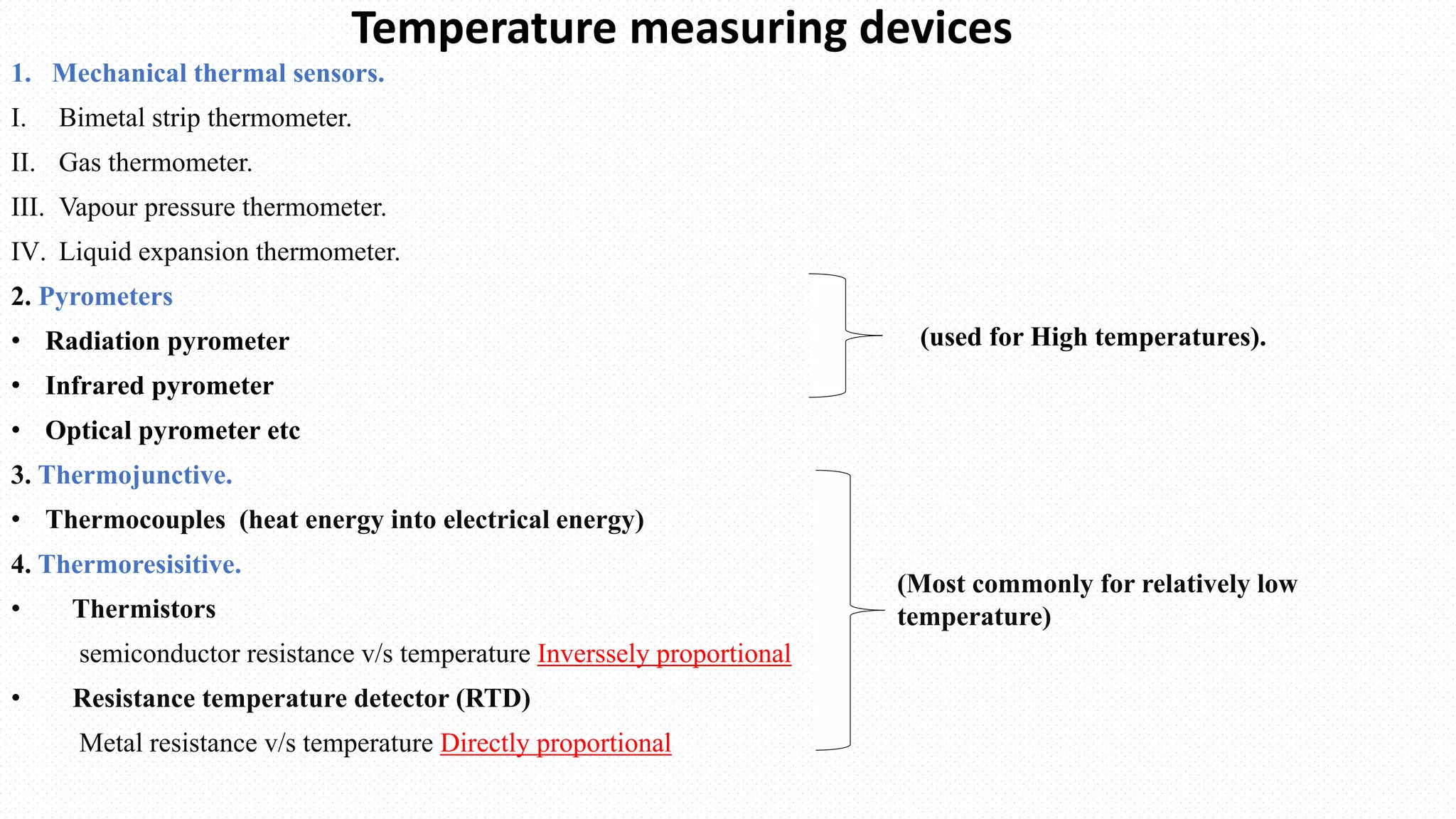
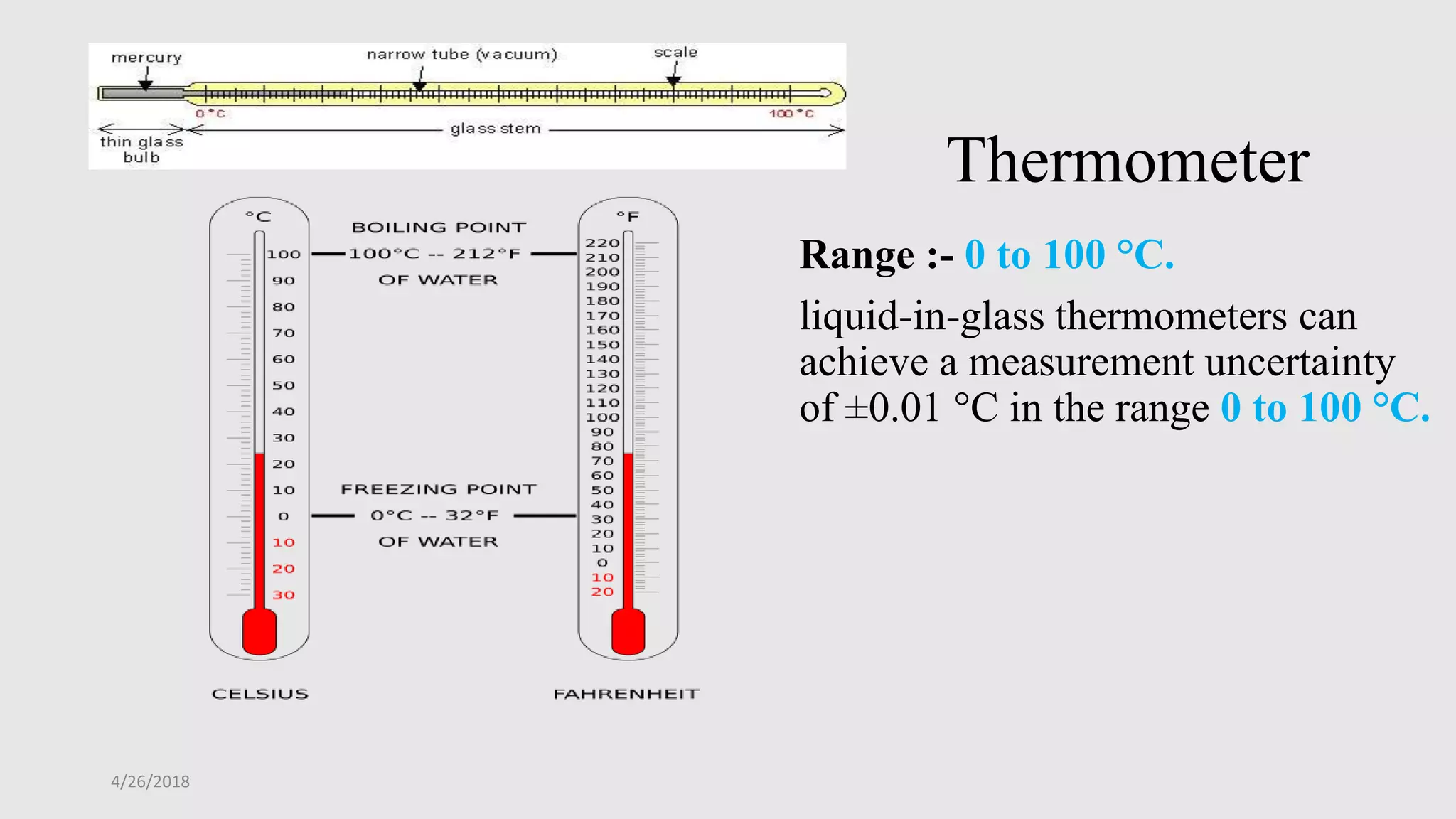
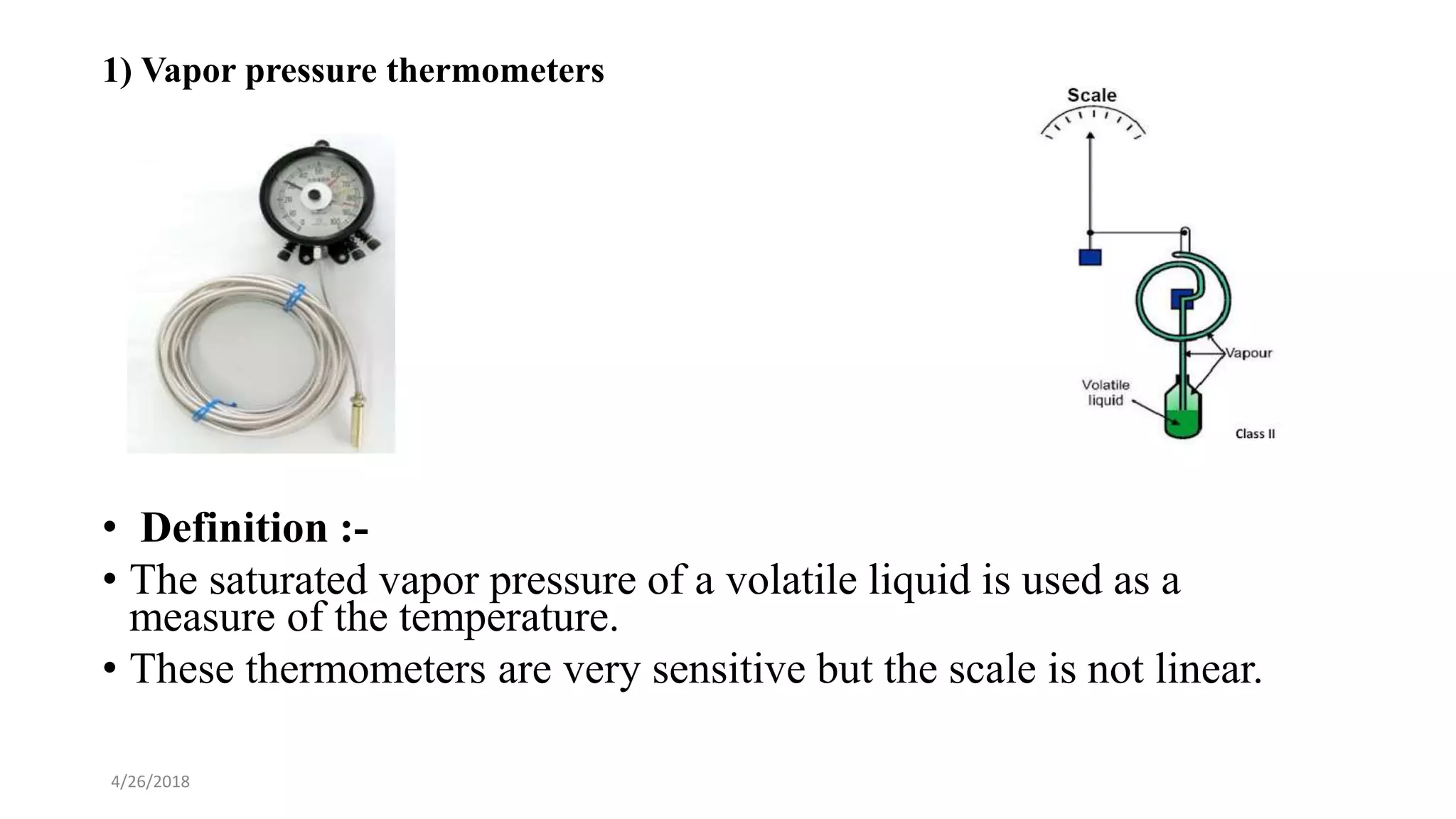
