This document provides an introduction to foundational concepts of innovation including:
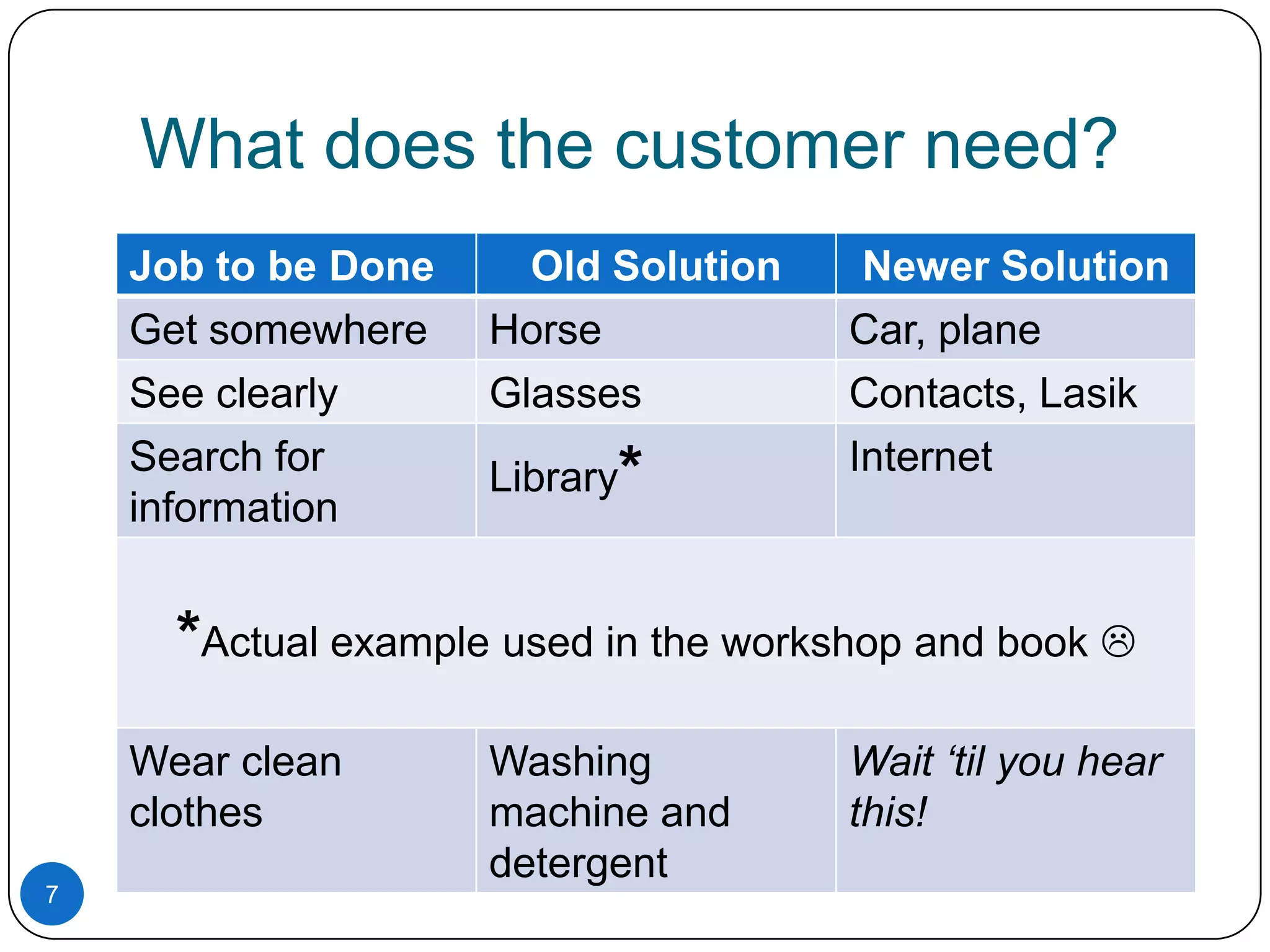
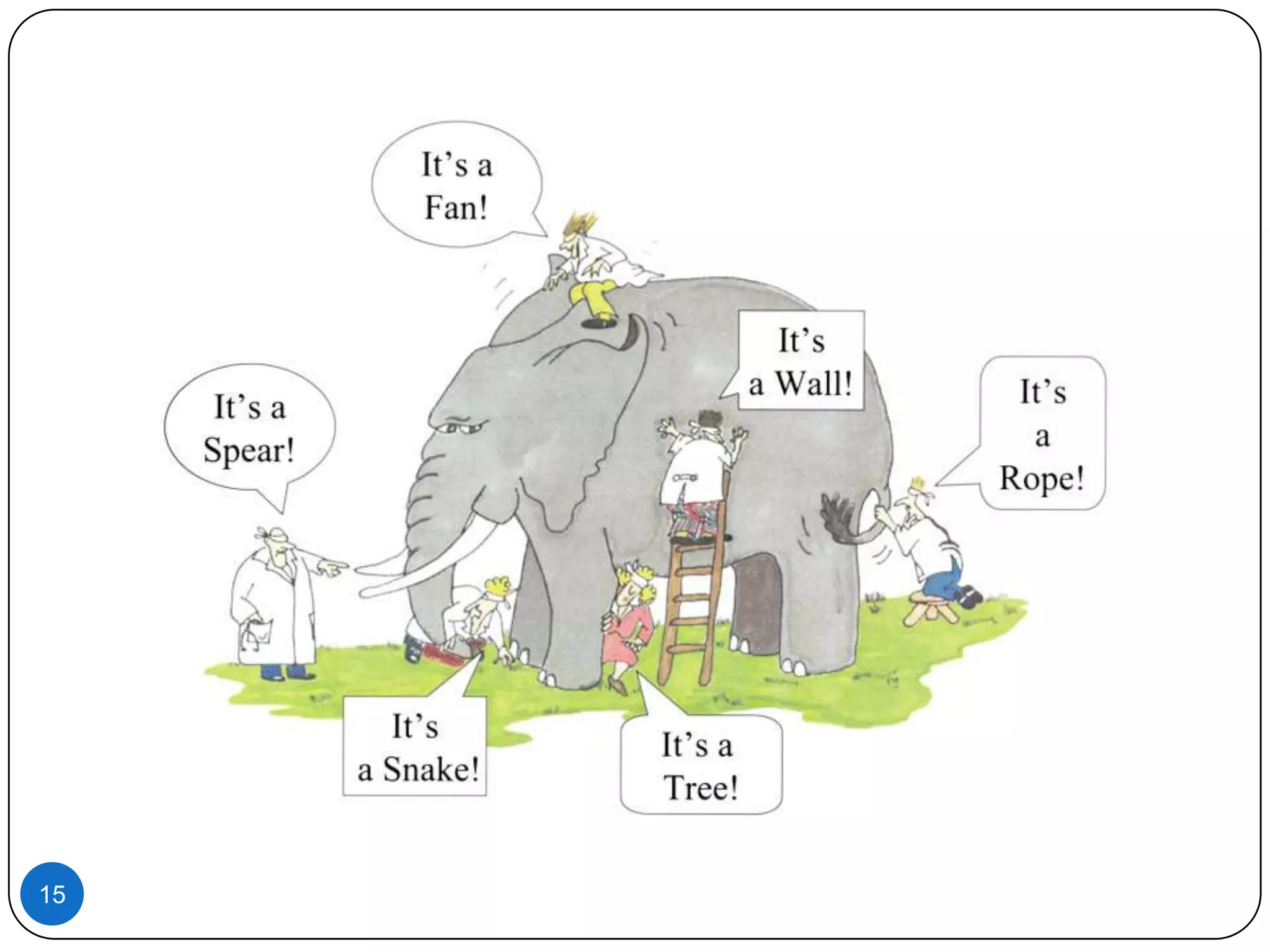
1. Customers hire products and services to fulfill jobs or tasks that need to be done. How the job is defined impacts innovation opportunities.
