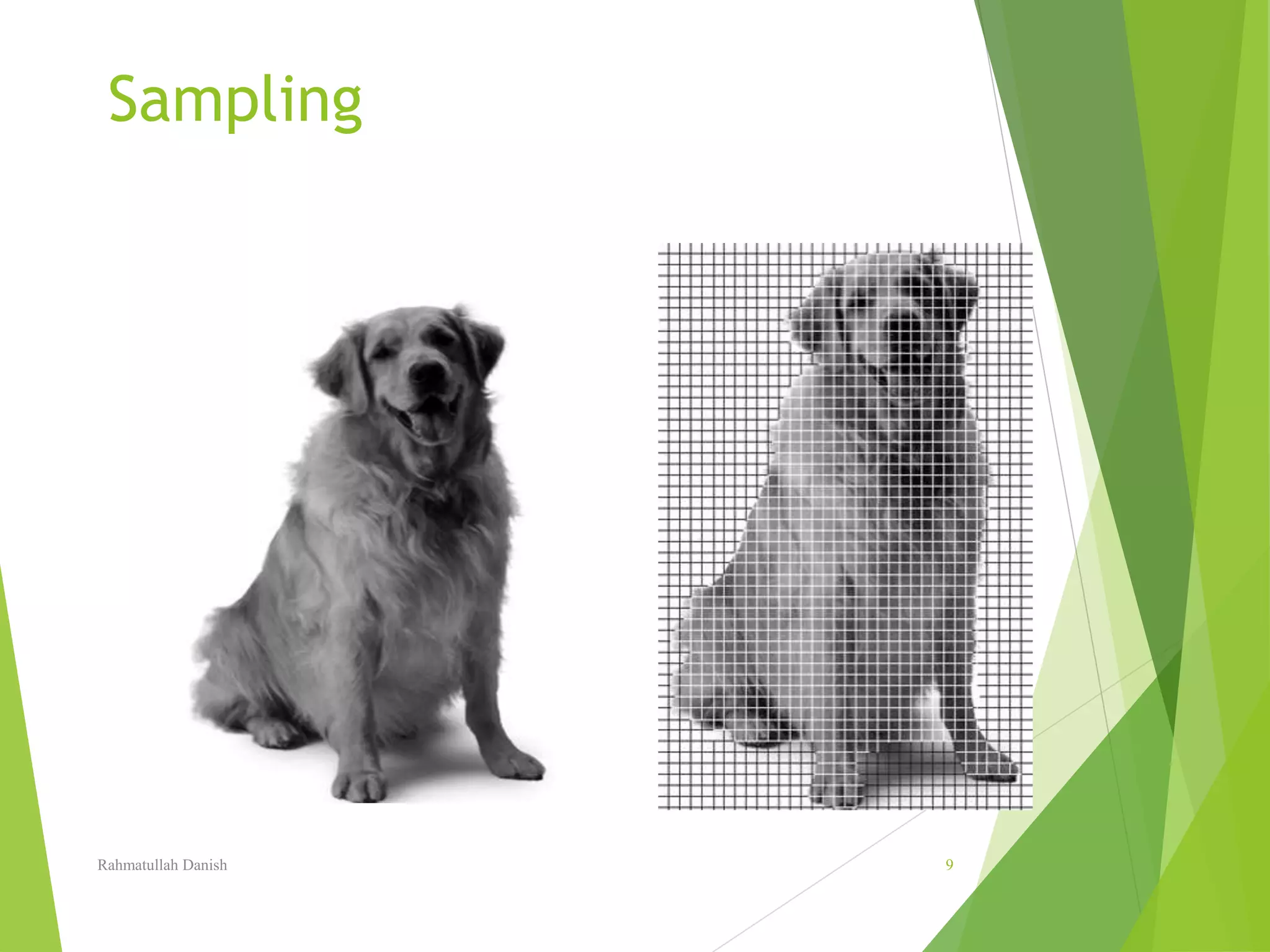
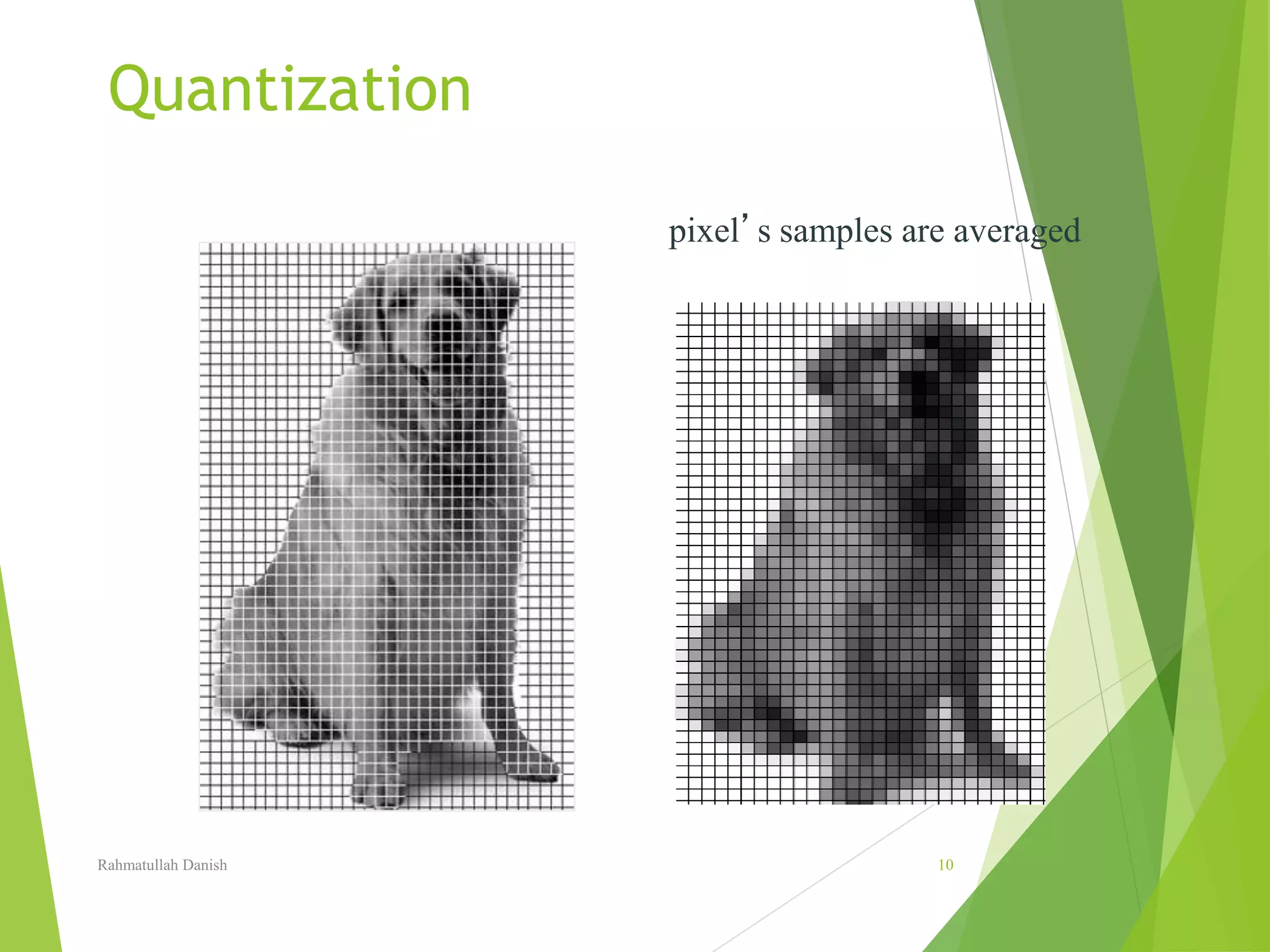
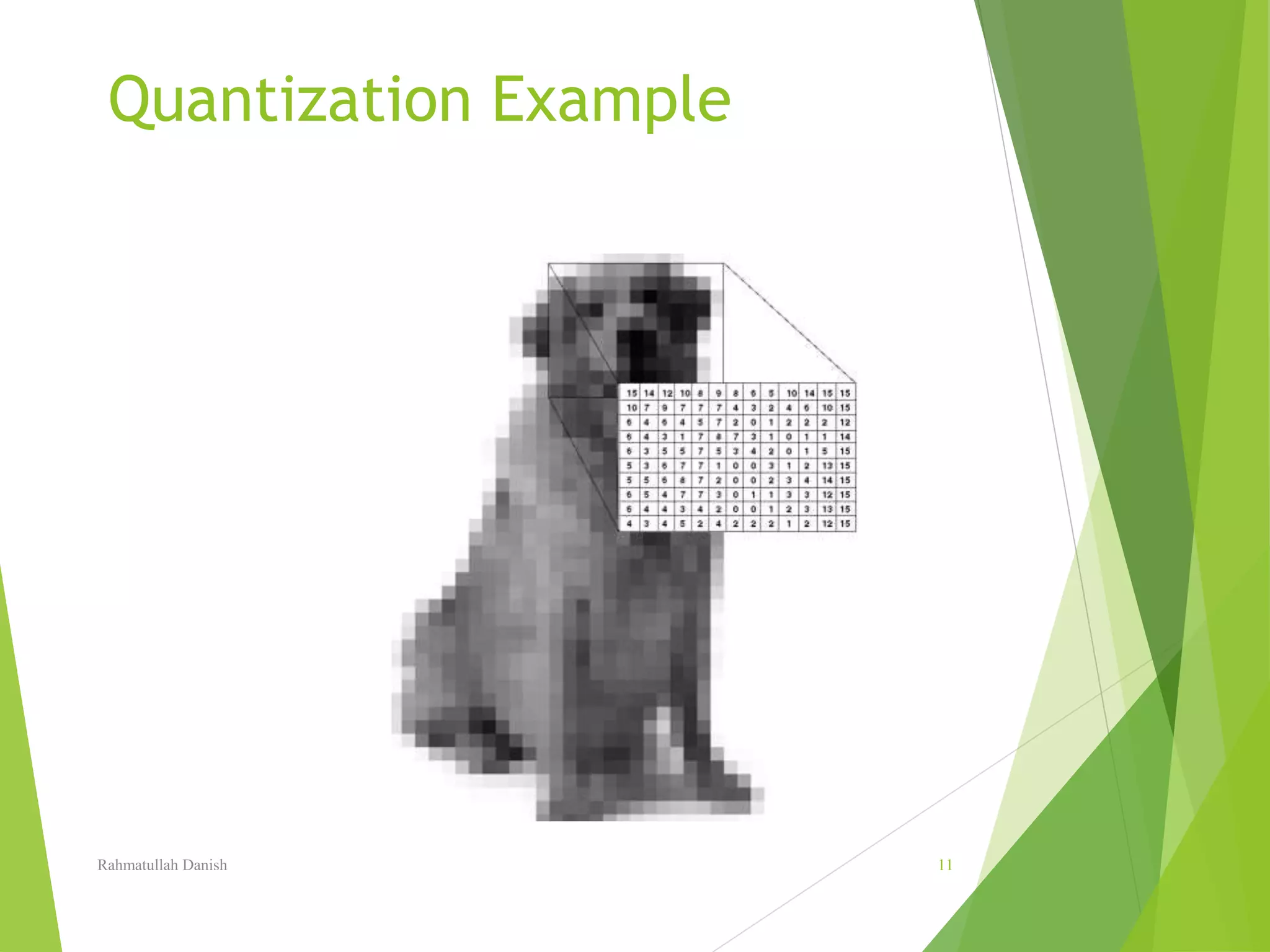
