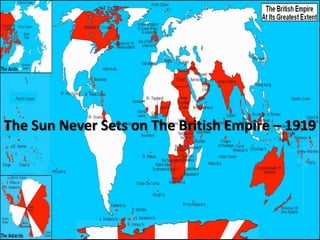
This document discusses European imperialism from the 15th to early 20th centuries. It defines imperialism as the extension of rule or influence by one nation over another. Major motivations for European imperialism included nationalism, economic incentives like trade and resource extraction, and social justifications like the belief in European racial and cultural superiority. The document outlines different forms of colonial control employed by Europeans, patterns of colonial management, resistance movements against imperialism, negative consequences like loss of native independence and culture, and some potential "positive" consequences like reduced local warfare and infrastructure development.