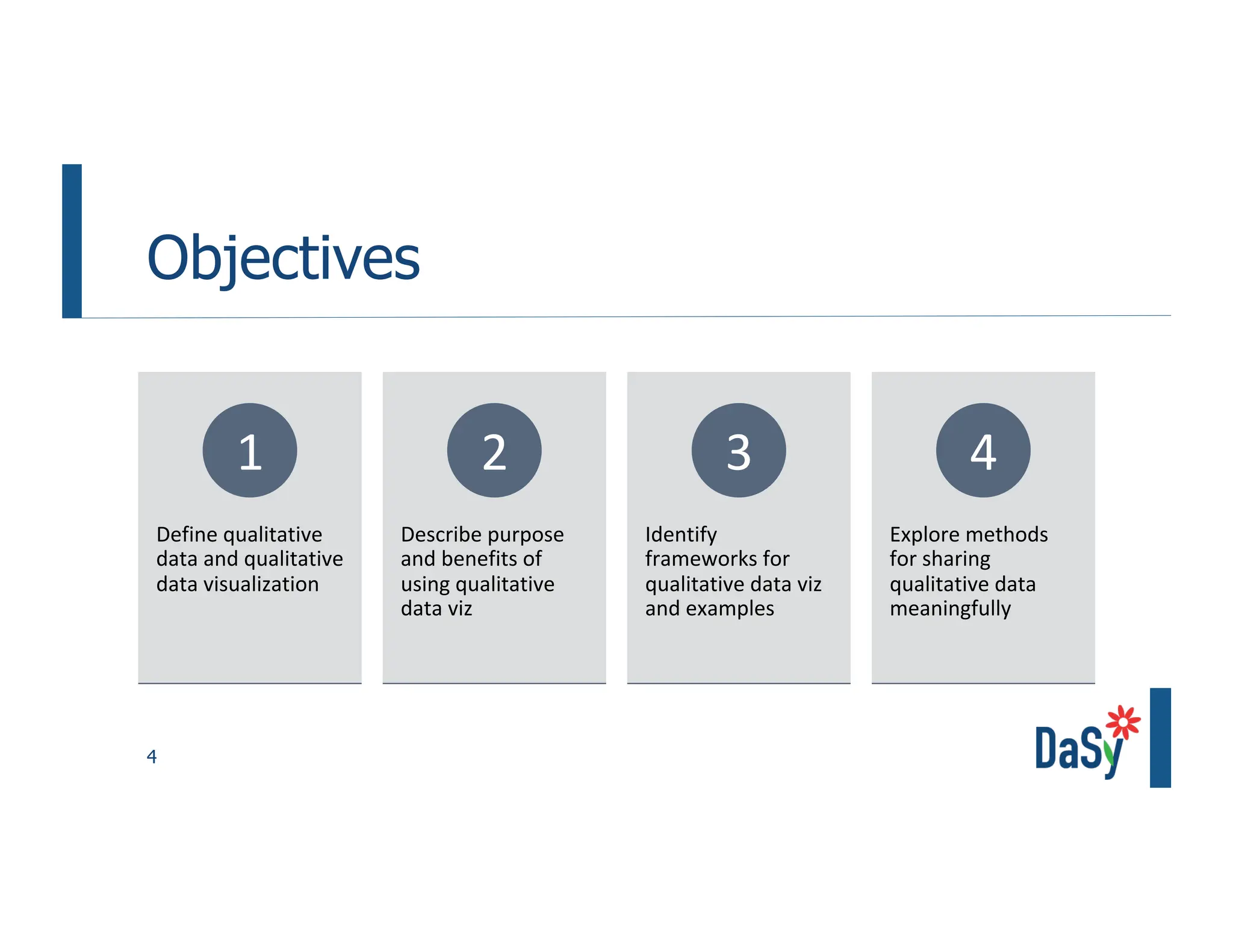
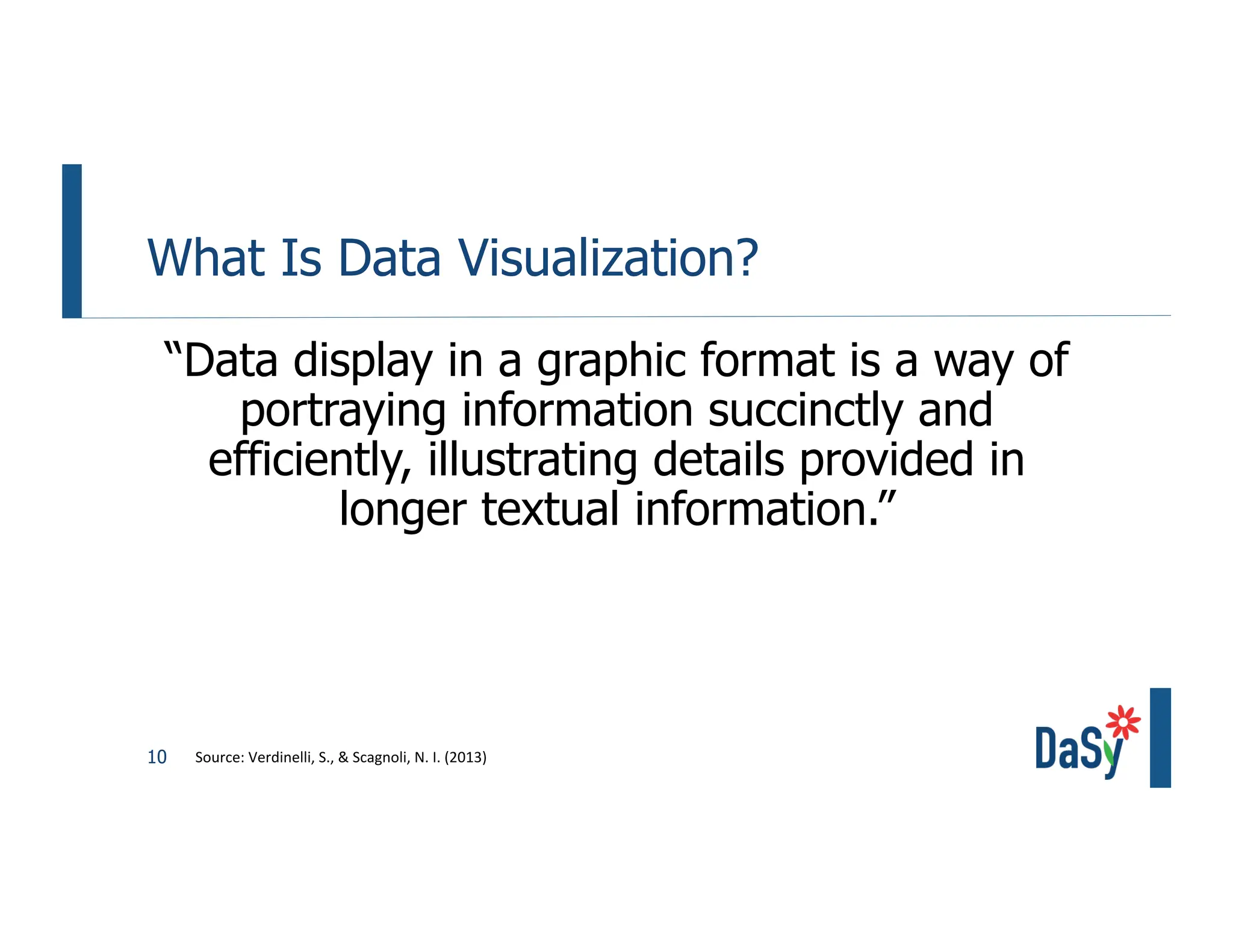