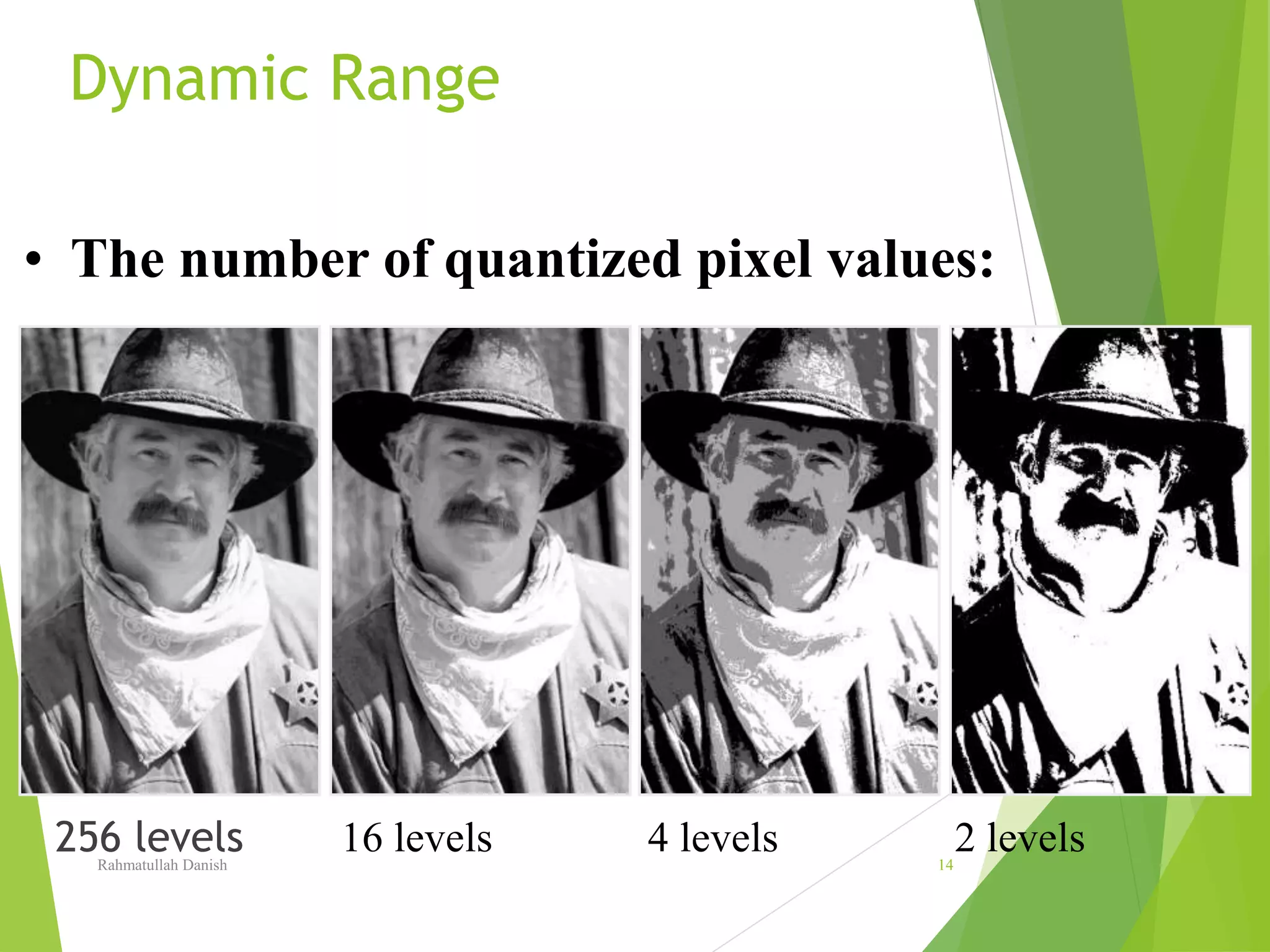
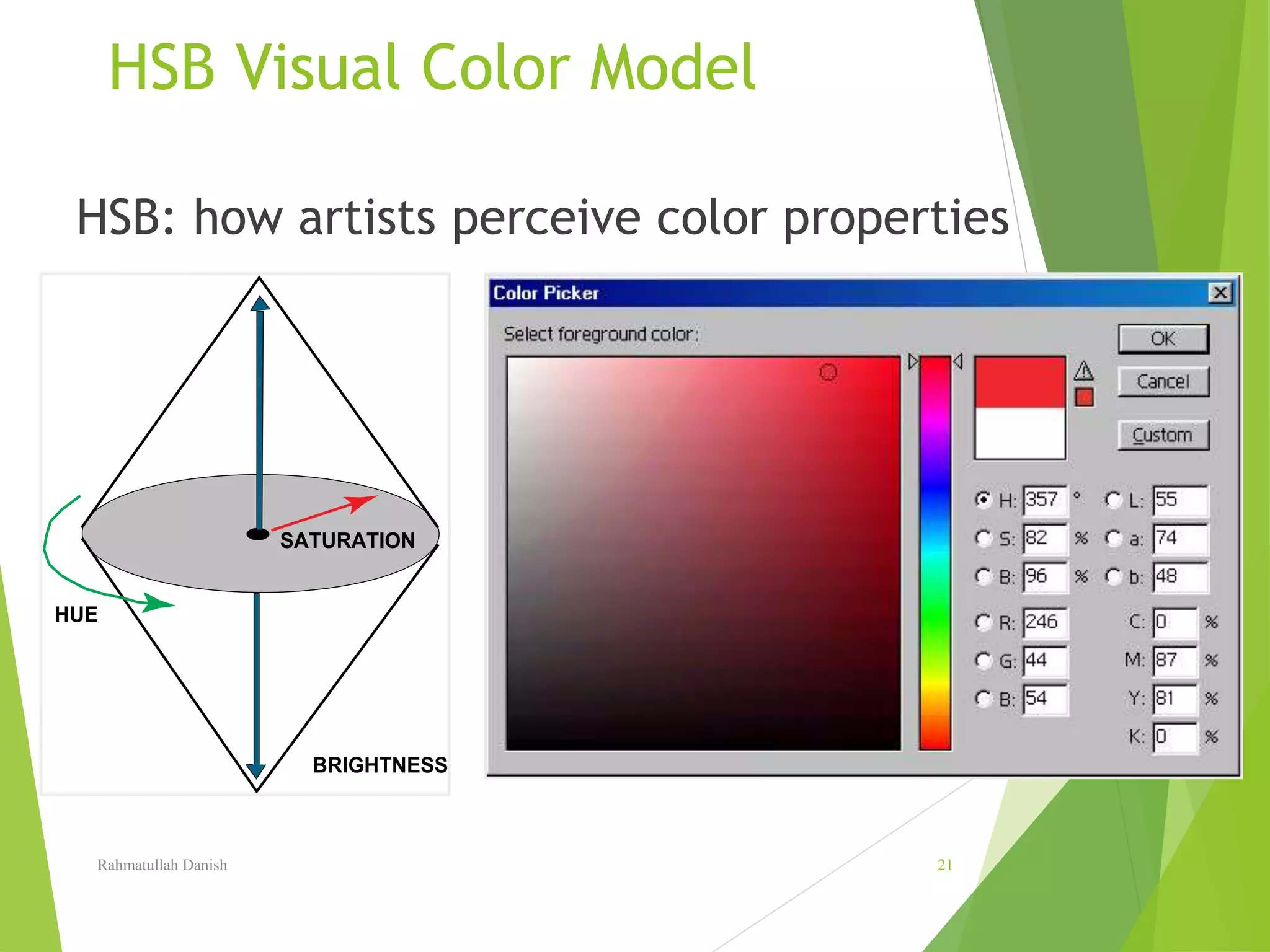
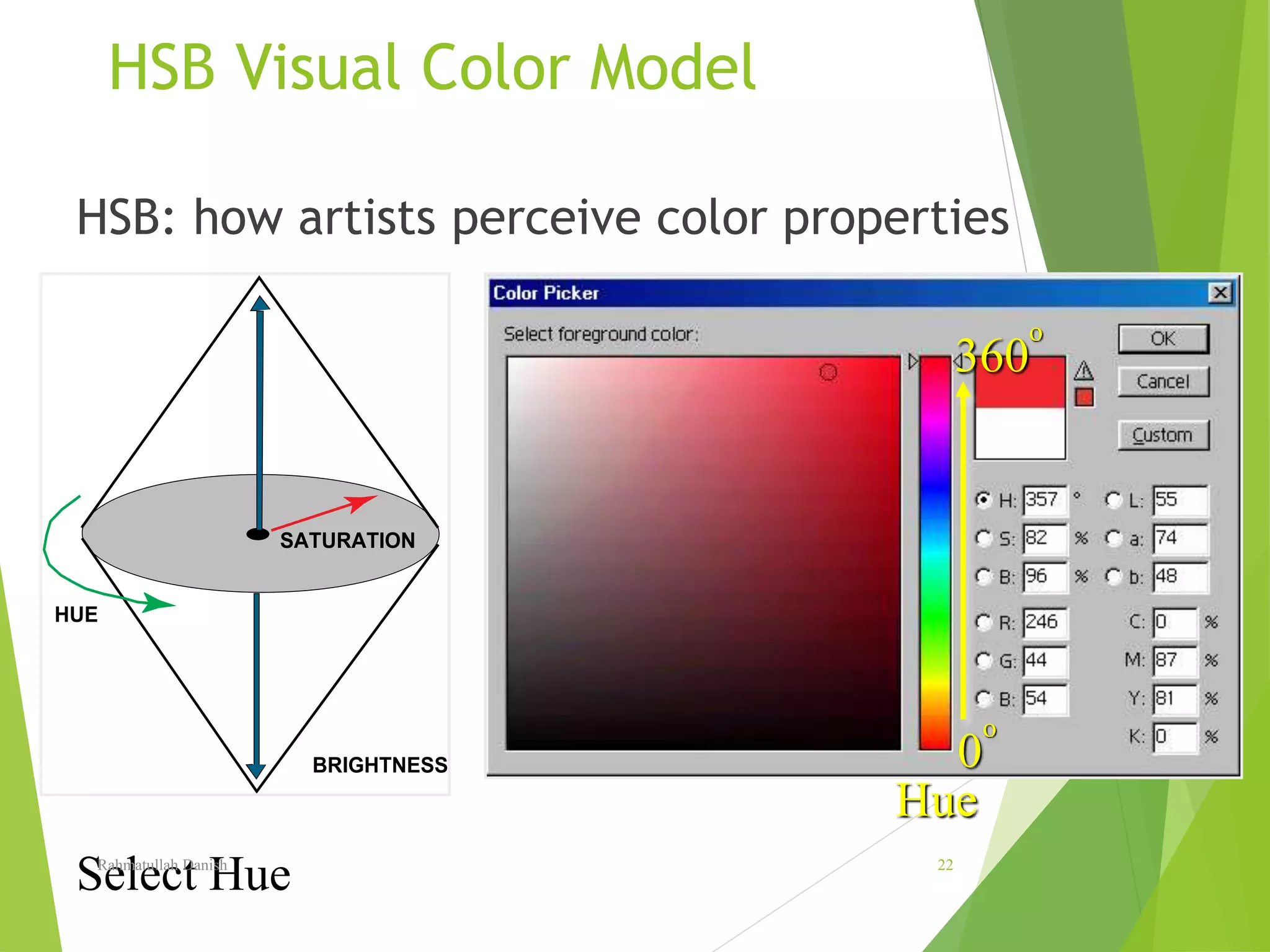