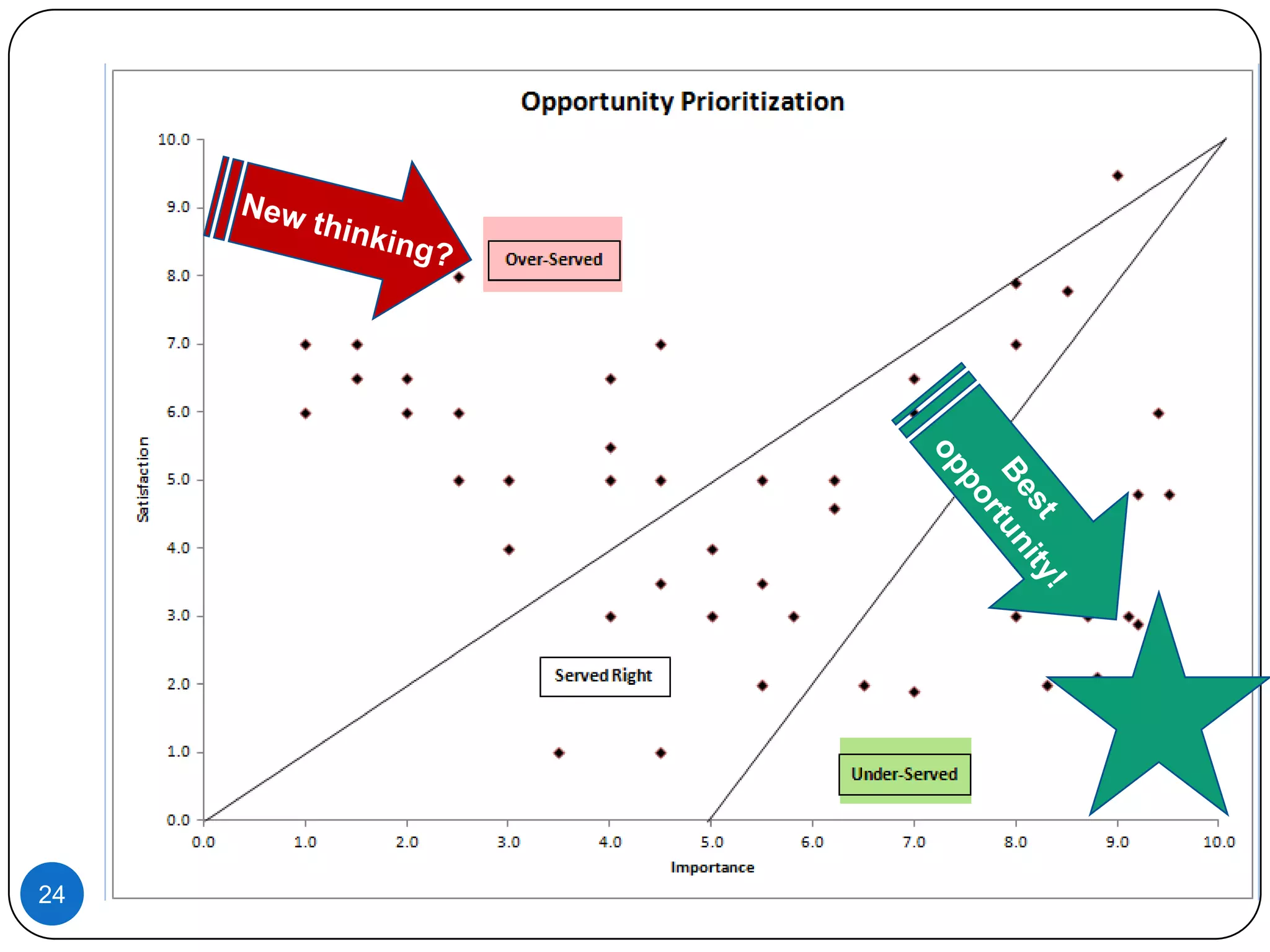
2. Customers determine what defines success or failure for the job based on their outcome expectations.
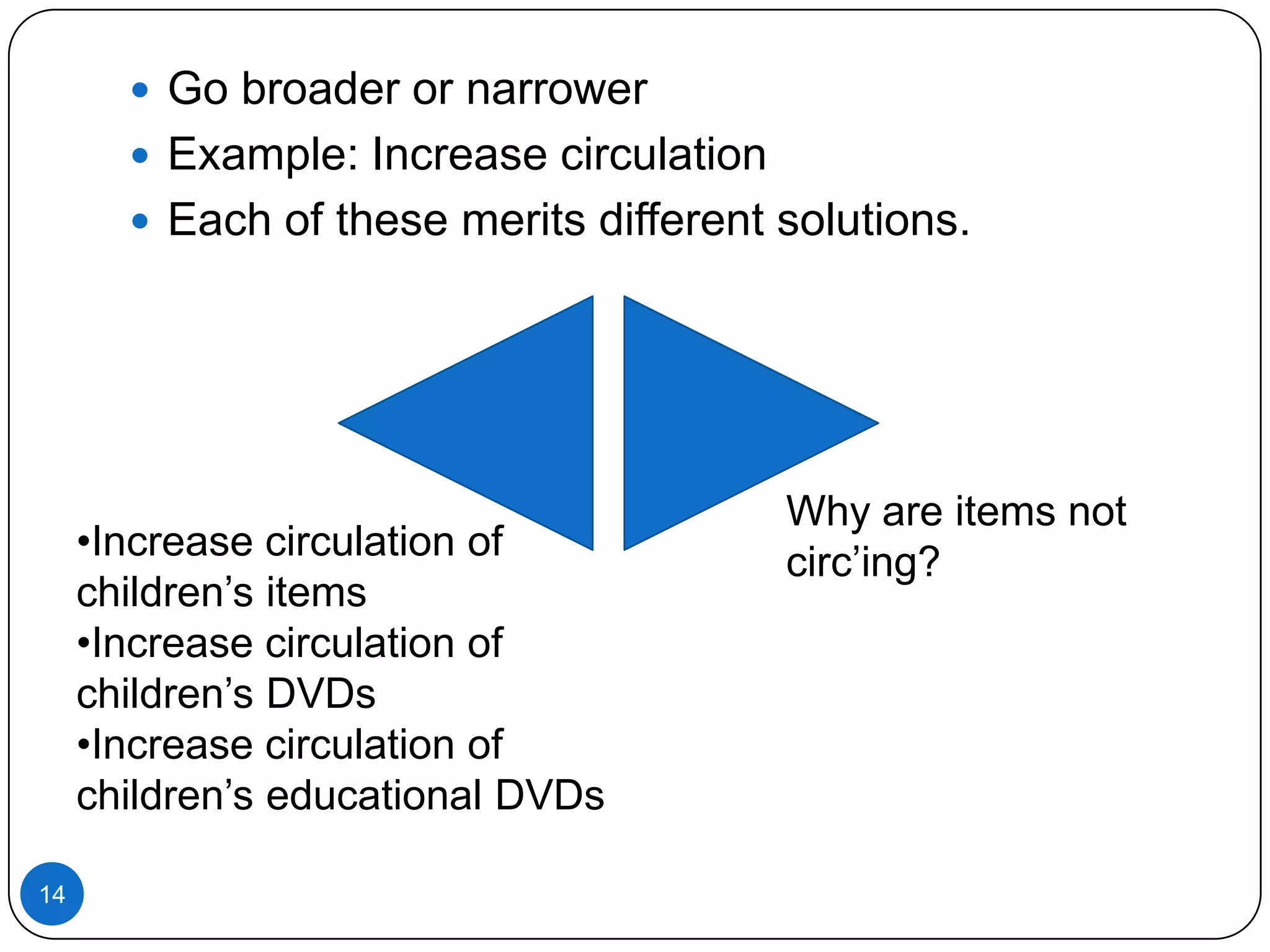