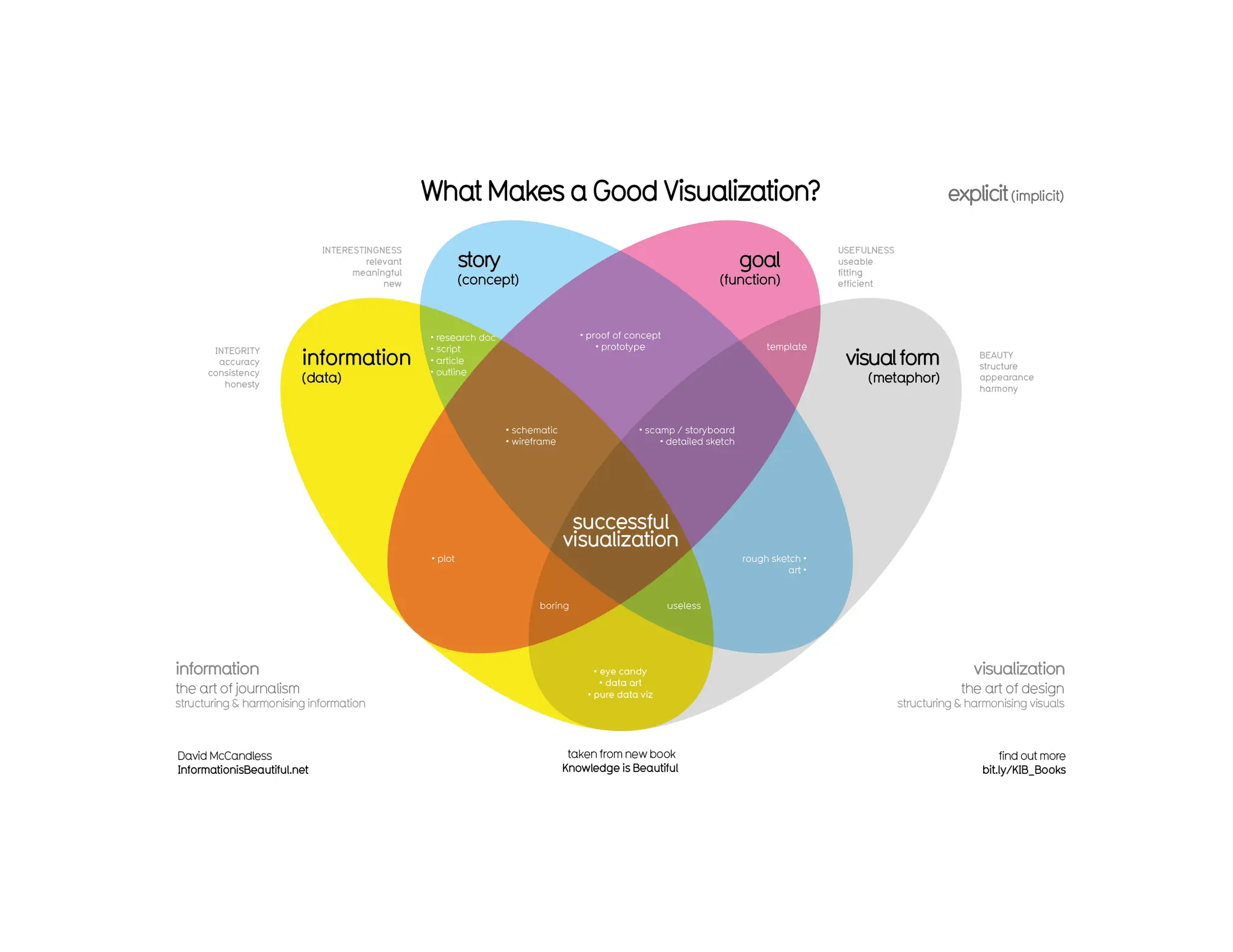
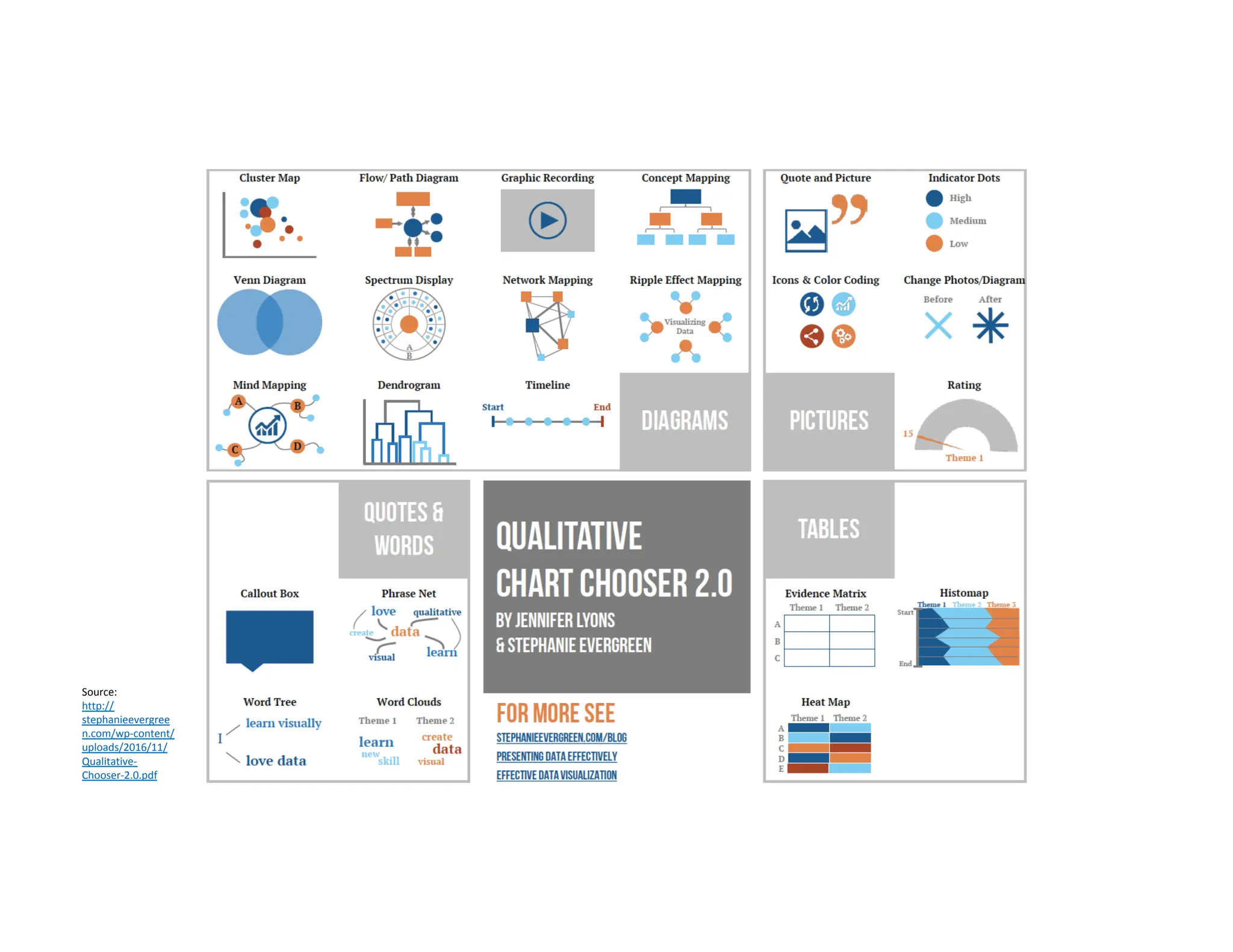