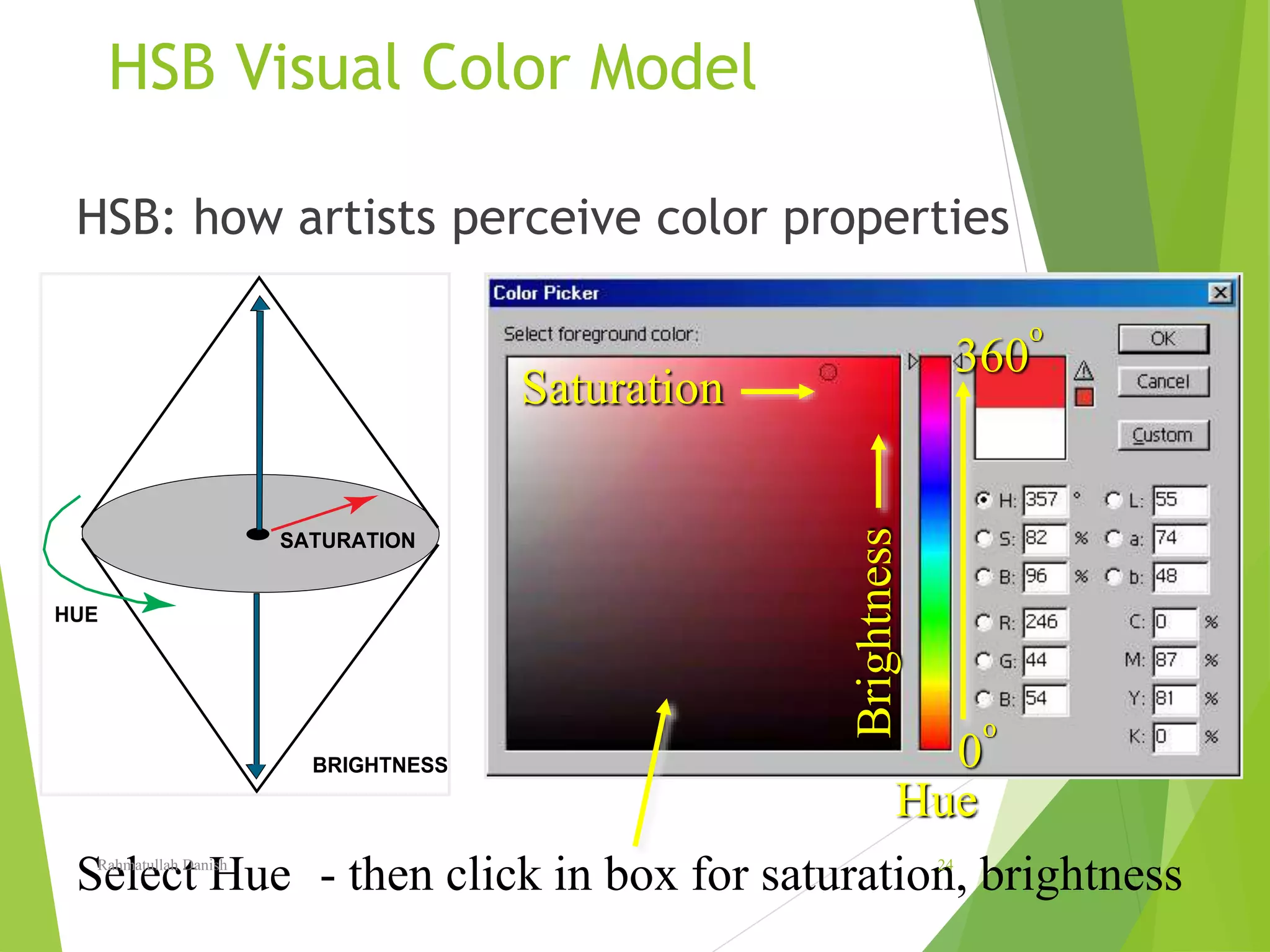
1. The document discusses various topics related to digital image