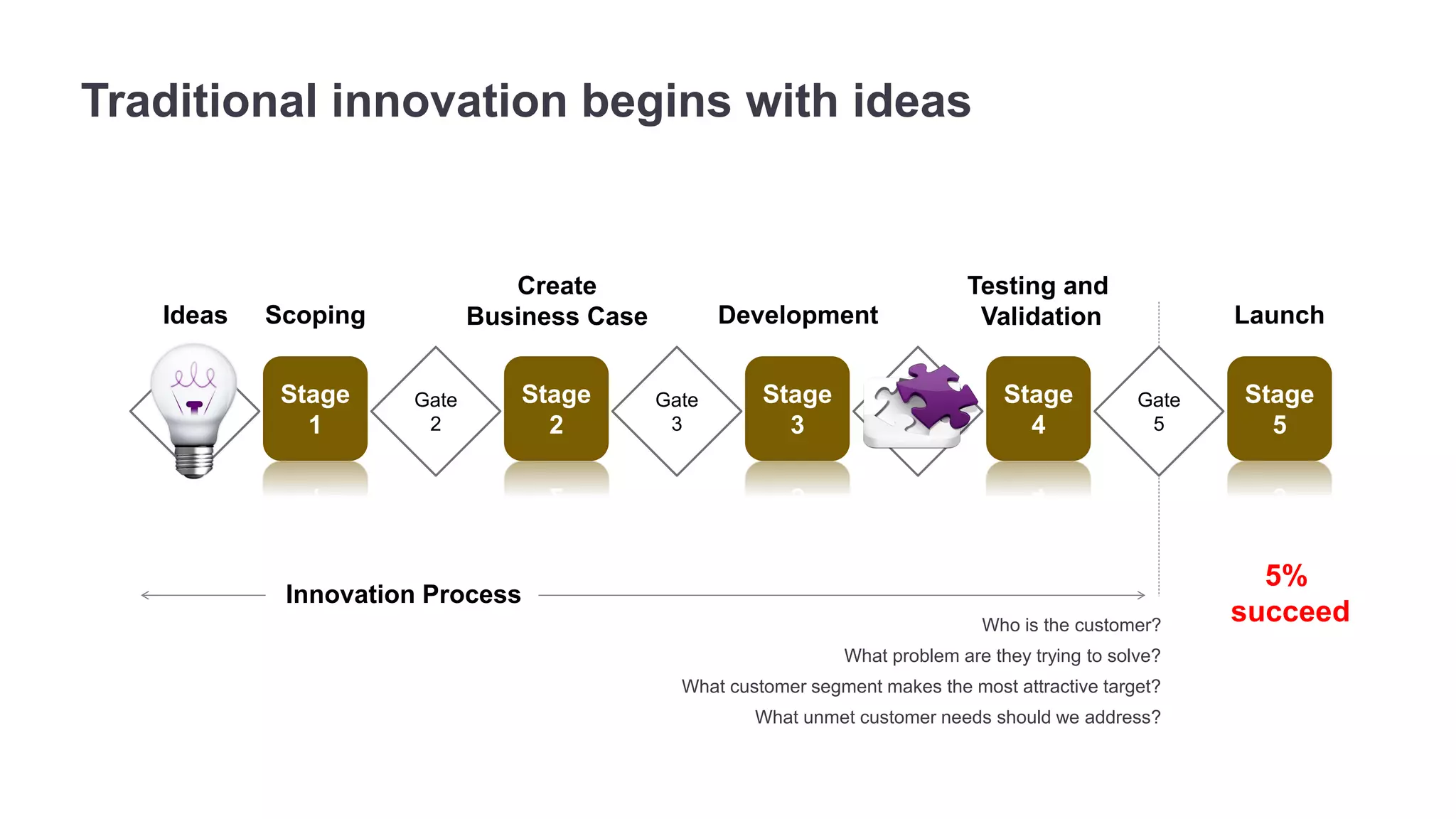
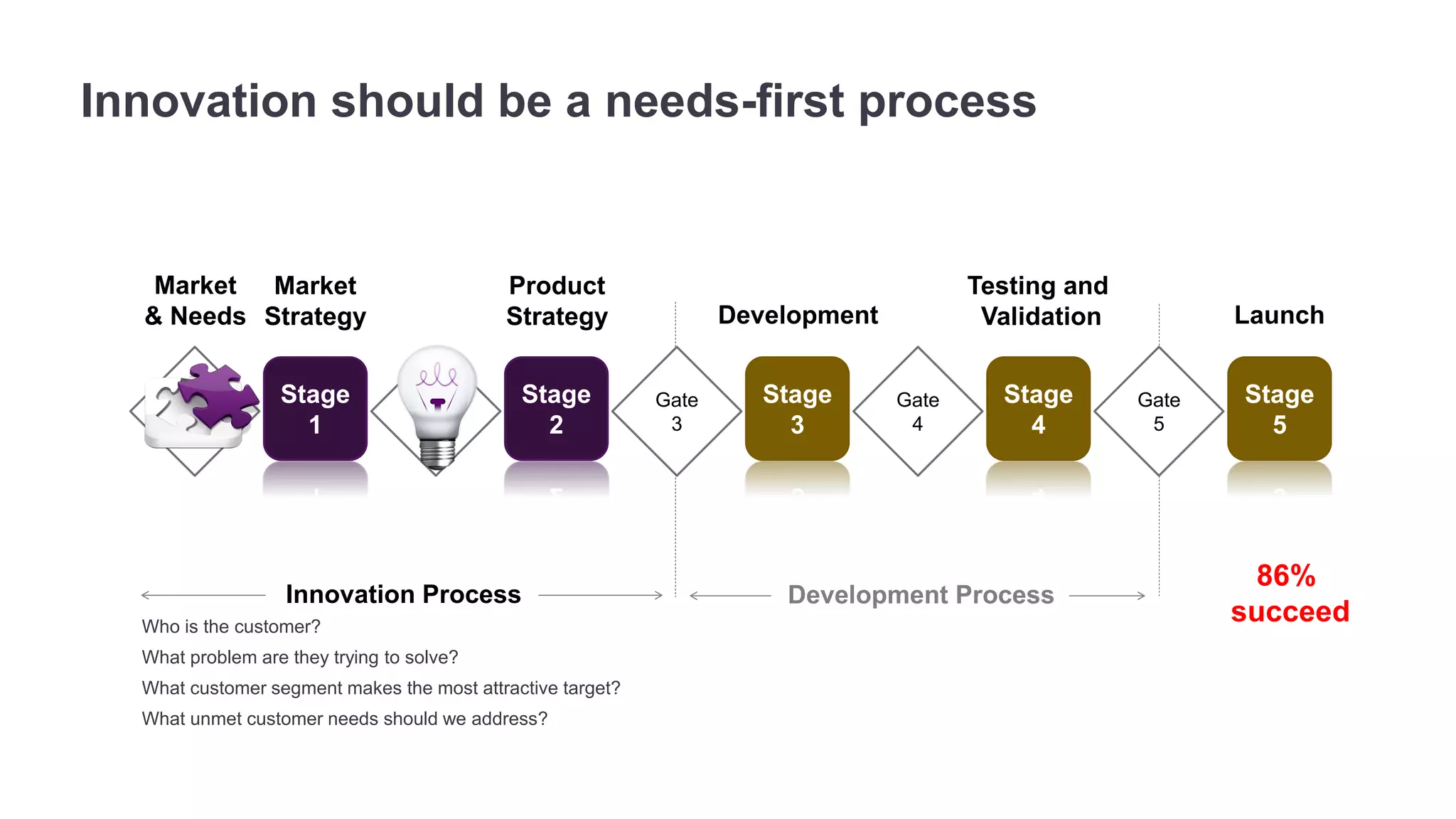
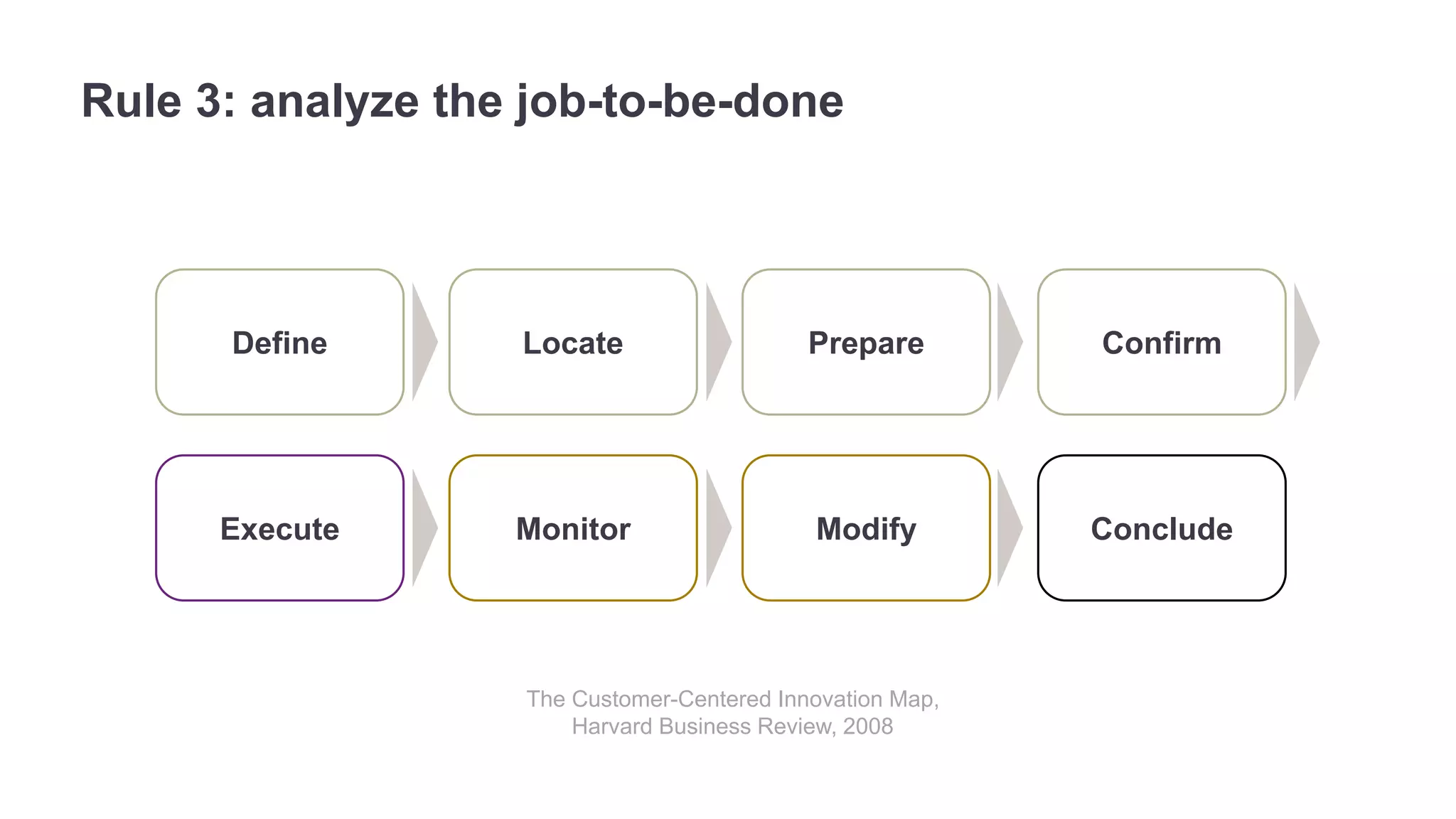
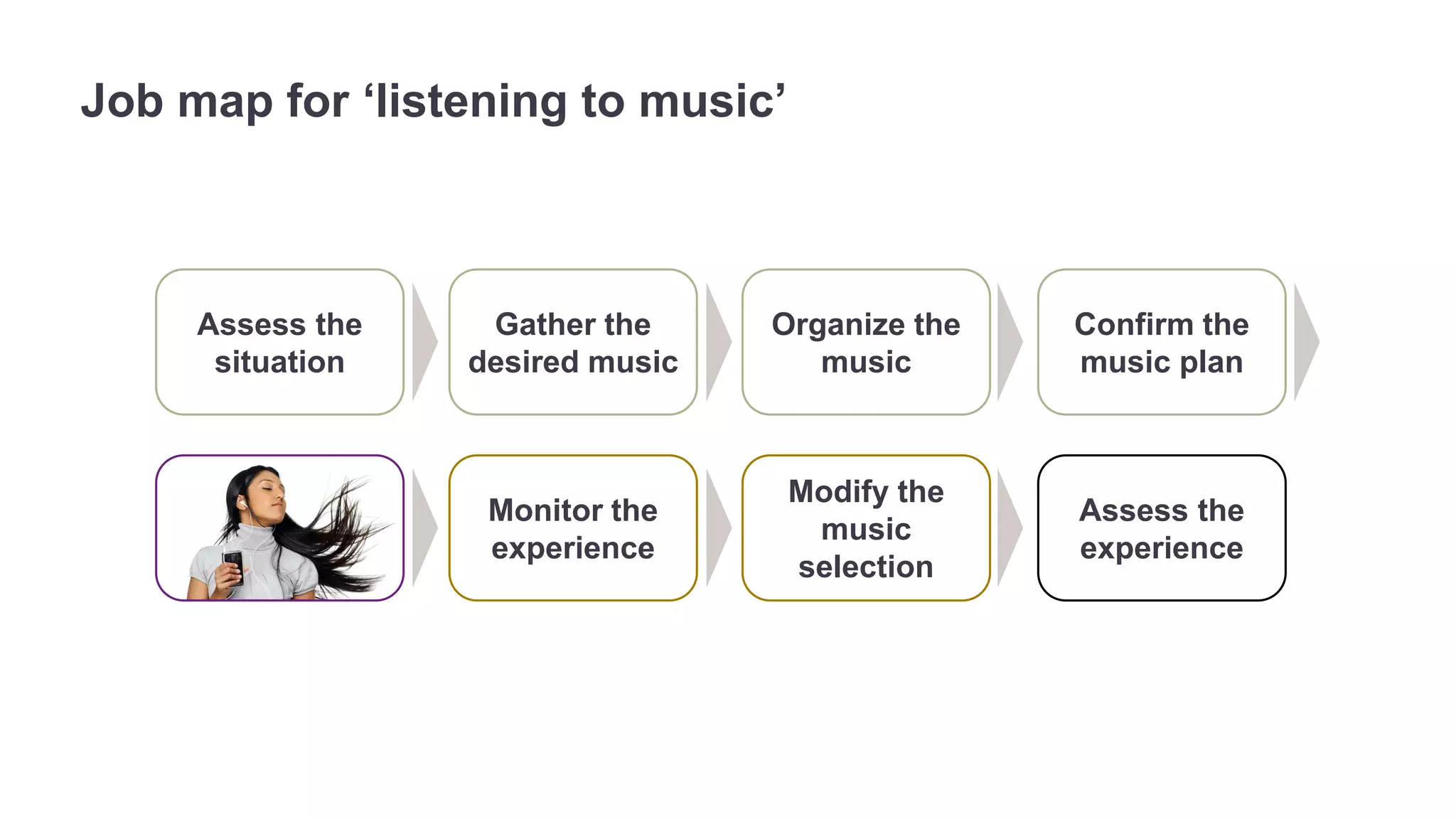