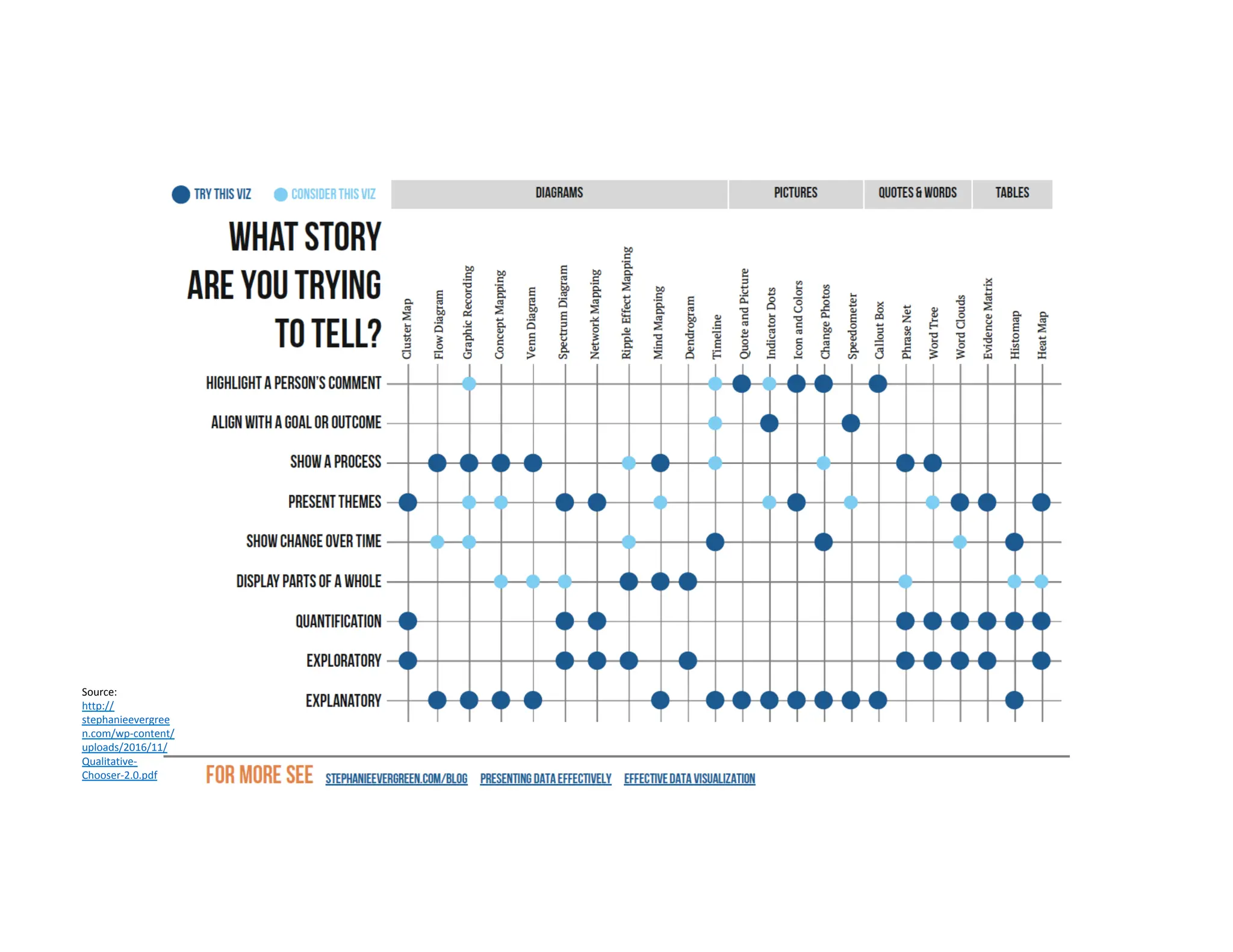
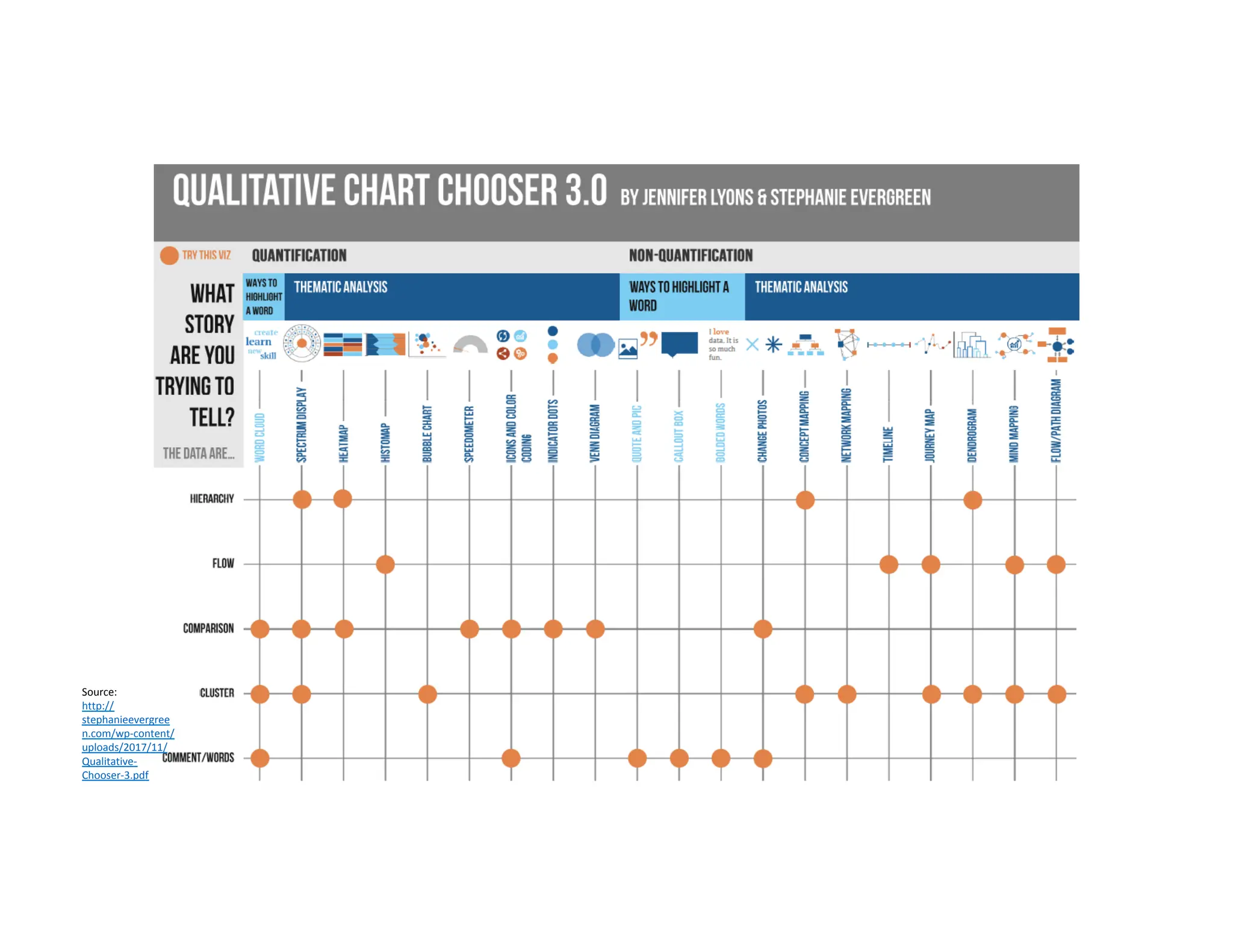