representation and processing. It describes how images are digitized through sampling and quantization.
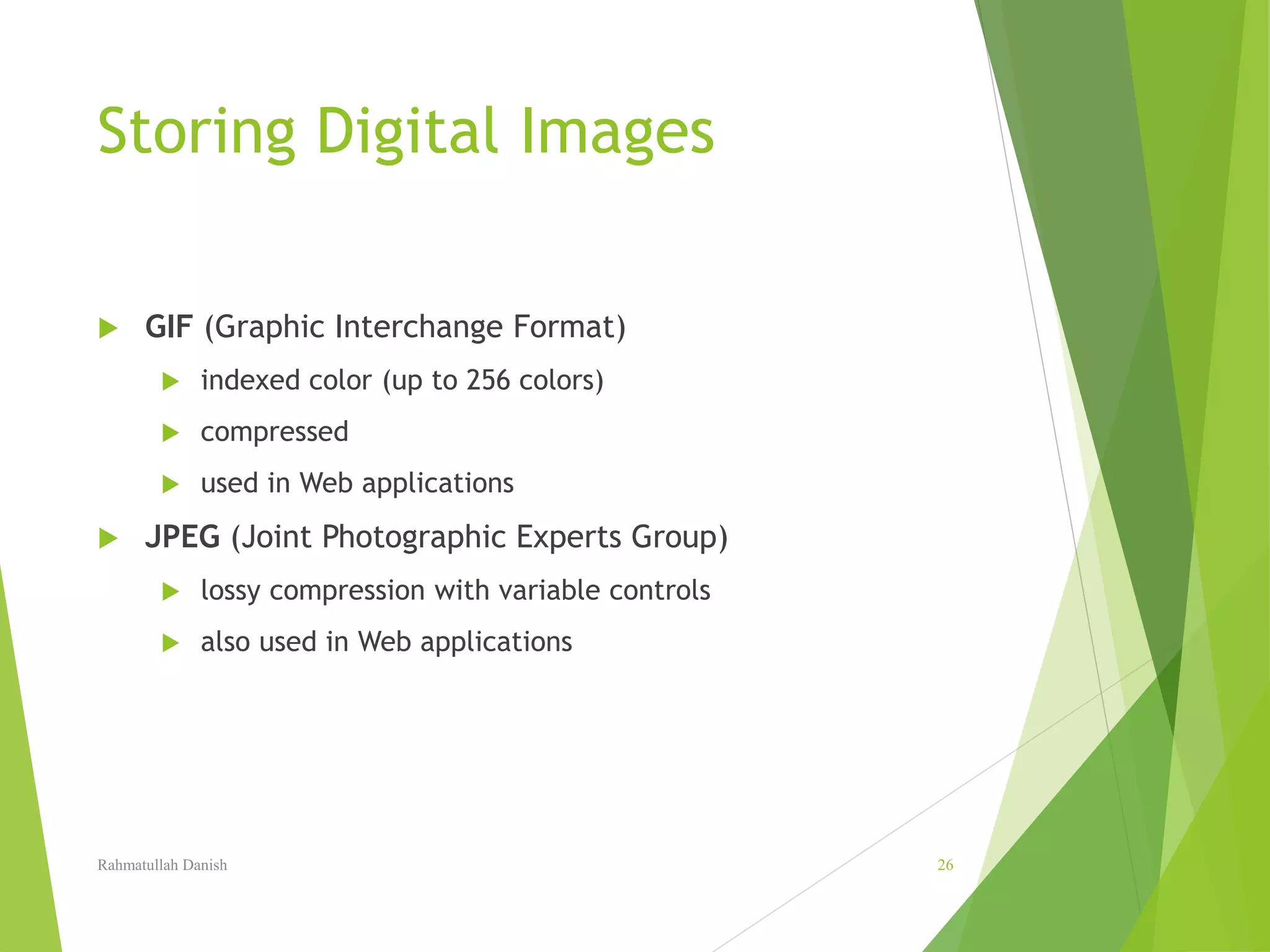
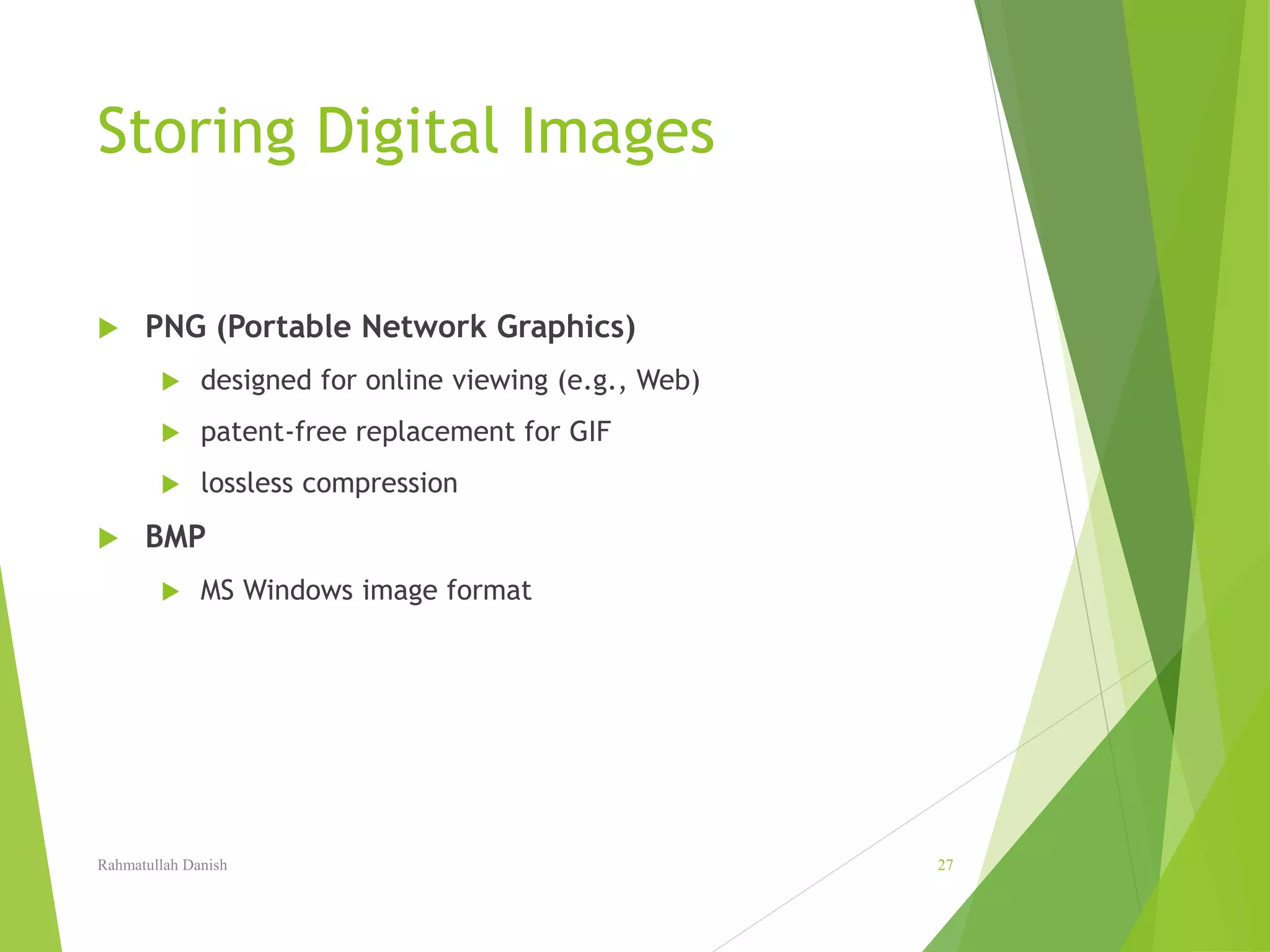
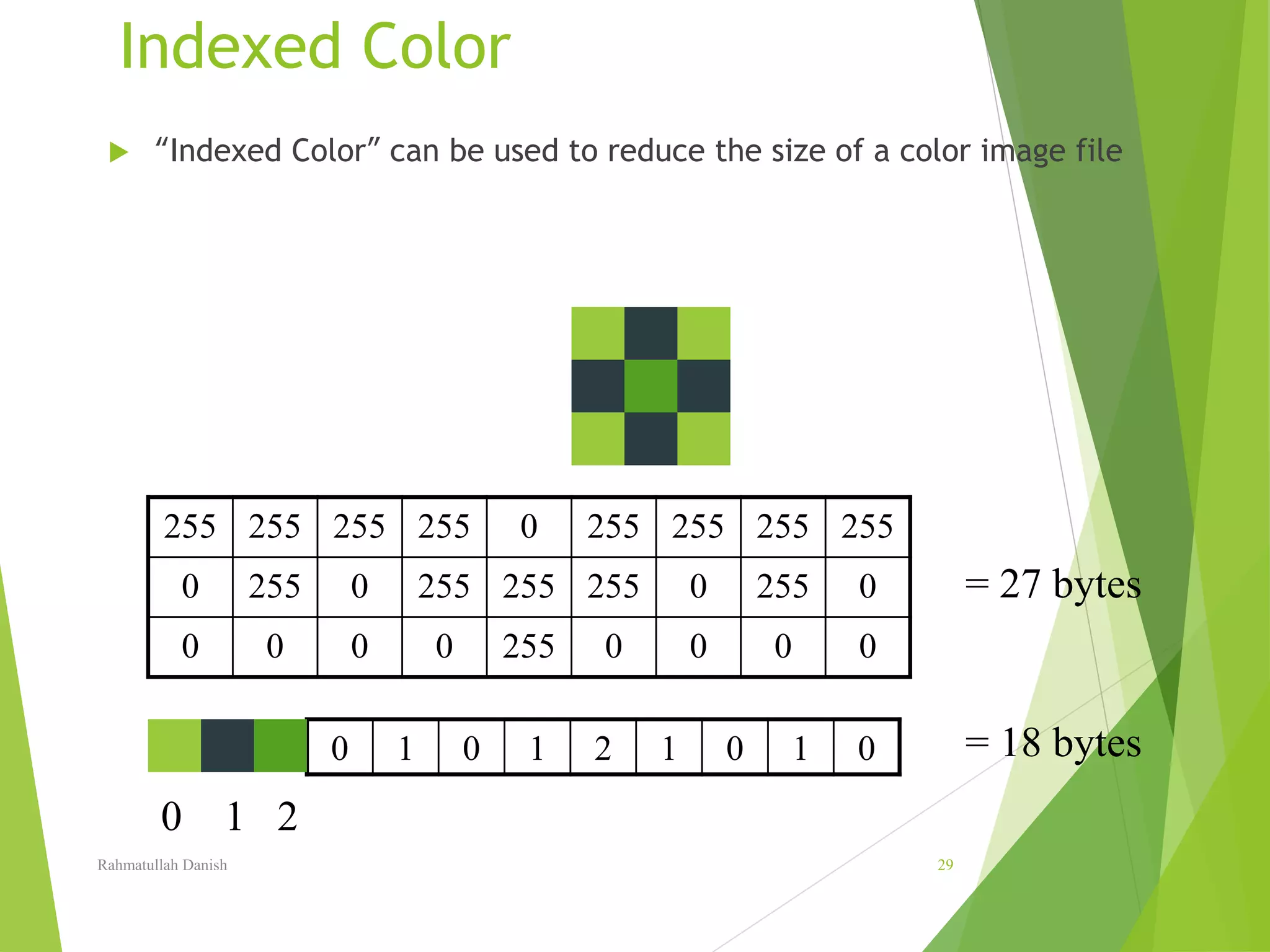