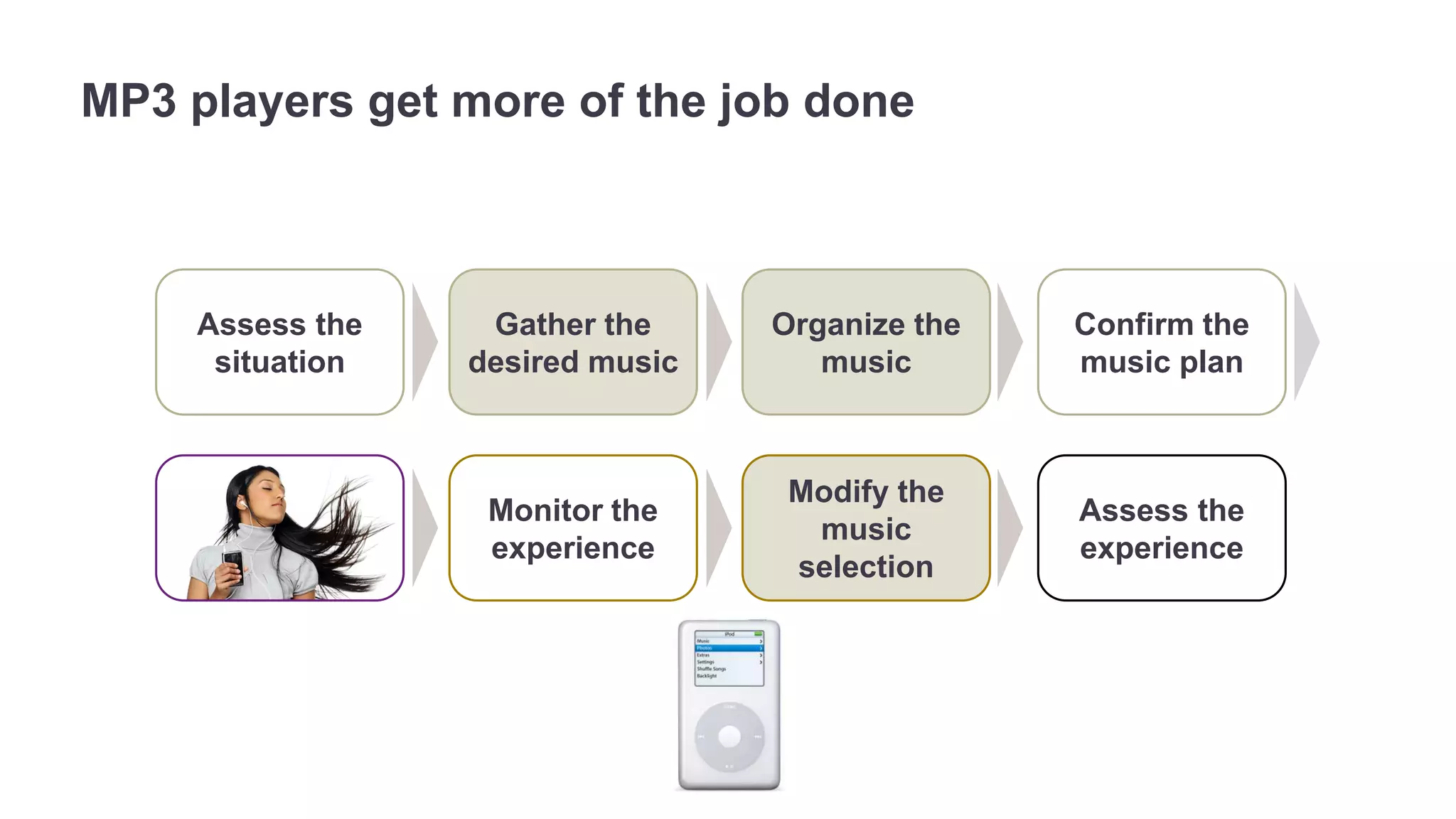
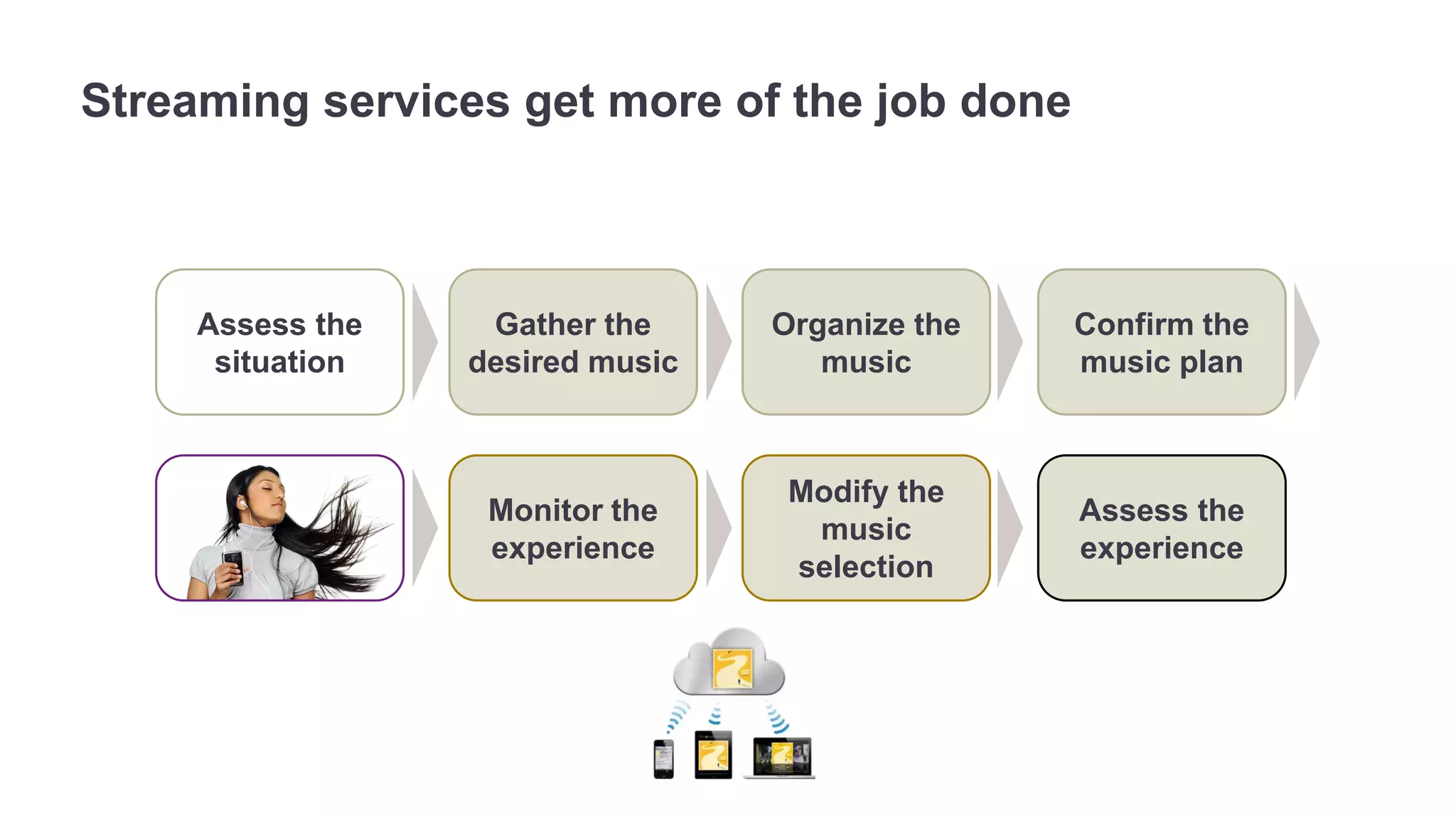
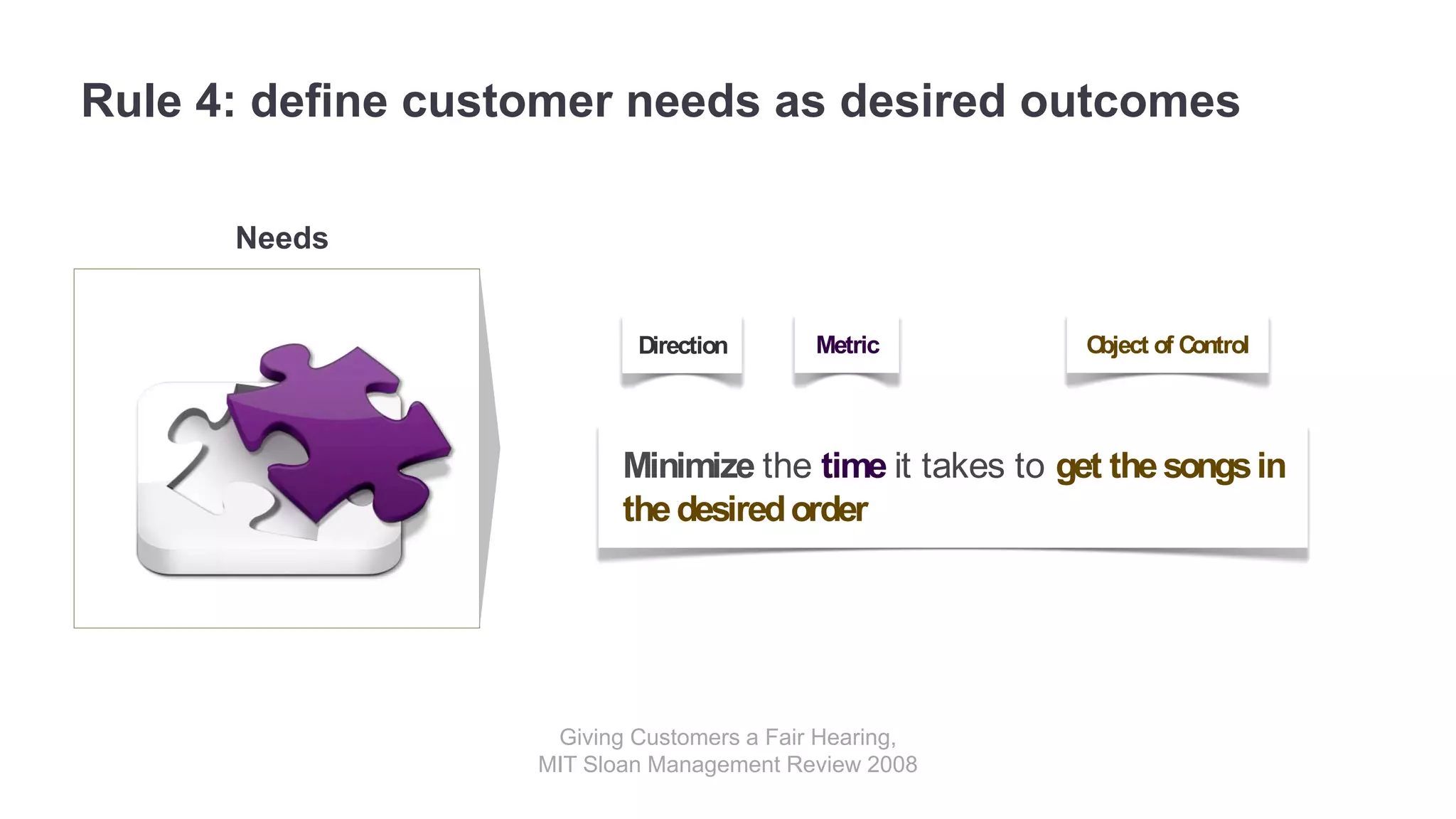
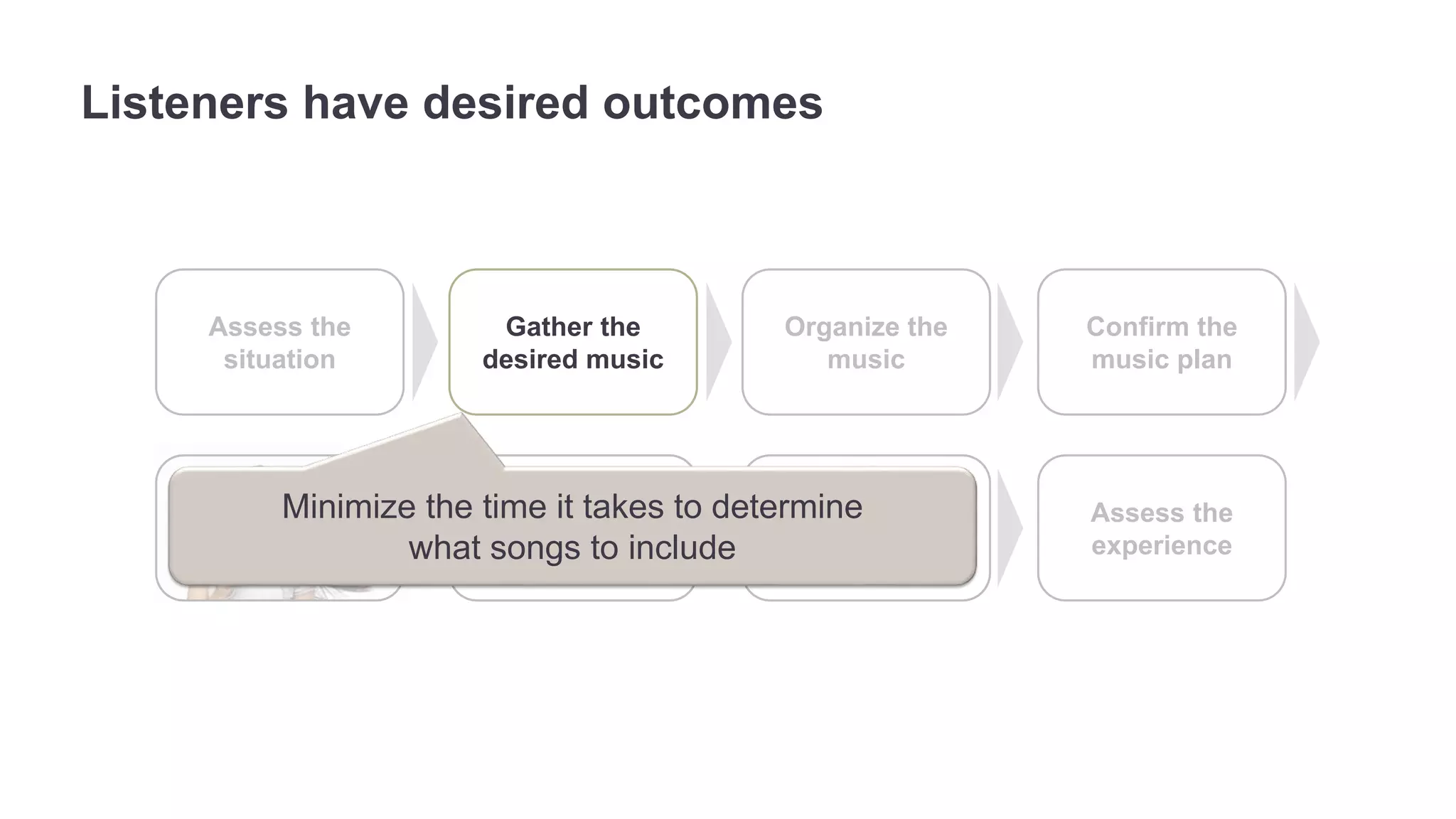