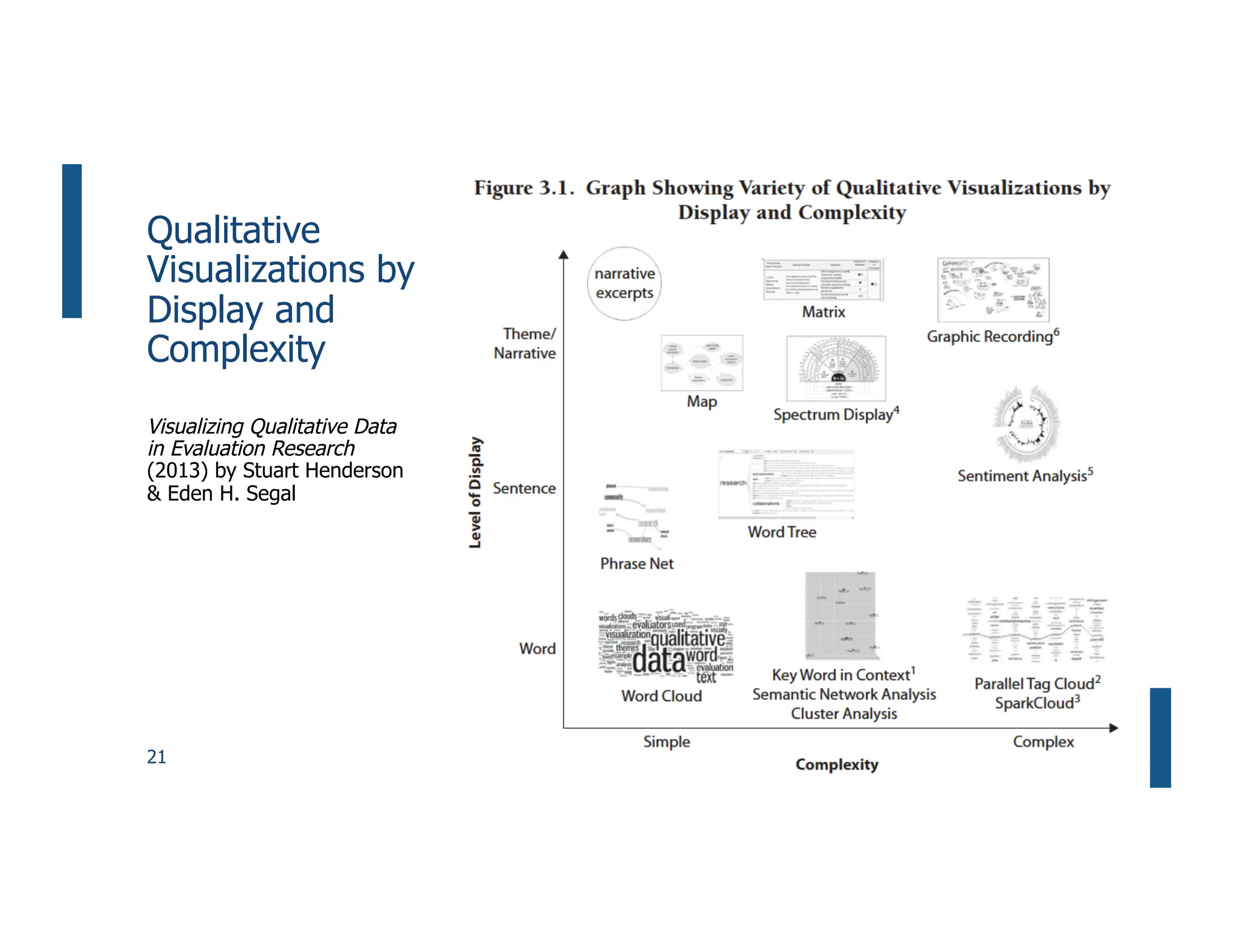
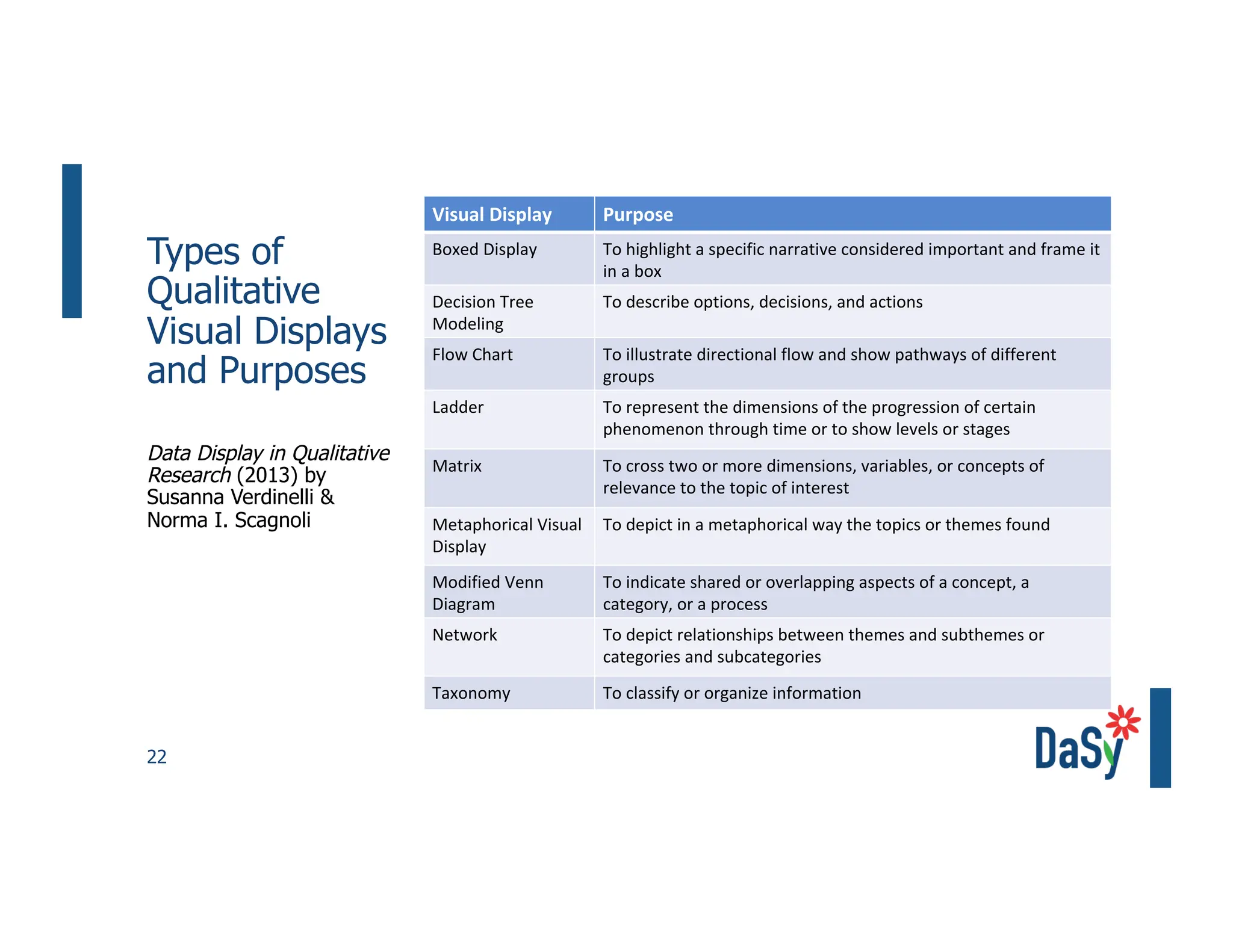