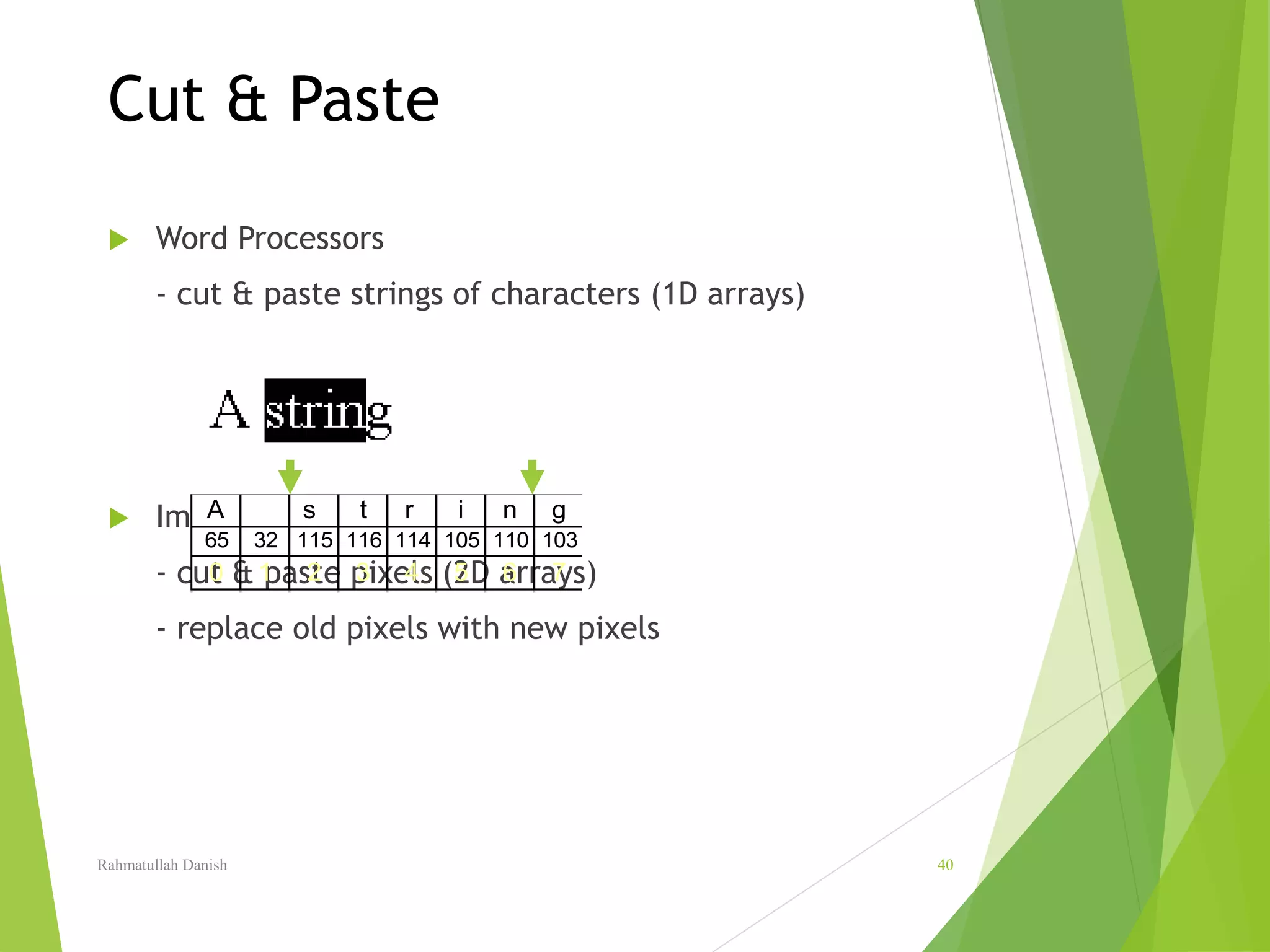
2. Pixel values, image resolution, file formats for storing images like JPEG and GIF are explained. Techniques for image editing like selection tools, painting tools, layers and blending are also covered.
