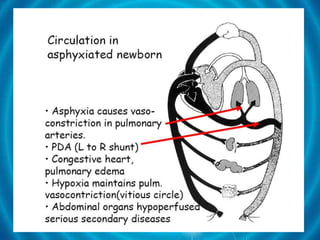
Immediate care of newborns involves clearing the airways of mucus, maintaining proper temperature regulation, and caring for the umbilical cord. To clear airways, suction should be used gently in the mouth and nose without delay. The baby's temperature should be monitored and maintained at 21°C through wrapping in warm blankets. Finally, the umbilical cord is clamped and cut, and the eyes are cared for to prevent infection.