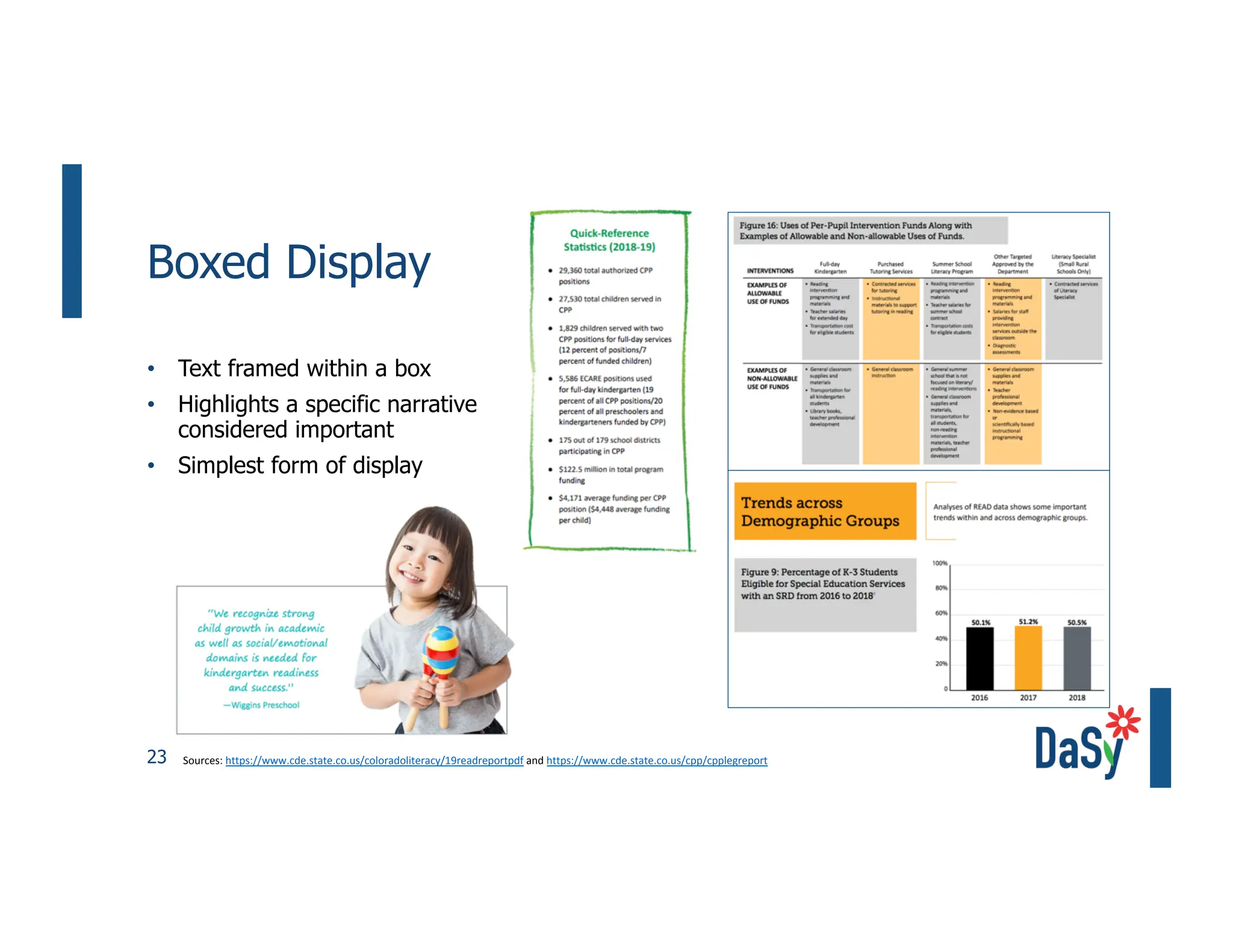
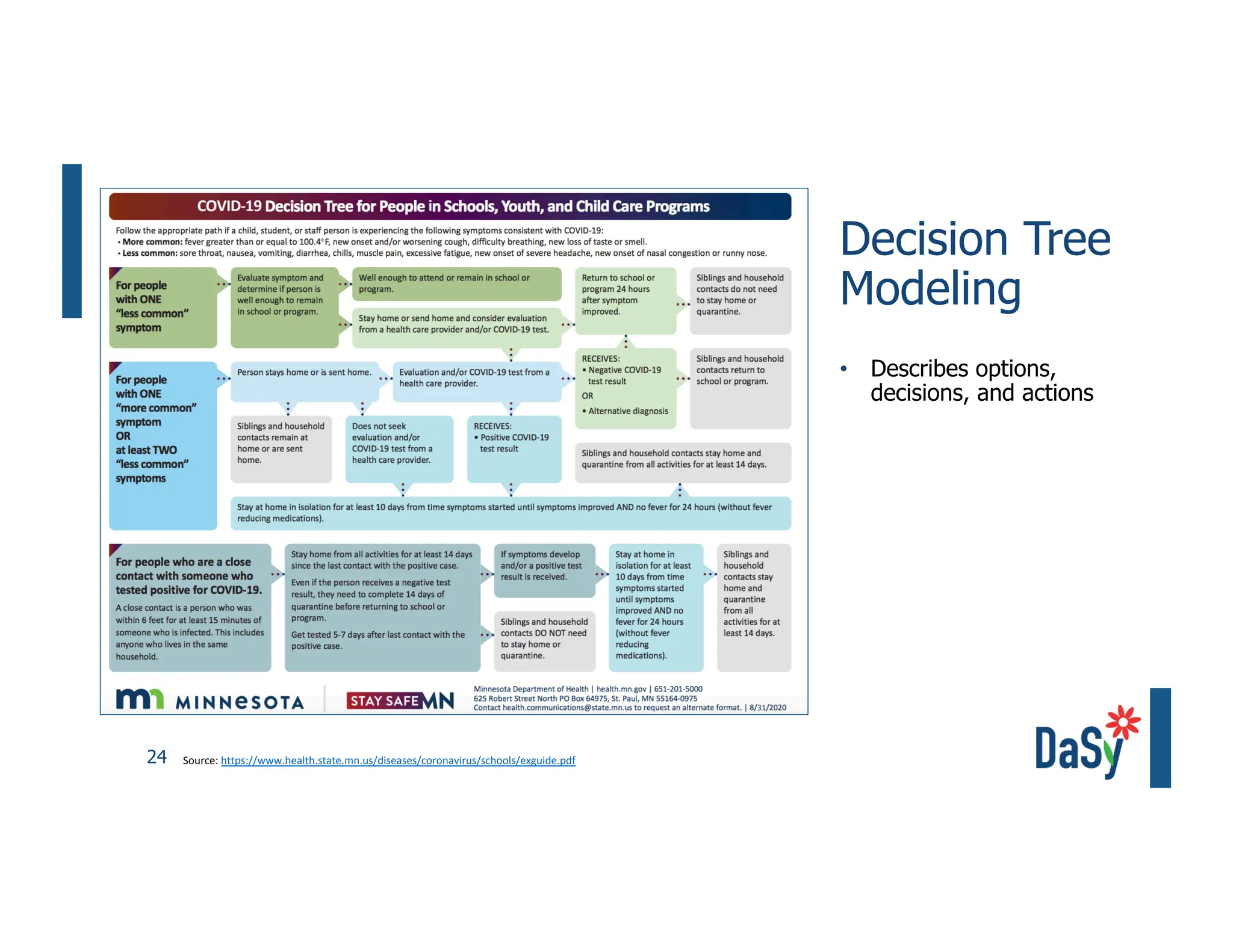
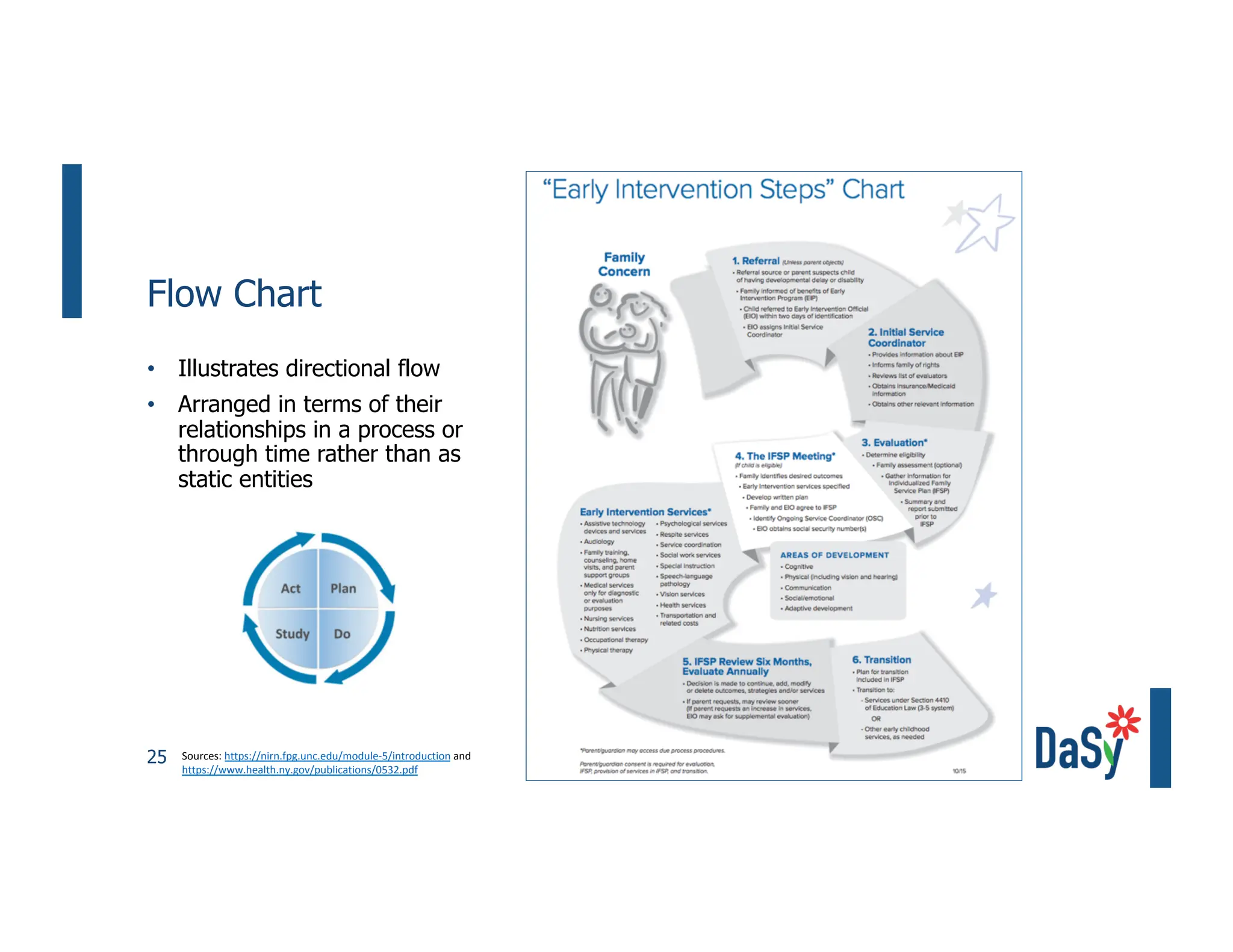
