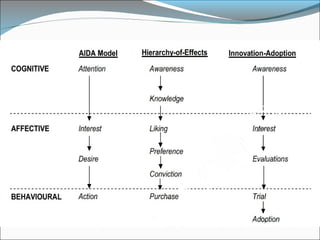
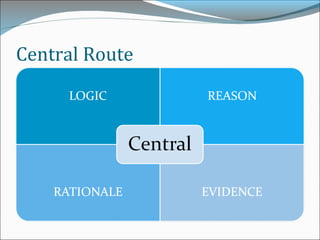
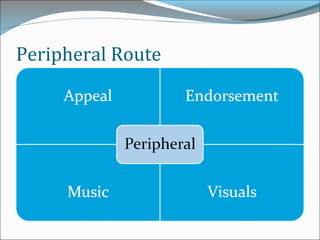
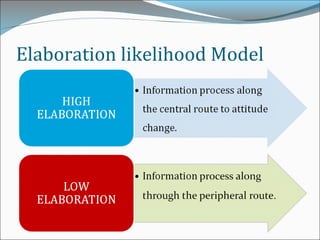
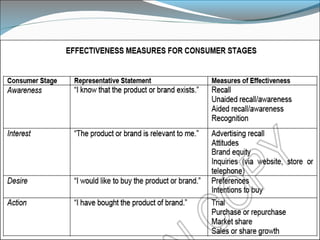
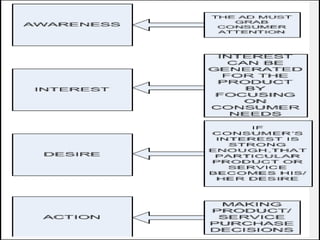
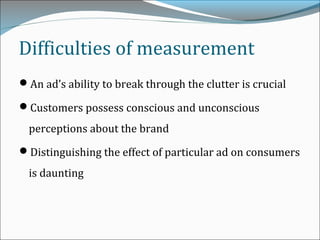
This document discusses consumer perspectives on advertising. It begins by explaining that advertising aims to understand consumer interests and reactions. It then discusses what advertising is, why companies advertise, and traditional models of how consumers process advertisements. It introduces the Elaboration Likelihood Model, which describes central and peripheral routes of persuasion. The document also covers subliminal advertising, measurement of advertising effectiveness using models like AIDA, and challenges in measuring effectiveness. It concludes that effective advertising requires understanding consumers.