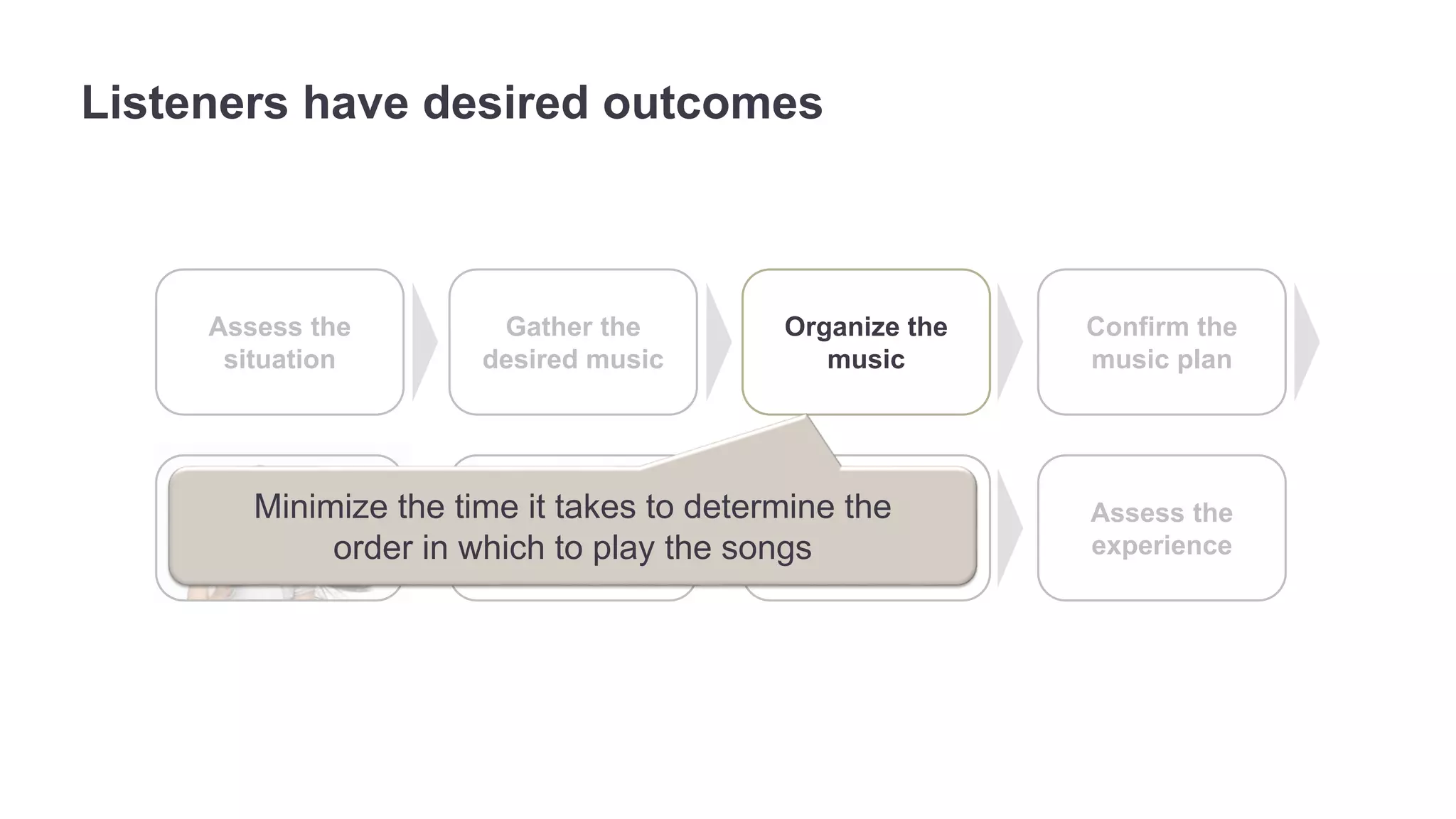
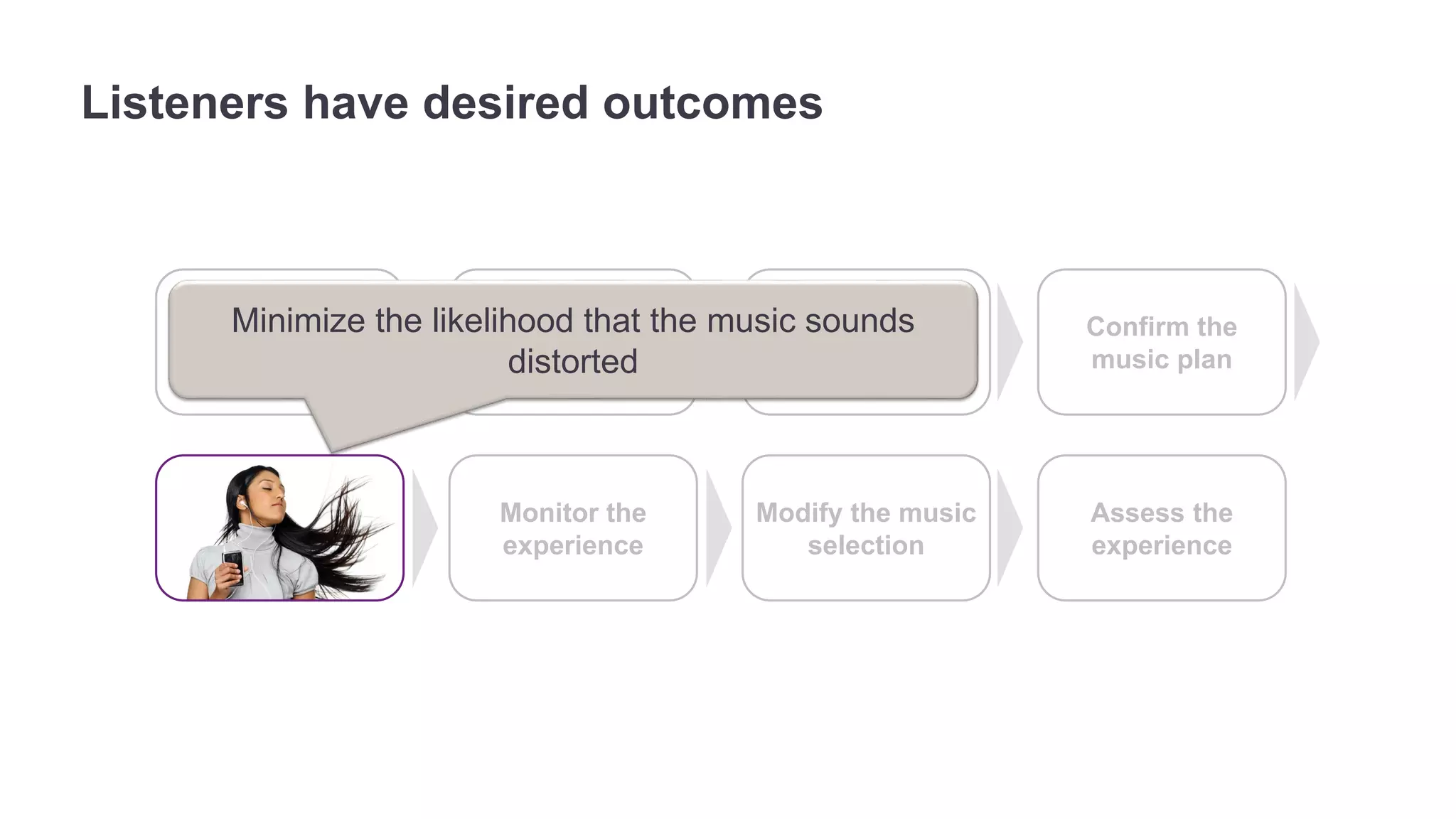
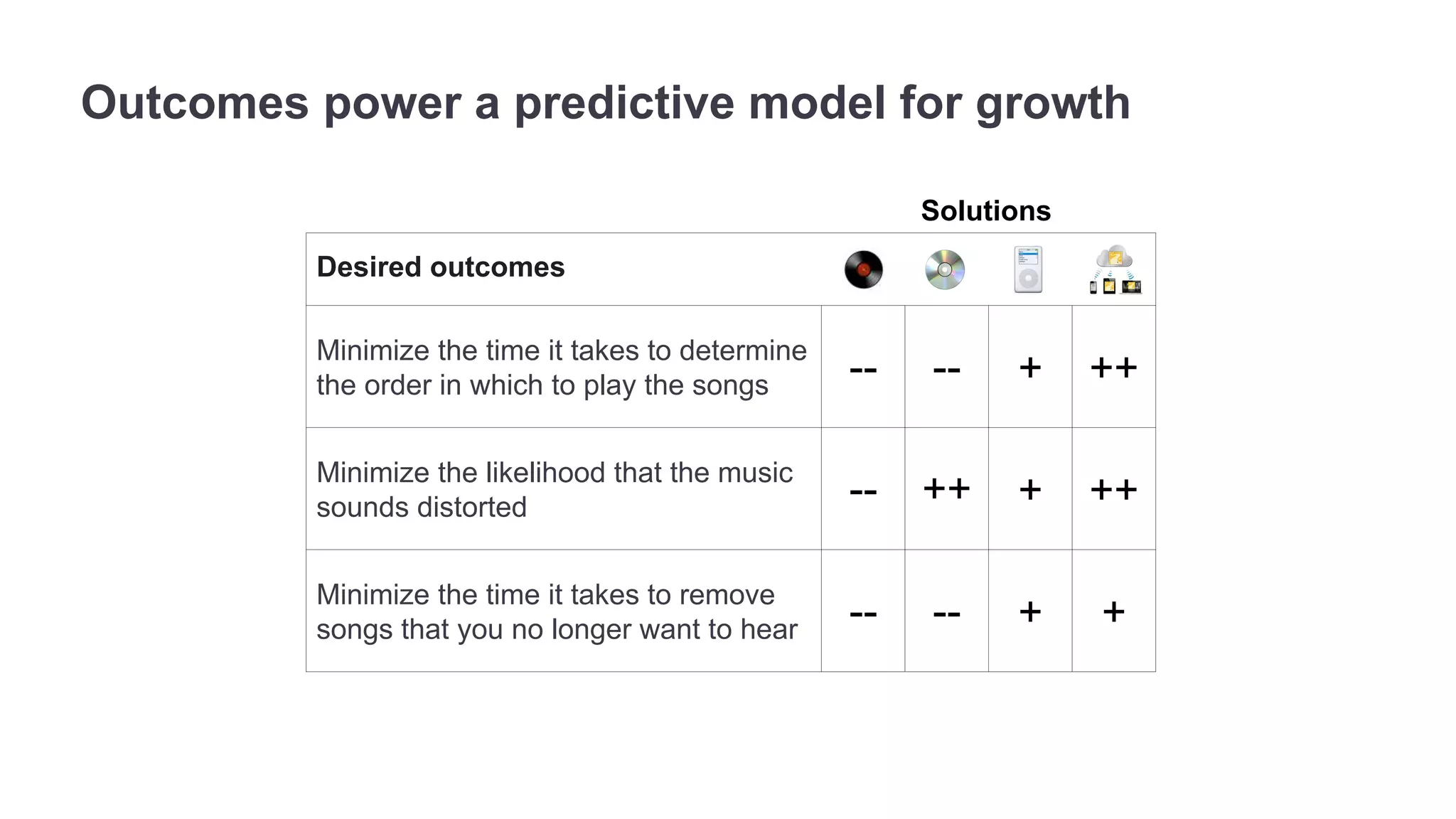
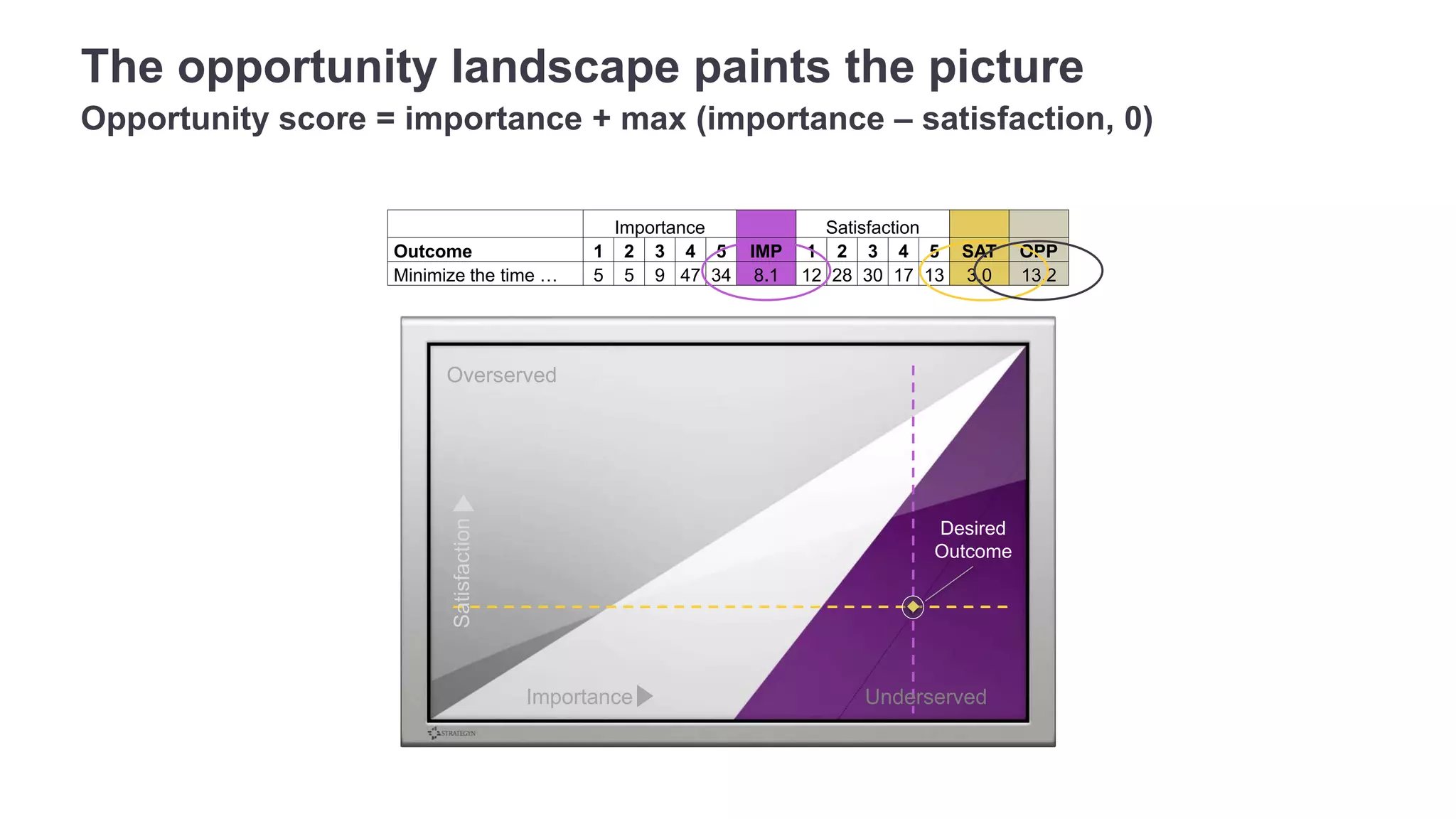
