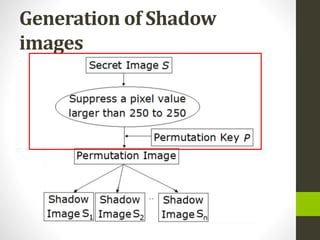
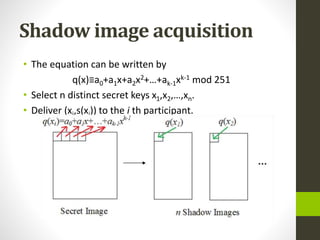
This document discusses image secret sharing, which is a technique to securely distribute a secret image among multiple participants. It describes Shamir's secret sharing algorithm, which divides a secret image into shadow images using polynomial interpolation. At least k shadow images are needed to reconstruct the original secret image. The document outlines the steps to generate and distribute shadow images and then recover the secret image. It also covers advantages like robustness and flexibility, disadvantages like potential information leakage, and applications like secure storage and password generation.