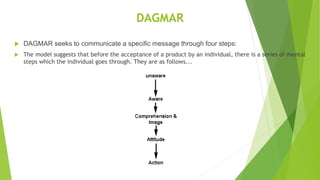
The document discusses advertising objectives such as increasing sales, encouraging trial and usage, and changing consumer attitudes. It also covers topics like DAGMAR, which is an approach for setting measurable advertising goals, brand objectives to make a brand top-of-mind for consumers, how consumer attitudes are shaped by advertising, different market structures defined by factors like competition and barriers to entry, and integrated marketing communication tools that combine different channels like advertising, PR, and digital marketing. The case study at the end discusses a cereal company that decreased its advertising budget despite falling sales, in an attempt to lower prices and become more competitive.