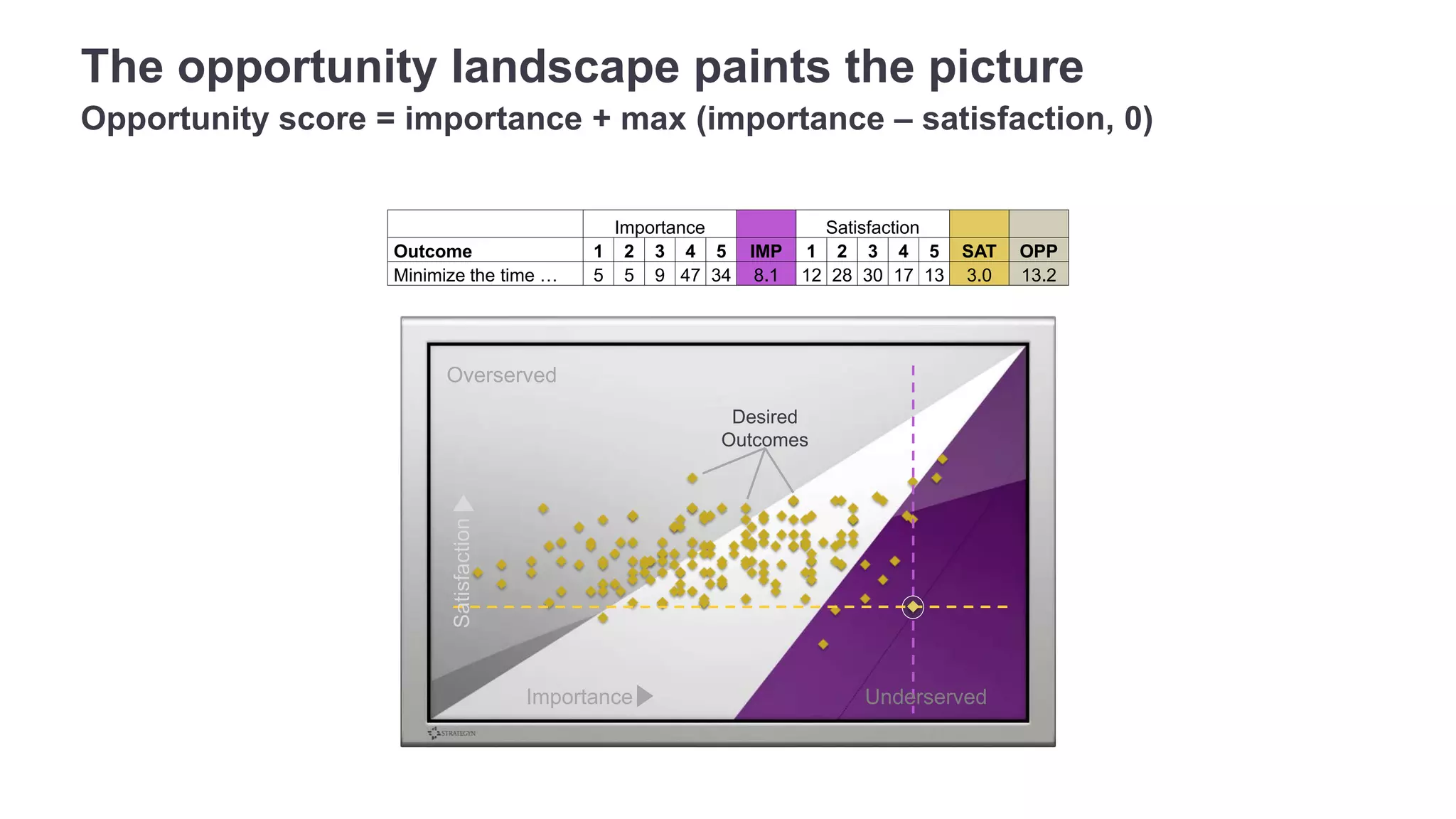
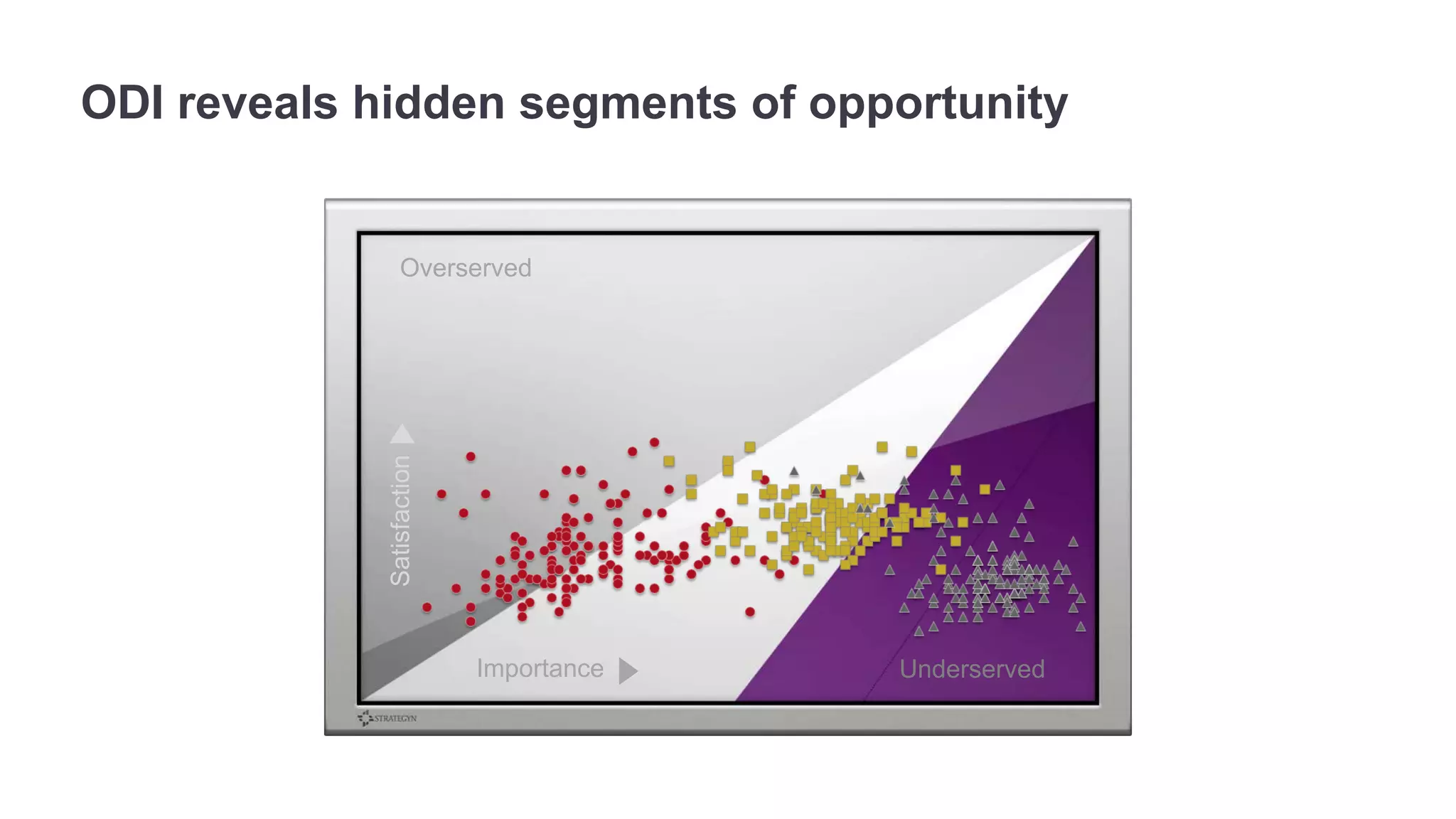
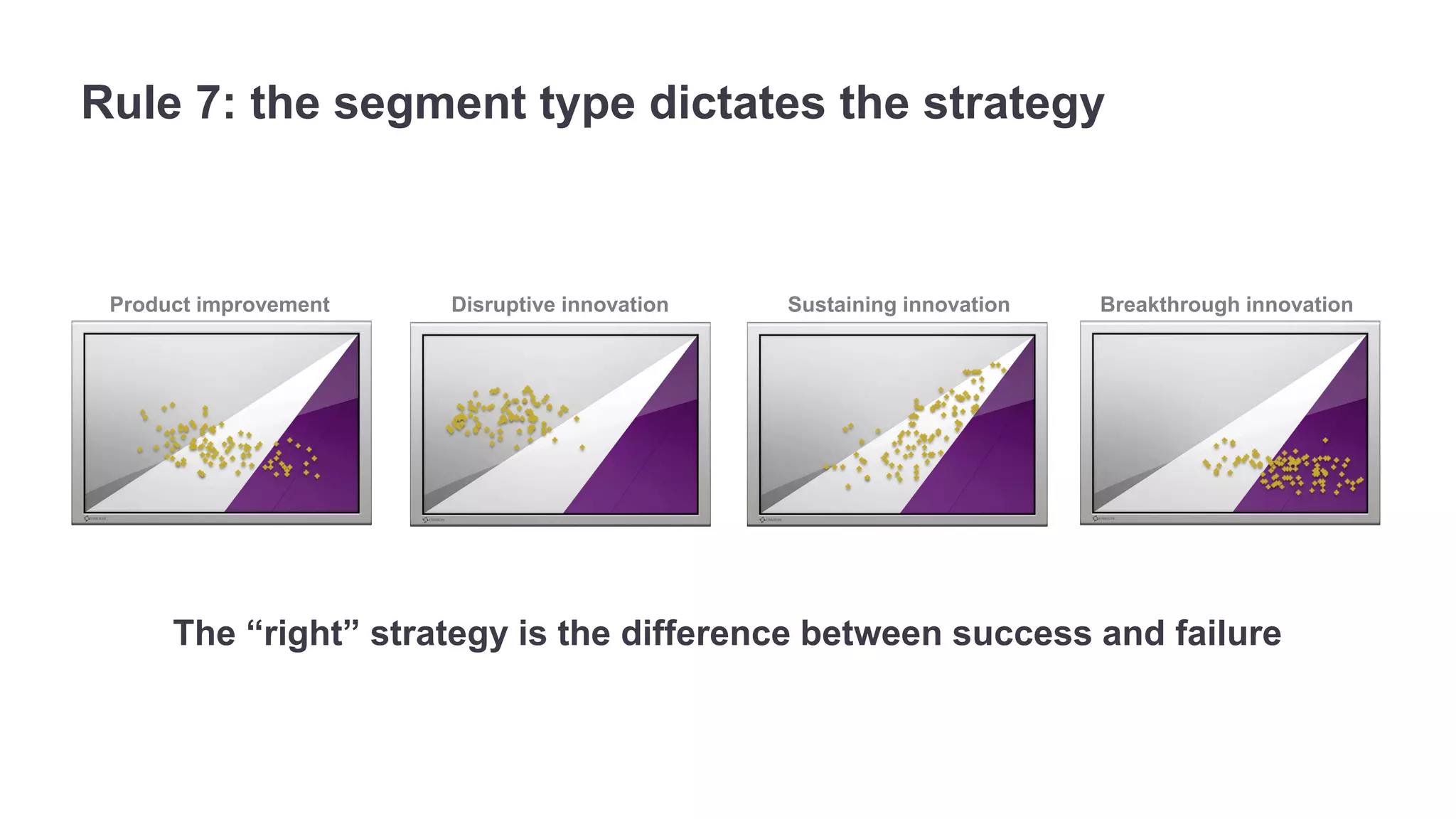
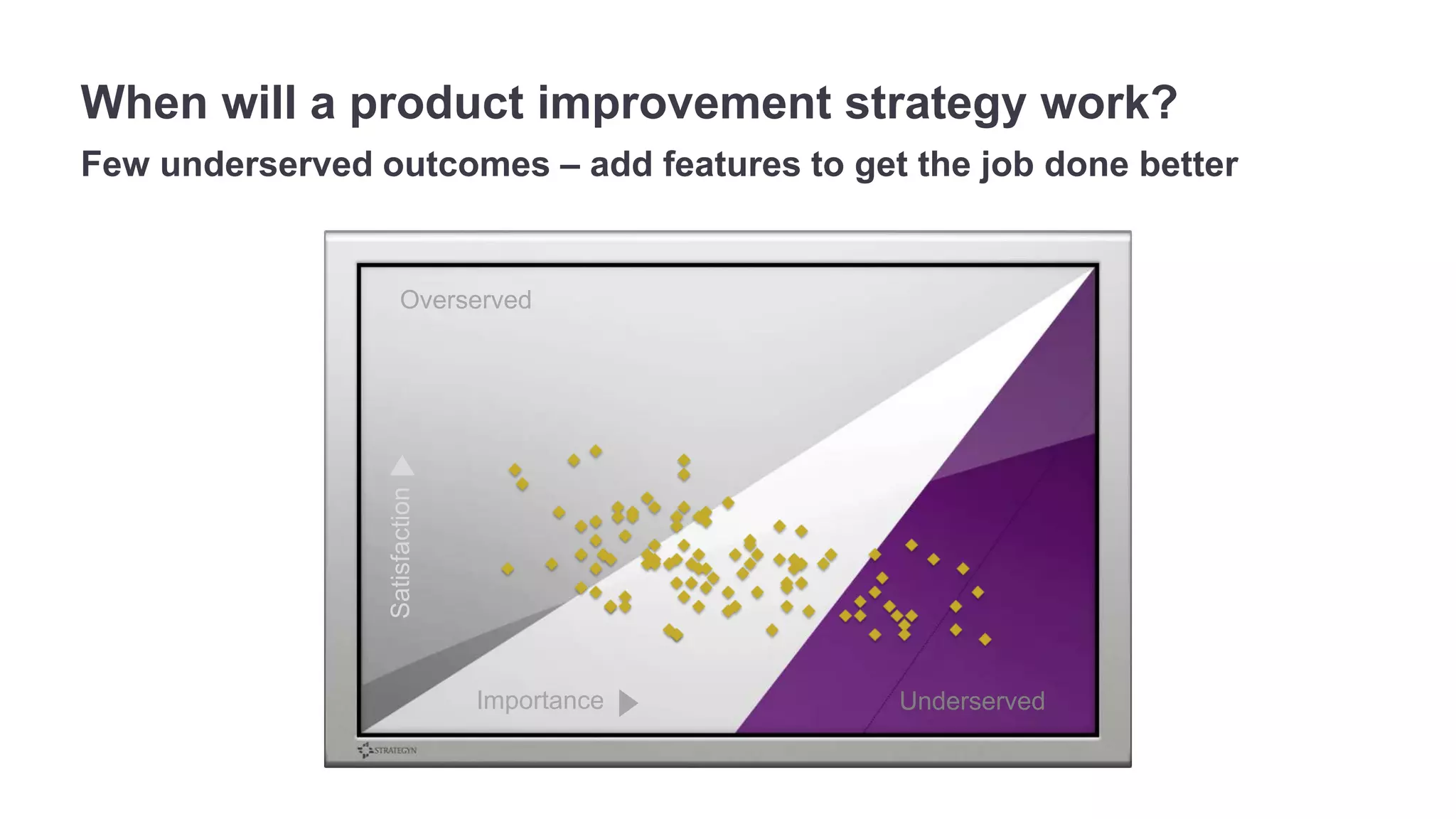