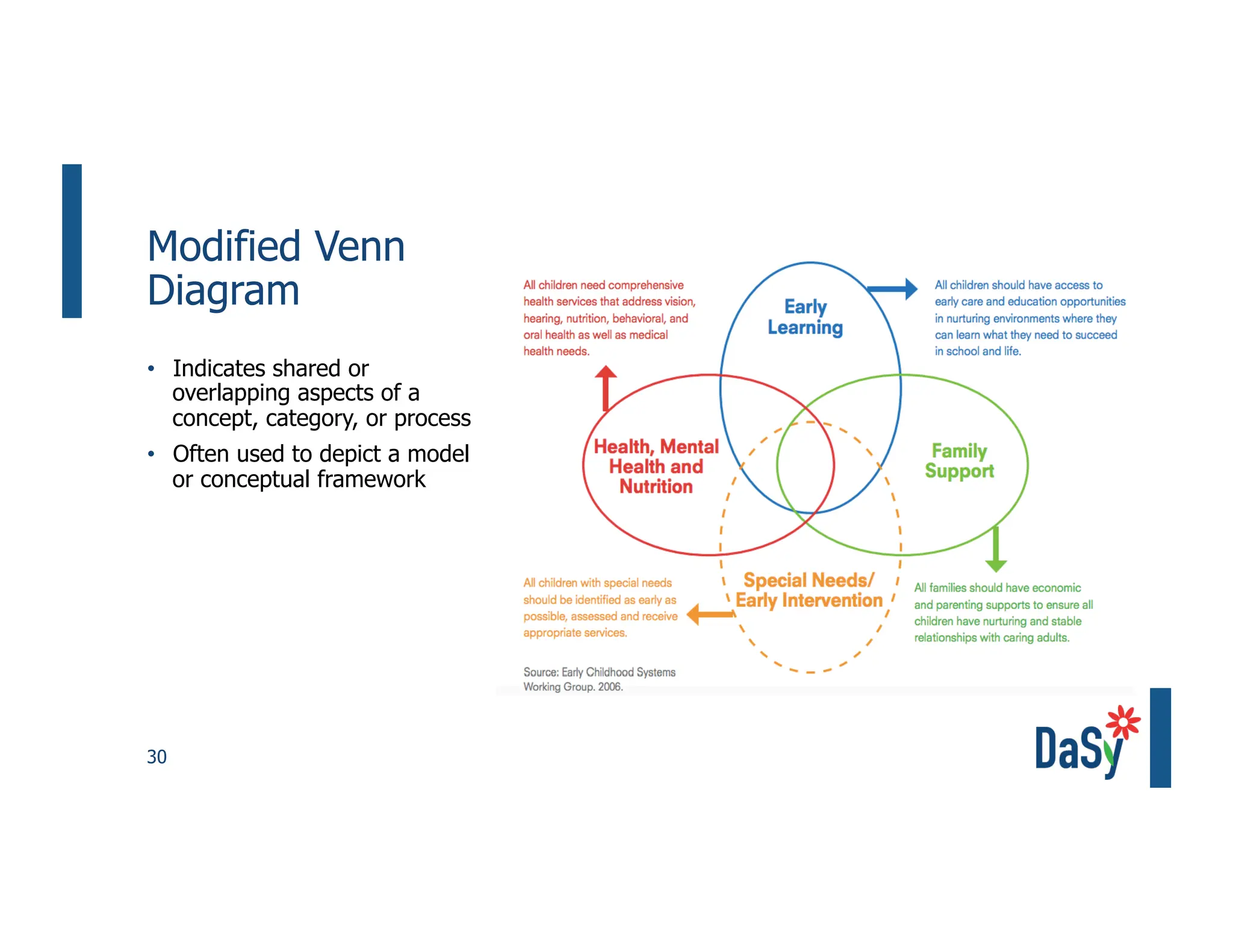
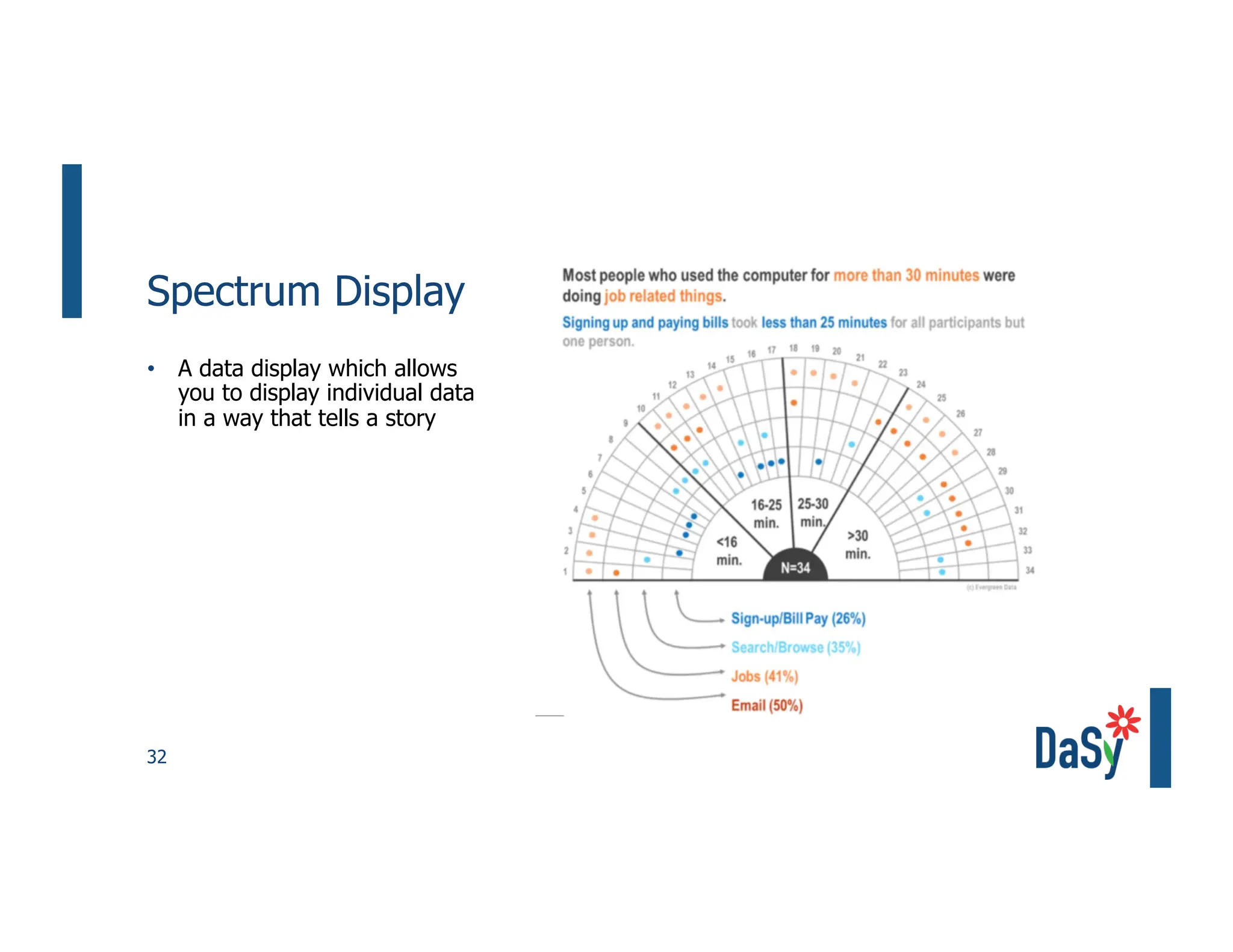
