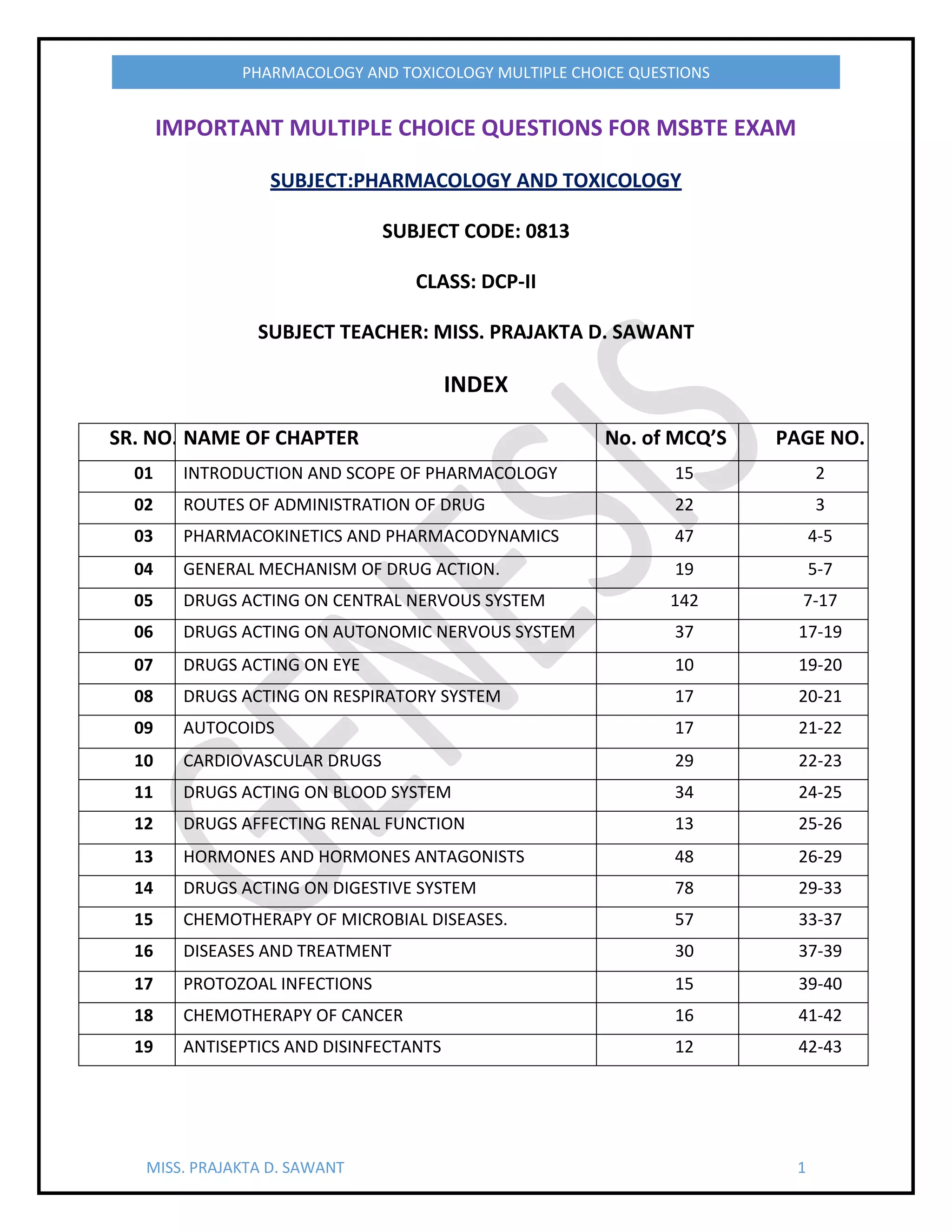
This document provides a multiple choice question (MCQ) bank for the Pharmacology and Toxicology exam for the DCP-II class. It is authored by Prajakta Sawant and contains MCQs organized across 19 chapters of the subject, including general pharmacology, routes of drug administration, pharmacokinetics, drugs acting on different body systems like CNS, CVS, and endocrine system. Each chapter provides 15-150 MCQs to help students prepare for the MSBTE exam. Key areas covered include general anesthetics, analgesics, antipryetics, anti-inflammatory drugs, autonomic nervous system drugs, and chemotherapy of infections.