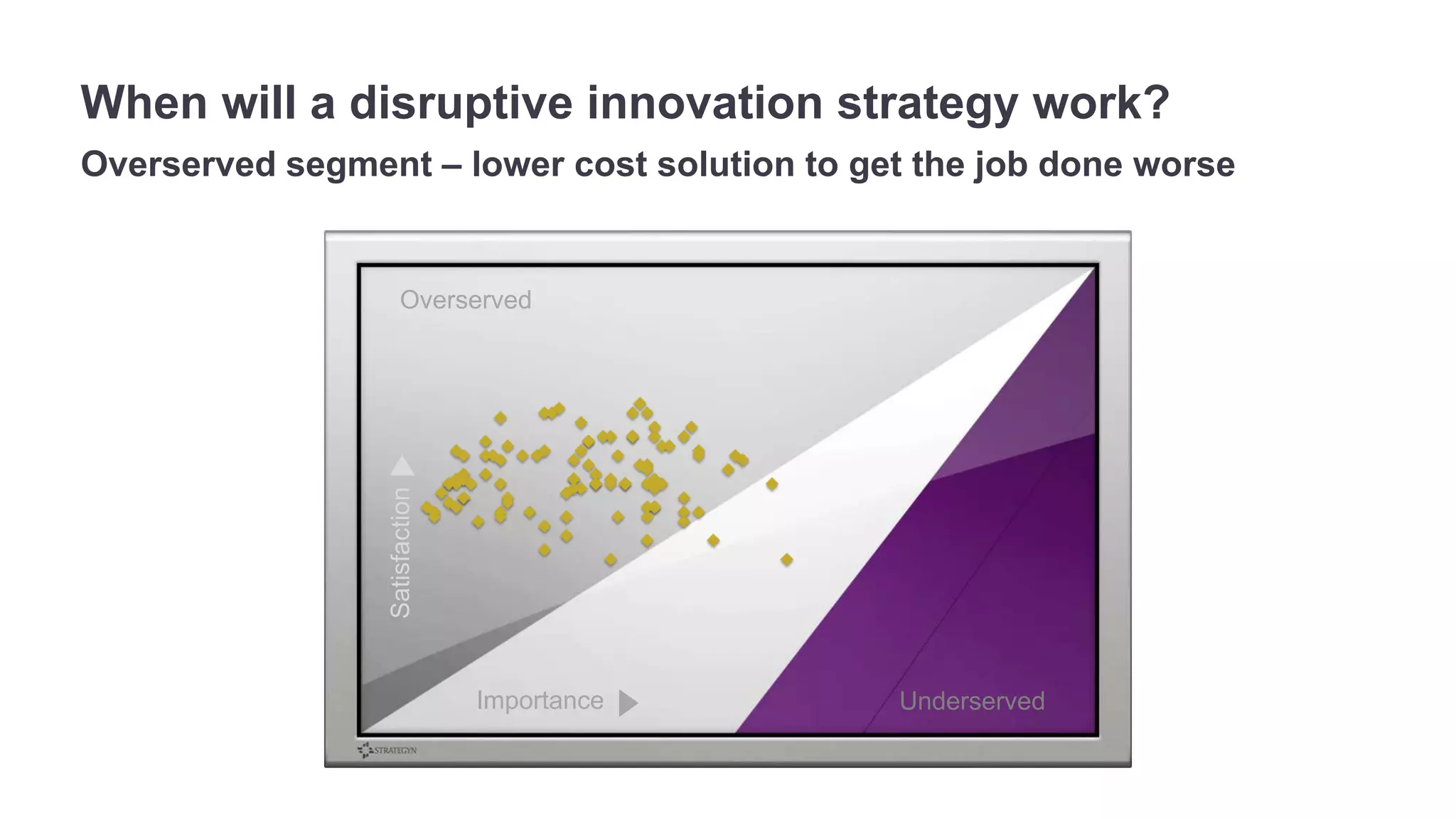
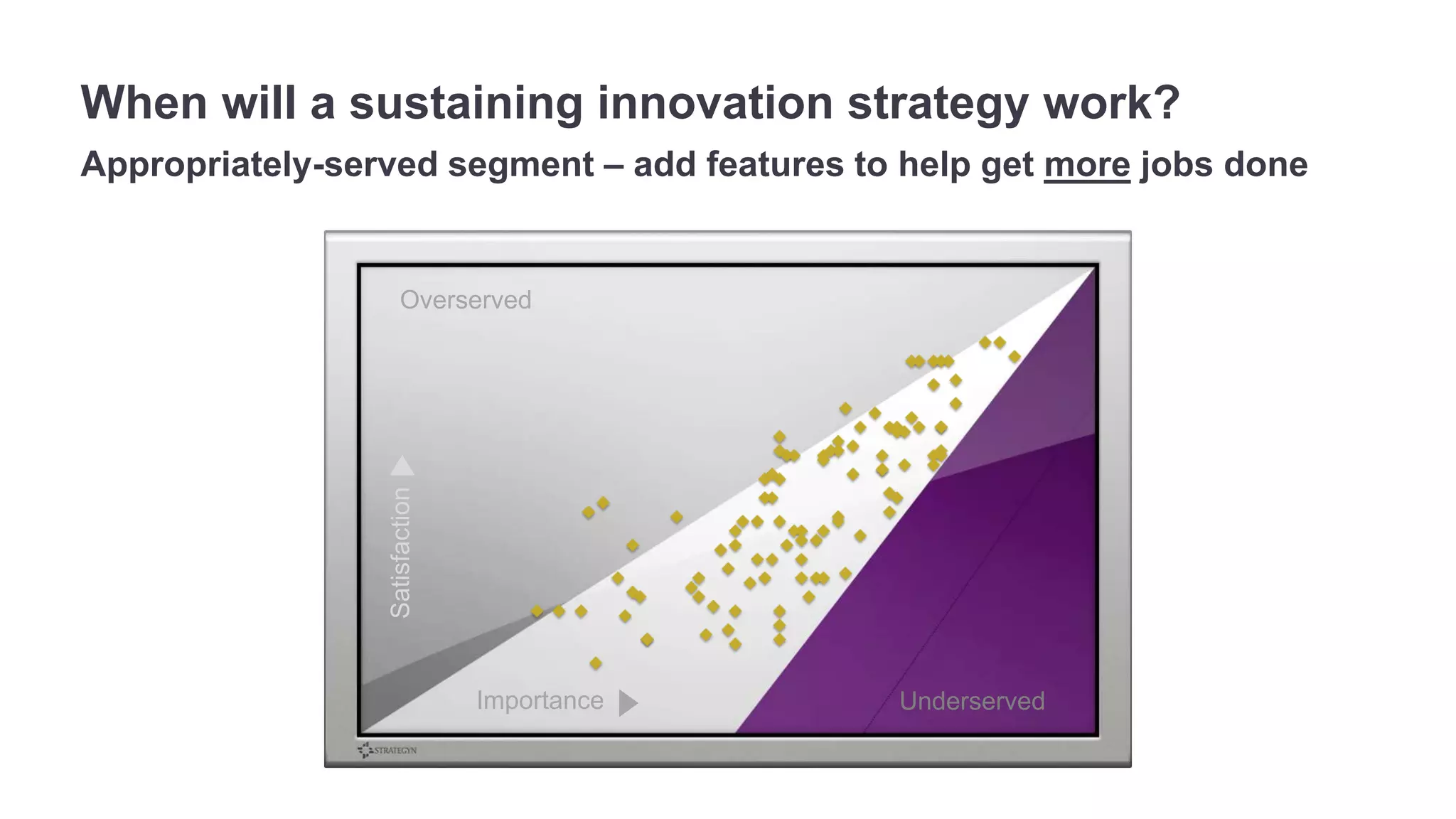
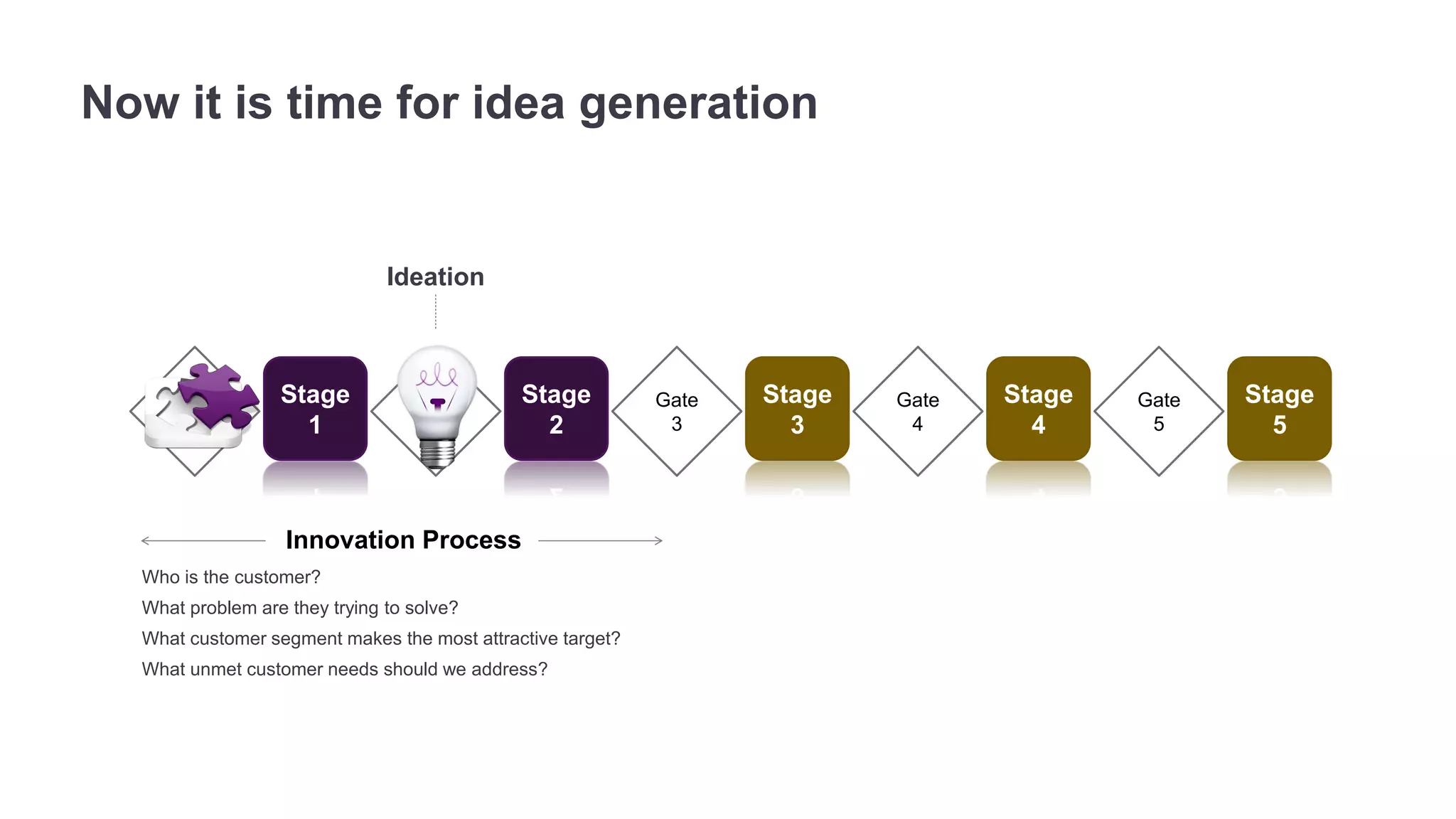
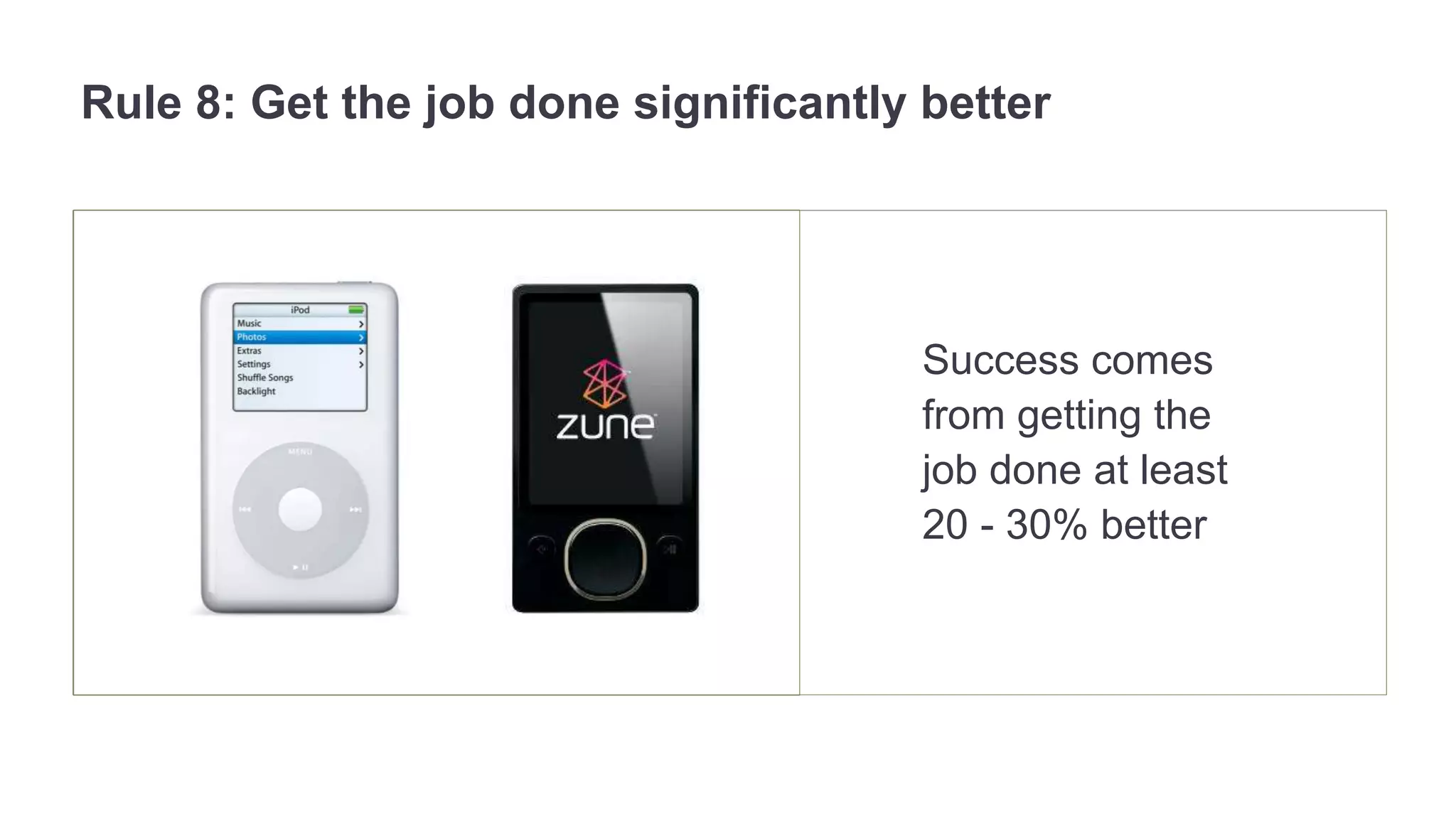