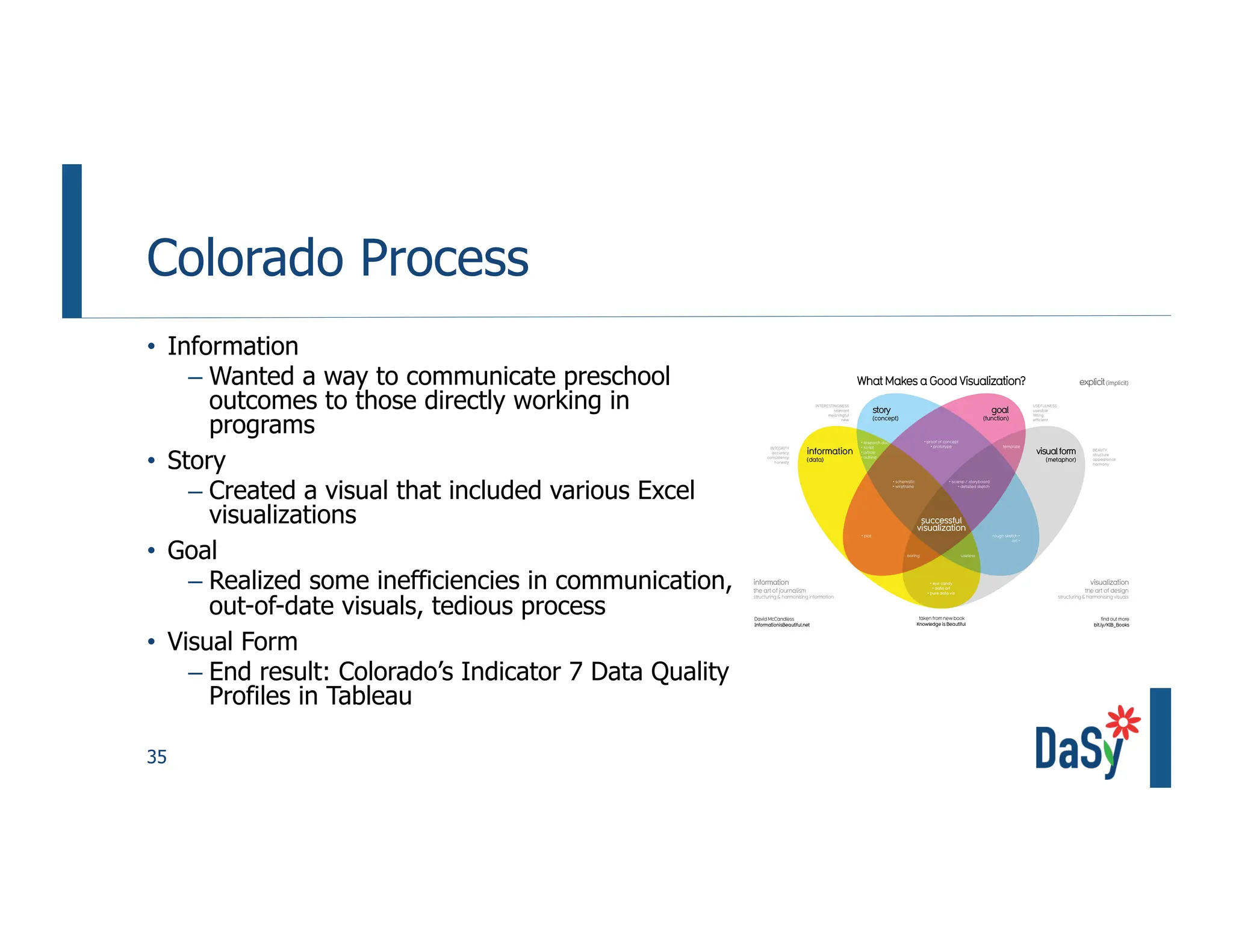
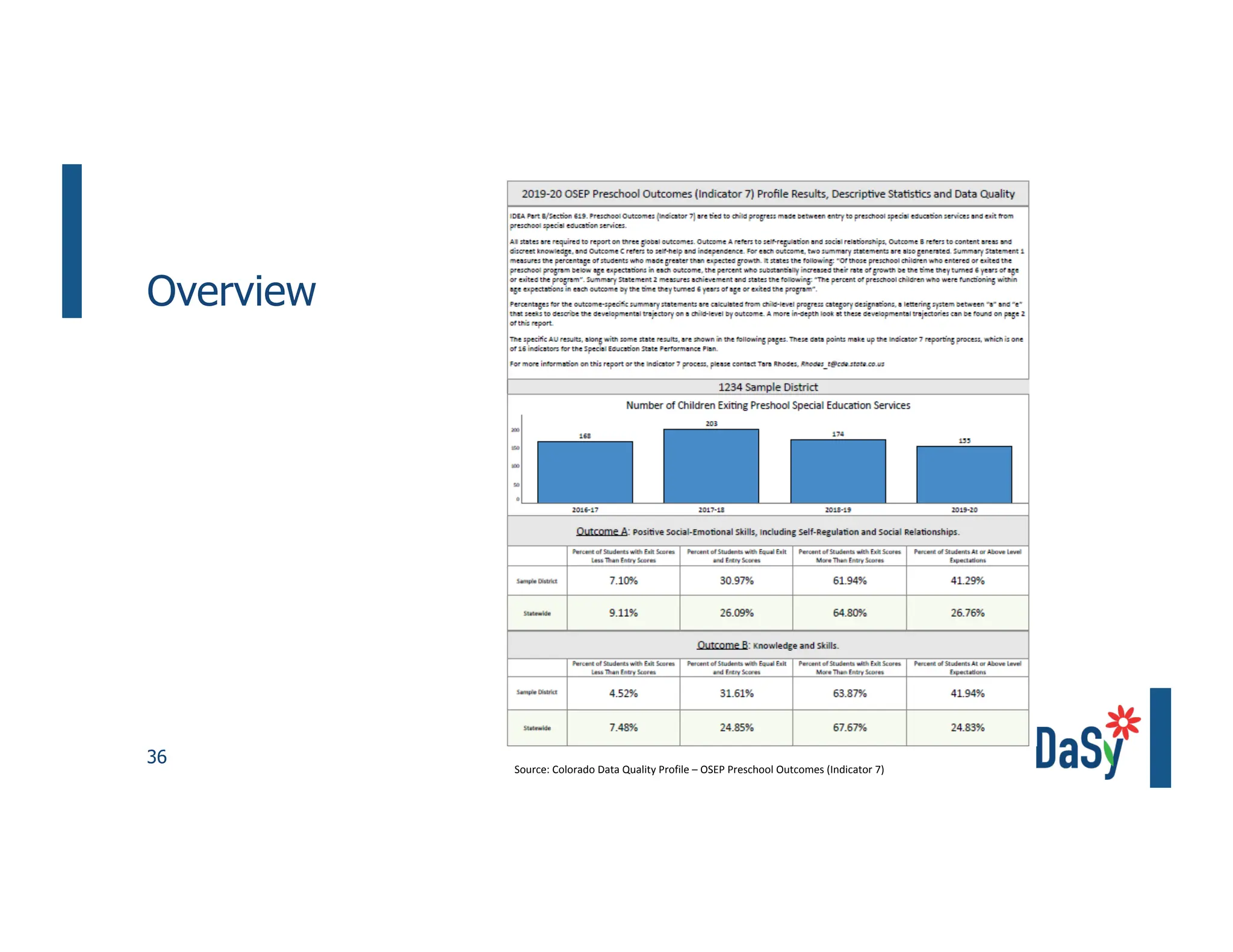
