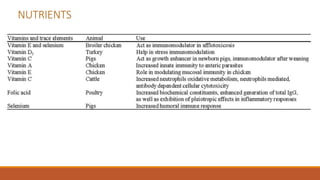
This document discusses immunomodulators, which are natural or synthetic substances that help regulate or normalize the immune system by increasing or decreasing immune responsiveness. It describes various types of immunomodulators including physiological products like cytokines and hormones, microbial products, synthetic chemical compounds, herbal products, adjuvants, and nutrients. Cytokines play a key role in modulating immune responses and functions of cytokines like TNF-α, IL-1, IL-10, IL-12, and IFN-γ in innate immunity and IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, TGF-β, and IFN-γ in adaptive immunity are discussed in detail. The use of cytokines as novel immunomodulators for vaccines