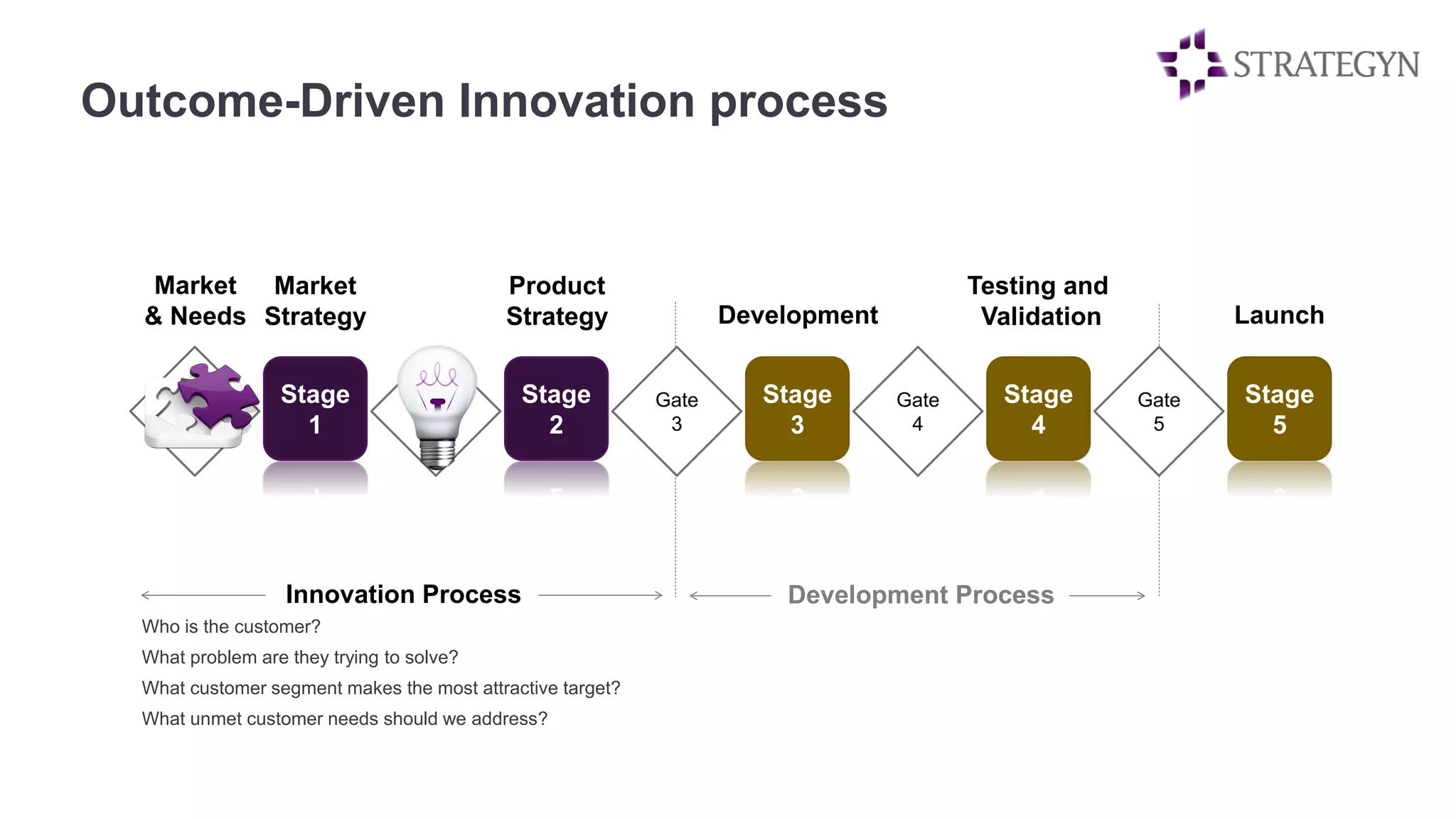
The document outlines the principles of outcome-driven innovation (ODI) through the lens of jobs-to-be-done (JTBD) theory, emphasizing the importance of identifying and addressing unmet customer needs. It details the innovation process stages, strategies for market definition, and ways to segment customers based on unmet outcomes. The document ultimately advocates for a needs-first approach to innovation to improve product success rates.