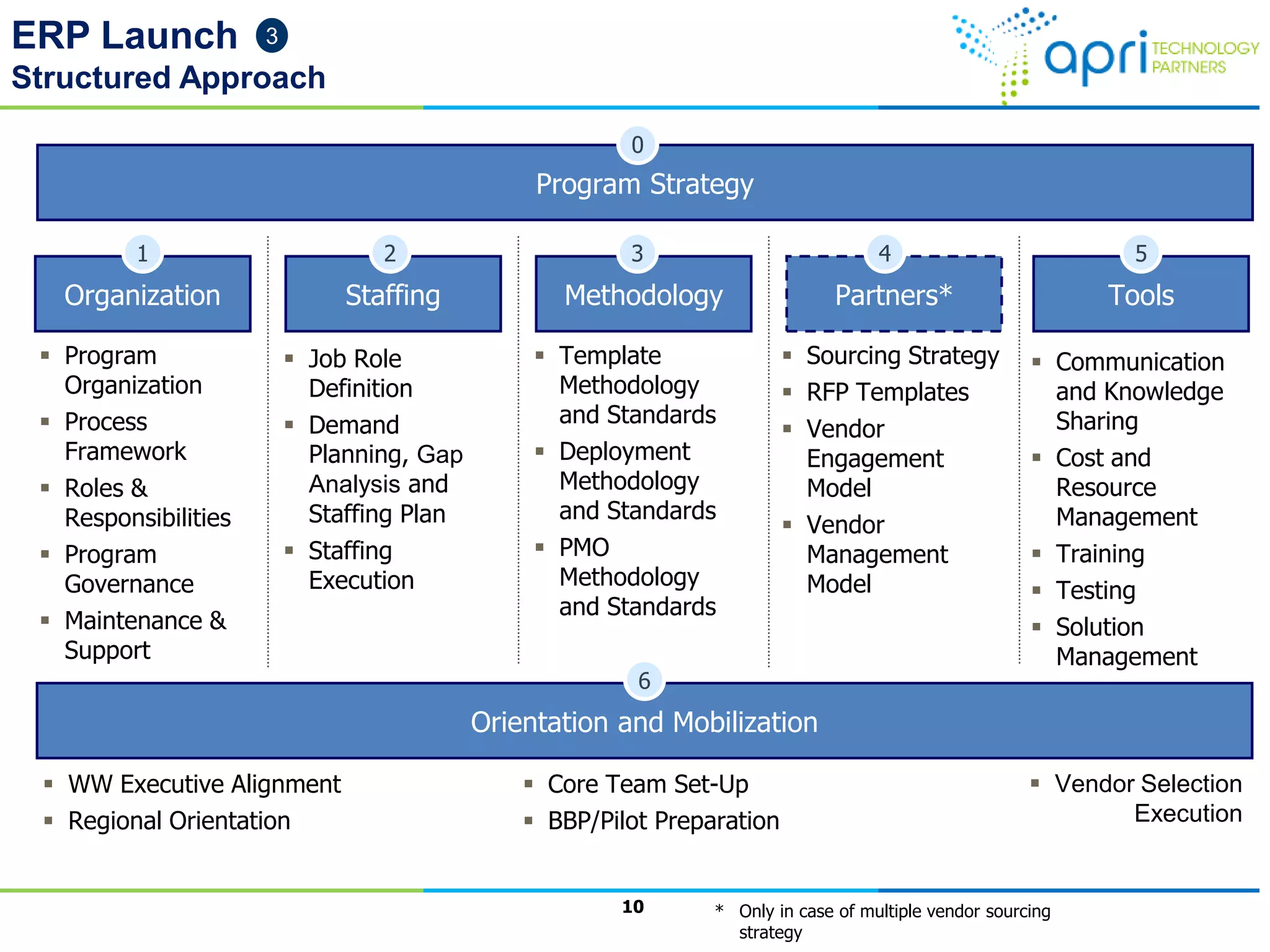
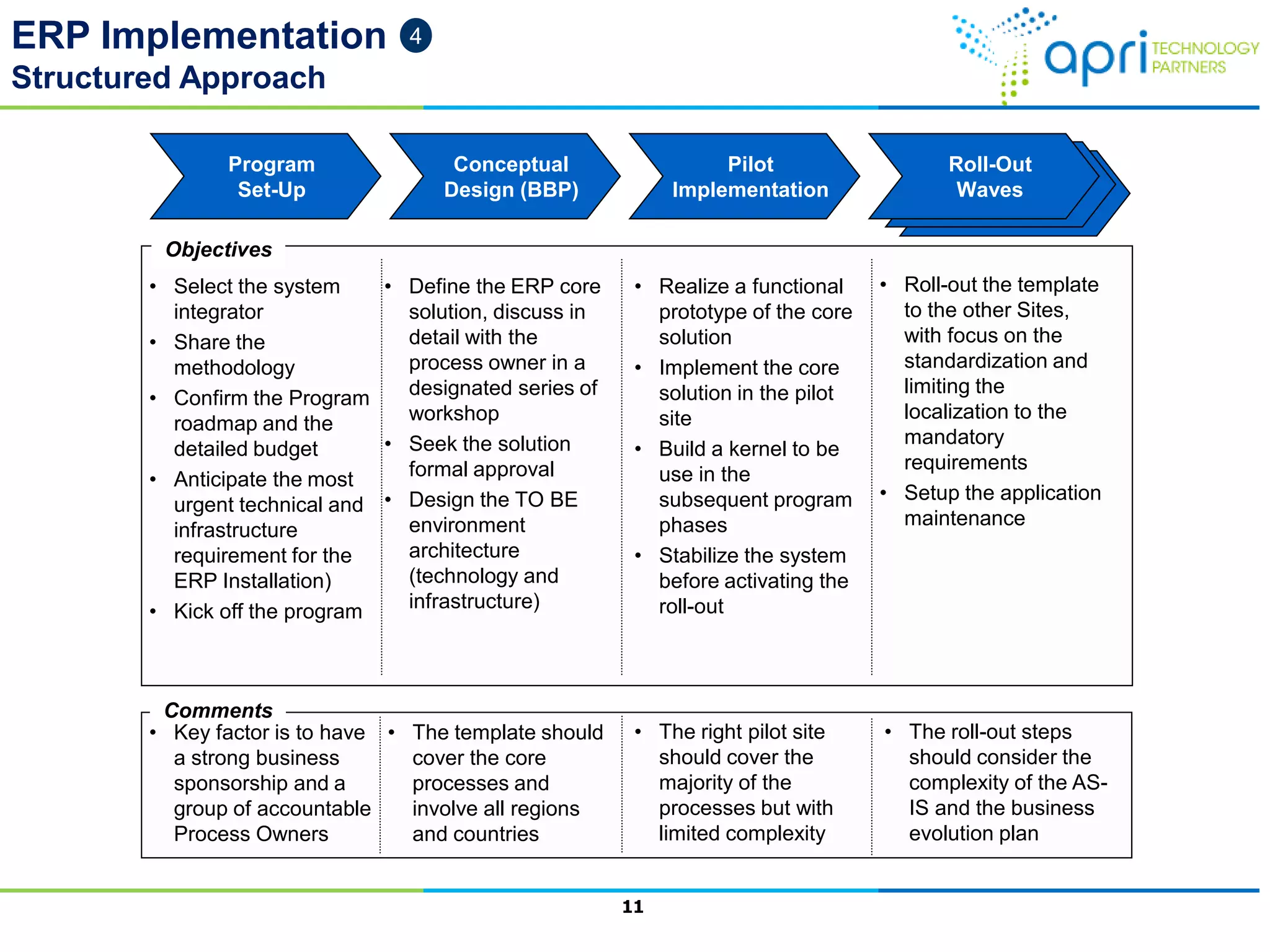
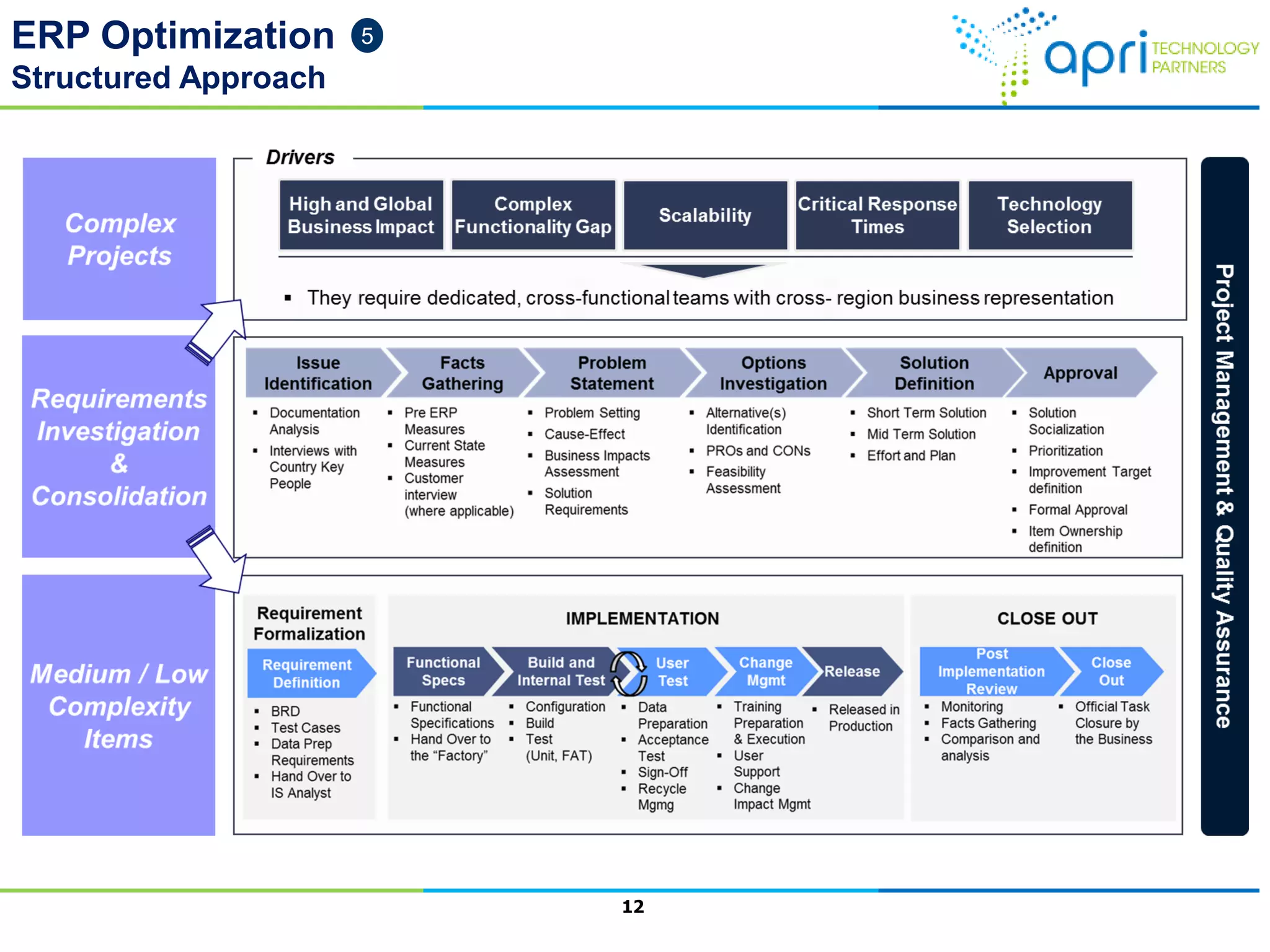
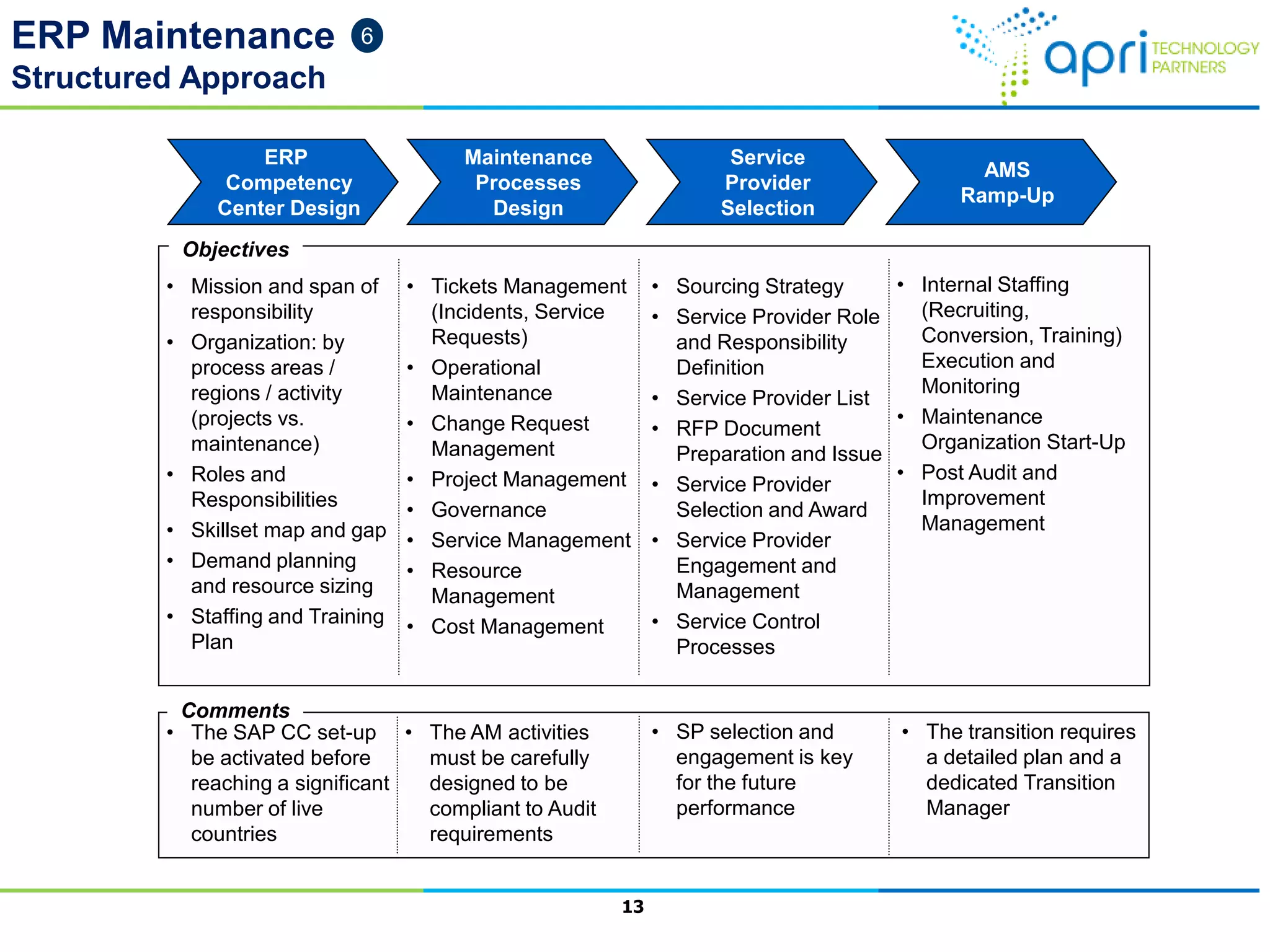
This document outlines a structured methodology for managing an ERP system through its entire lifecycle including selection, implementation, optimization, and maintenance. It discusses setting up an ERP governance program, selecting the right ERP through a multi-step process focusing on criteria and evaluation, launching the system in a phased approach starting with a pilot, optimizing processes on the new ERP, and establishing an ERP competency center for ongoing maintenance.