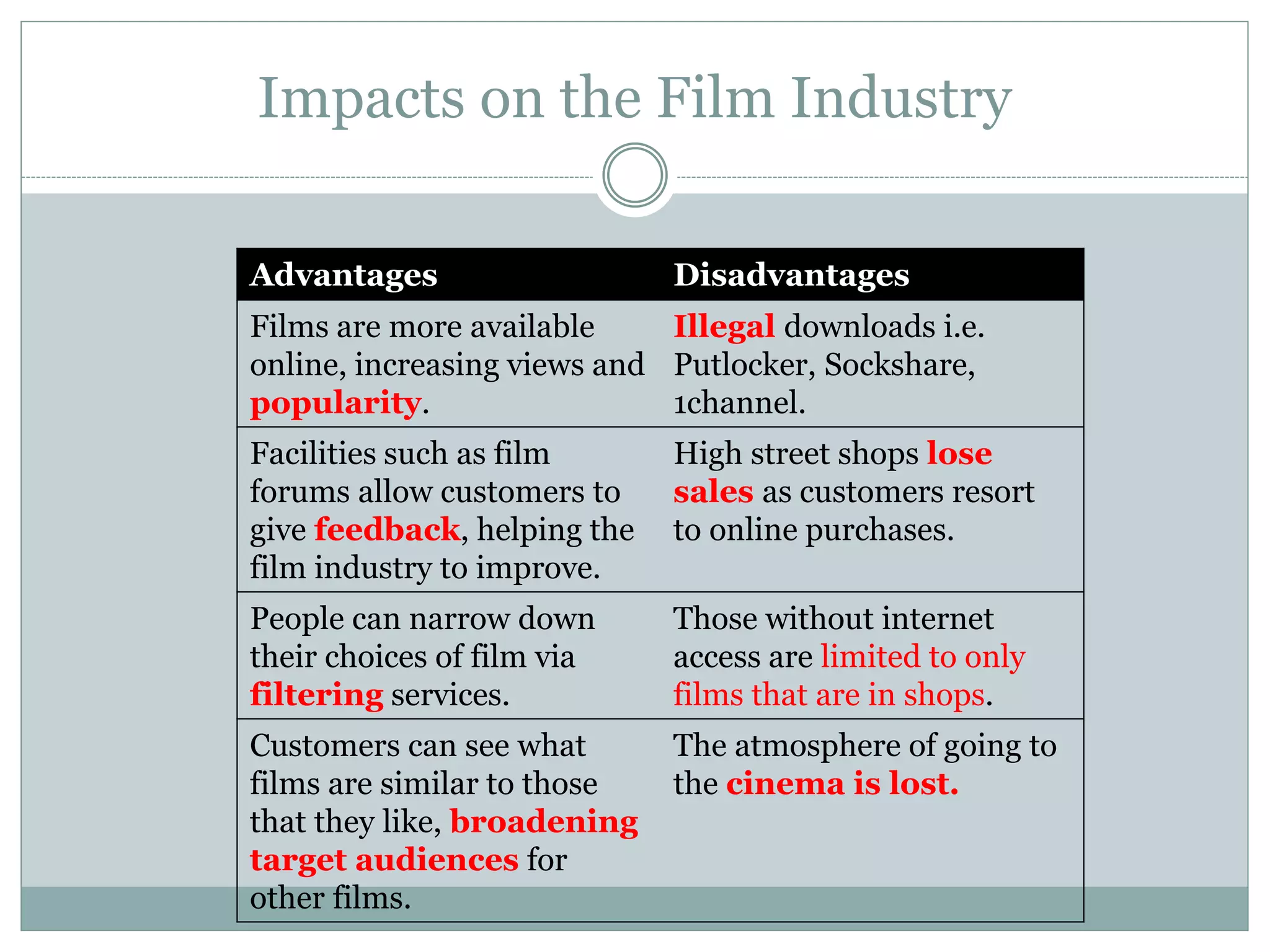
Digital technology has revolutionized film production, distribution, marketing and exhibition. It has made films cheaper and easier to make and distribute, while enhancing the viewing experience through technologies like 3D and IMAX. Audiences have become more active "produsers" through technologies like social media that allow them to engage more directly with content. This fragmentation makes it harder for institutions to reach all audiences with one message. Relationships between institutions and audiences have changed, with audiences now pulling content through various platforms rather than just having institutions push media to them. The film industry has been impacted through the "long tail" effect of increased online distribution broadening audiences, and through new technologies used in production and new forms of marketing and exhibition.