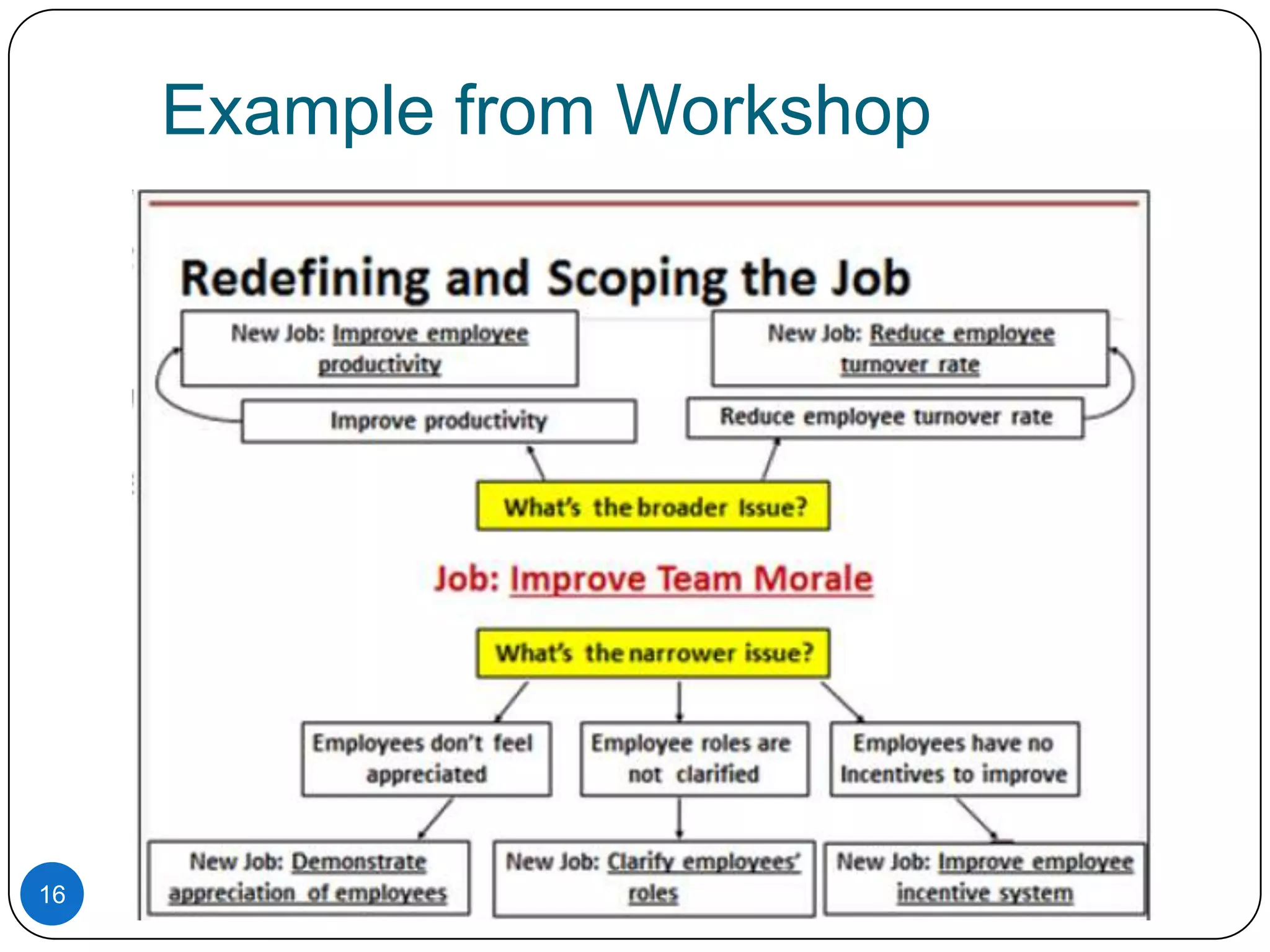
3. Properly scoping the job to be done, either by broadening or narrowing the focus, helps ensure innovation efforts target the right problem.
4. Understanding customer outcome expectations, like wanting something faster or cheaper, helps provide solutions customers truly value.