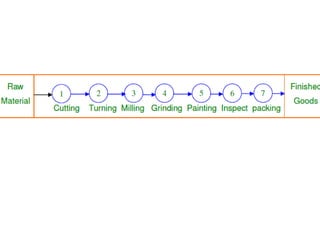
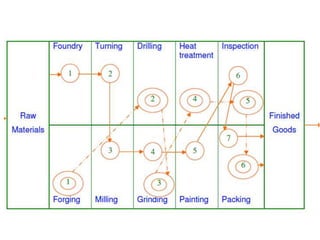
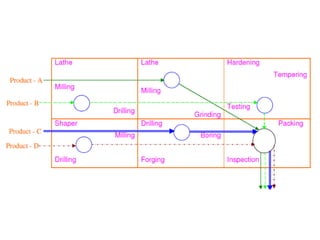
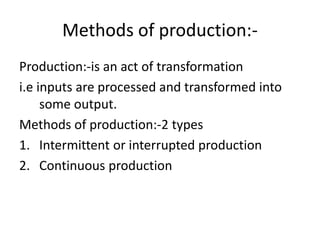
This document discusses different types of plant layouts and production methods. It describes four main types of layouts: product layout, process/functional layout, group/cellular layout, and fixed layout. It also discusses two main methods of production - intermittent/job production and batch production, and continuous/mass production. Finally, it covers work study techniques like method study and work measurement that are used to analyze work processes and improve efficiency.