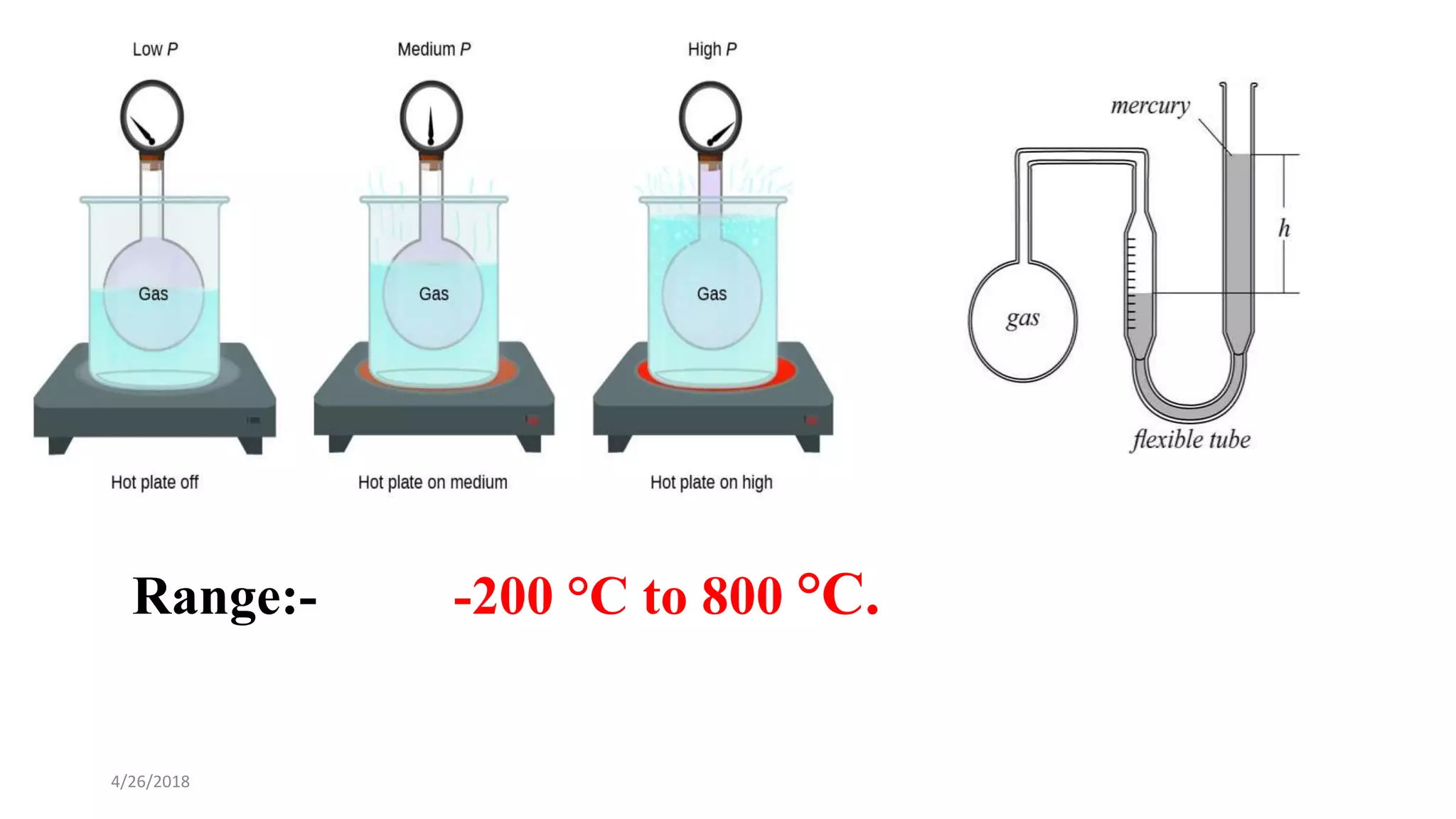
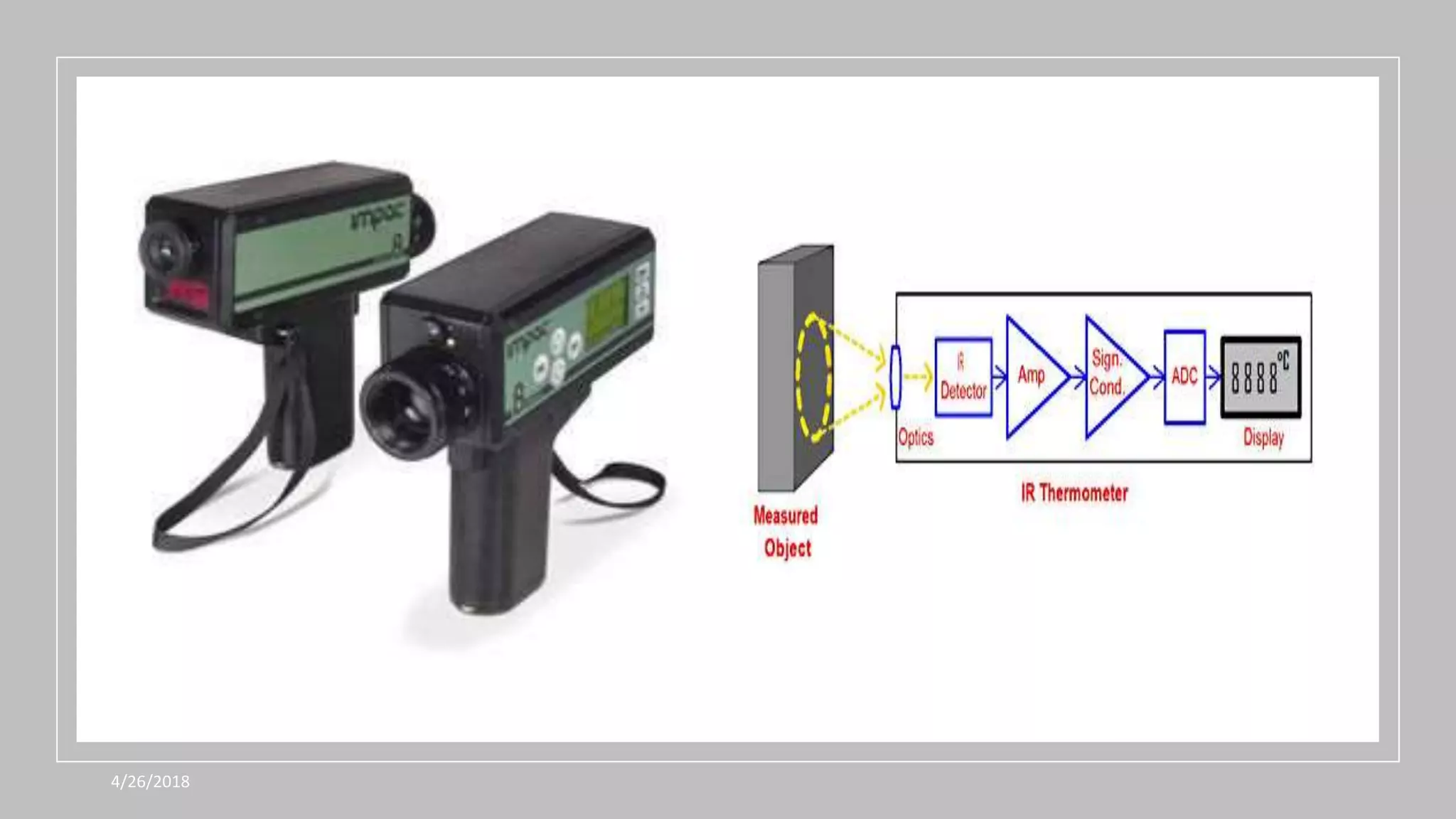
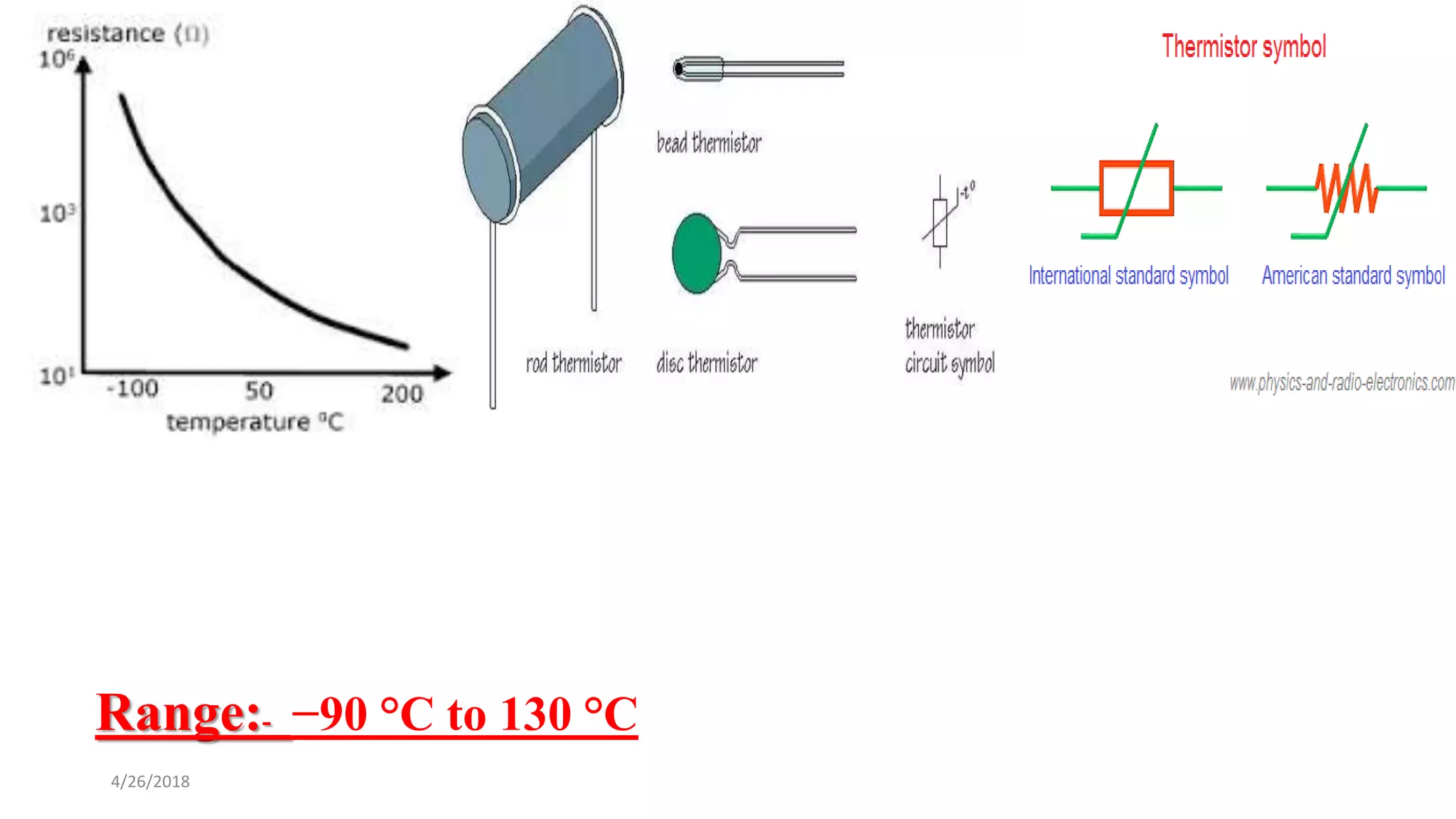