3. The document provides an overview of important concepts in digital image representation and processing including how images are digitized and stored as digital data, techniques for editing images, and methods for manipulating pixels within an image.




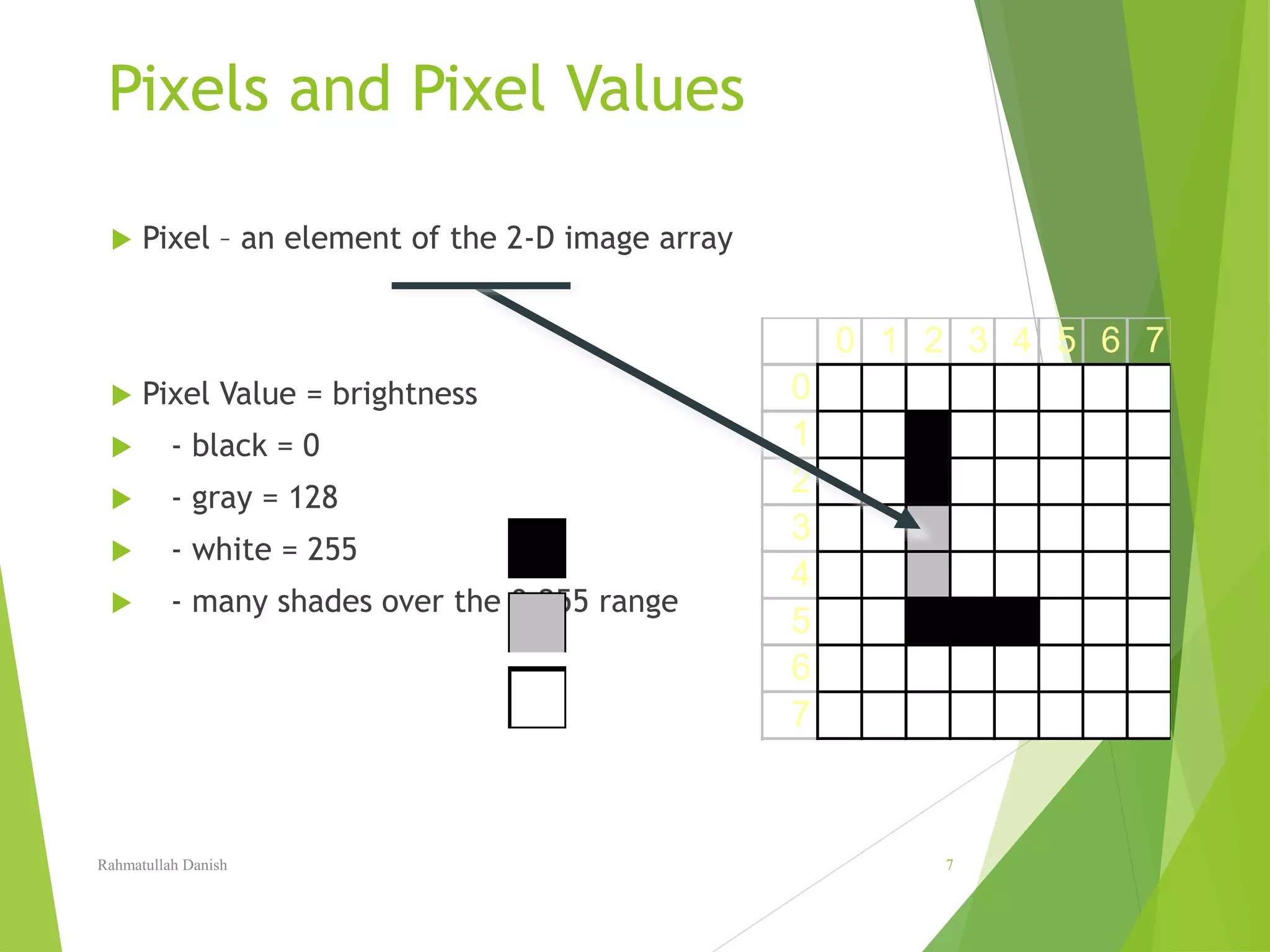
![Images - 2D array of values = pixels
Pixel = “Picture Element”
Image [x,y] = pixel value (number)
Rahmatullah Danish 6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/imagerepresentation-191110225940/75/Image-representation-6-2048.jpg)