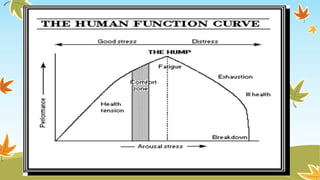
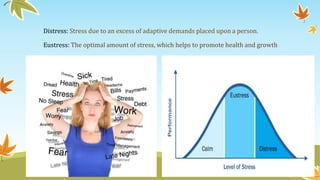
The document discusses the concept of stress in relation to illness, highlighting both beneficial and harmful effects of stress on mental health. It outlines coping strategies, the impact of physical illness on emotional well-being, and the role of social factors in the experience of stress. Additionally, it addresses responses to terminal illness and emphasizes the importance of supportive care for emotional and psychological needs.