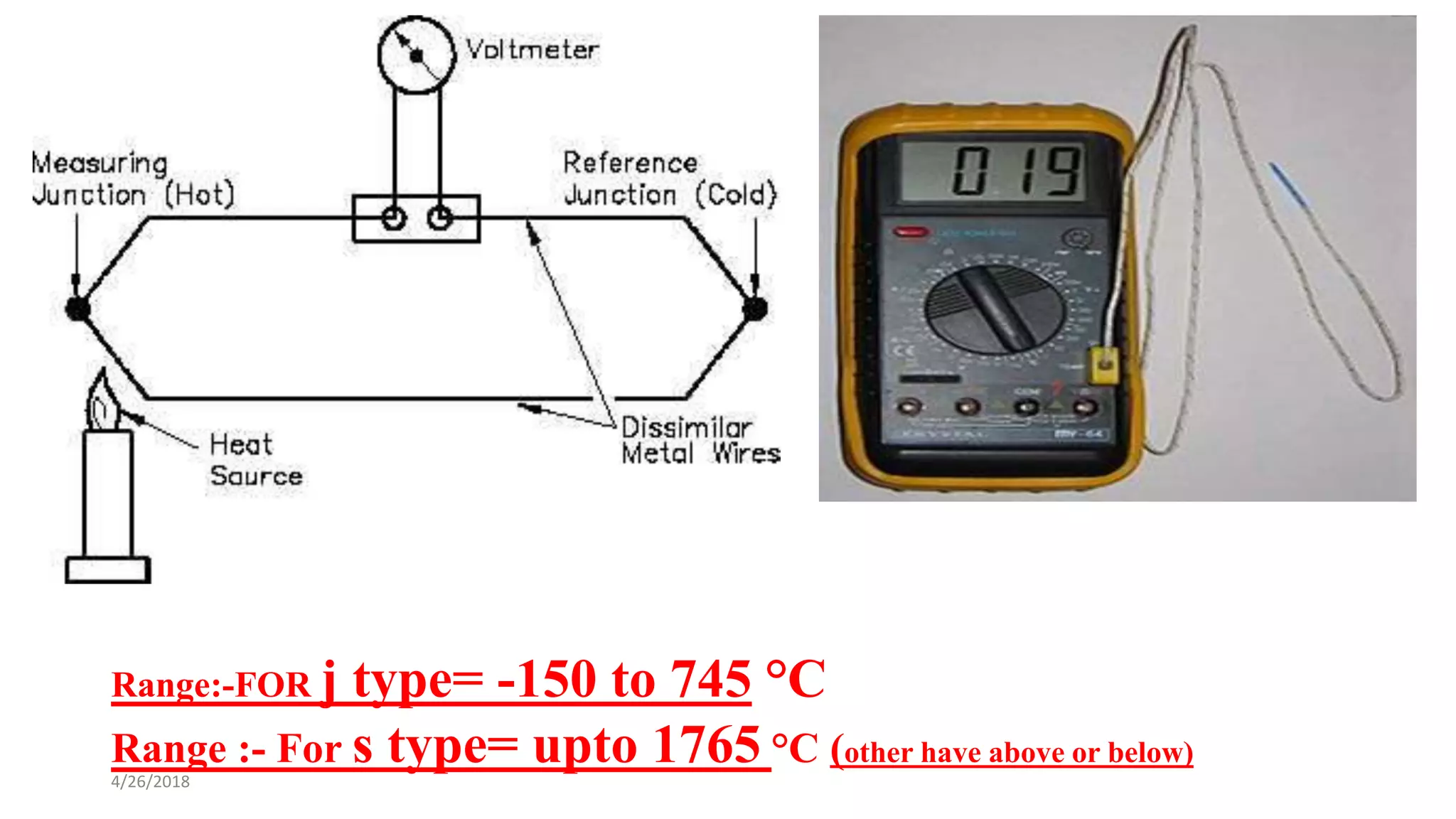
This document discusses various temperature measurement devices. It defines temperature and explains that it is a measure of how hot or cold a substance is. It then describes several common mechanical temperature sensors including bimetal strip thermometers, gas thermometers, vapor pressure thermometers, and liquid expansion thermometers. The document also discusses pyrometers, thermojunctive devices like thermocouples, thermoresistive devices like thermistors and RTDs, and provides the working principles and typical ranges for each.