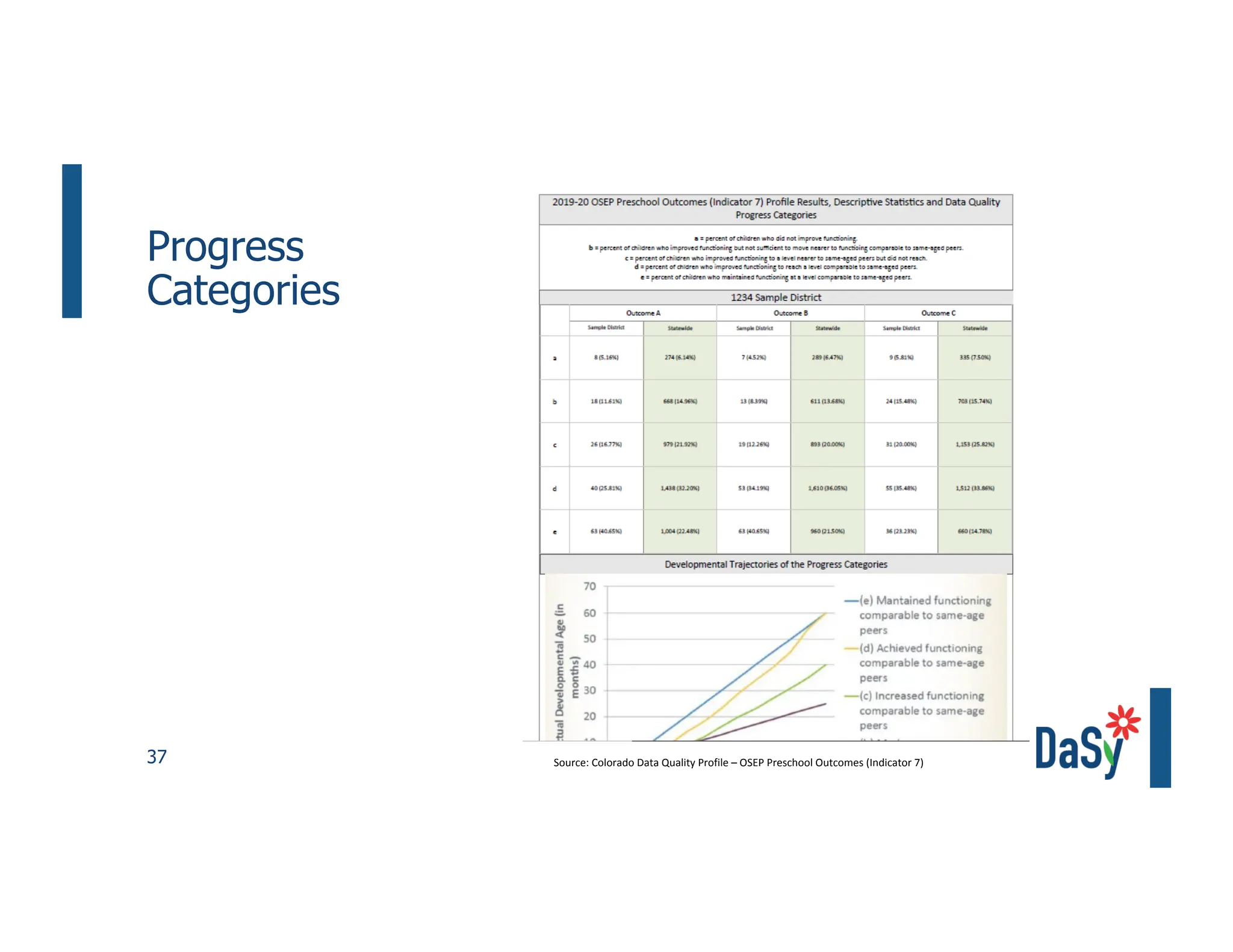
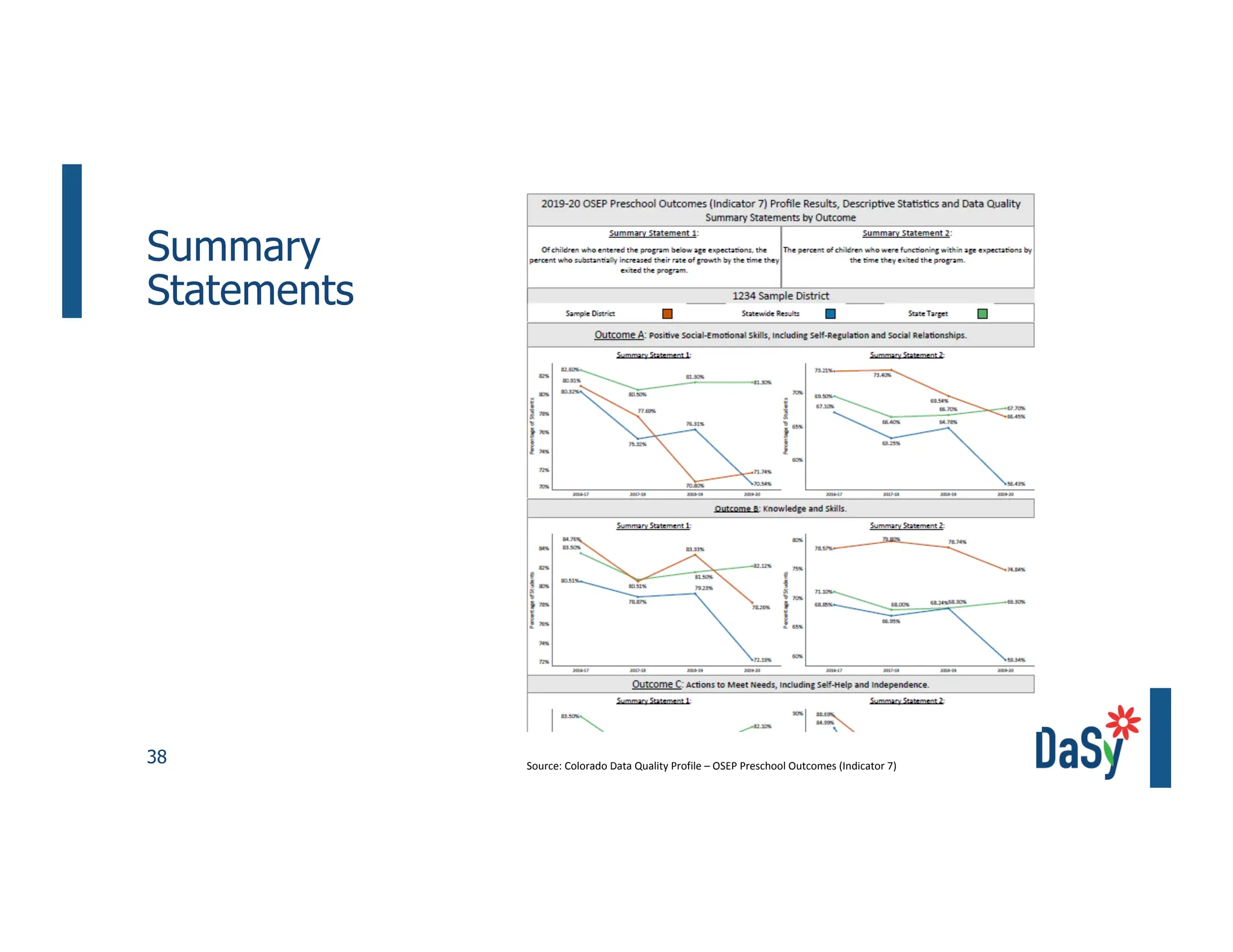
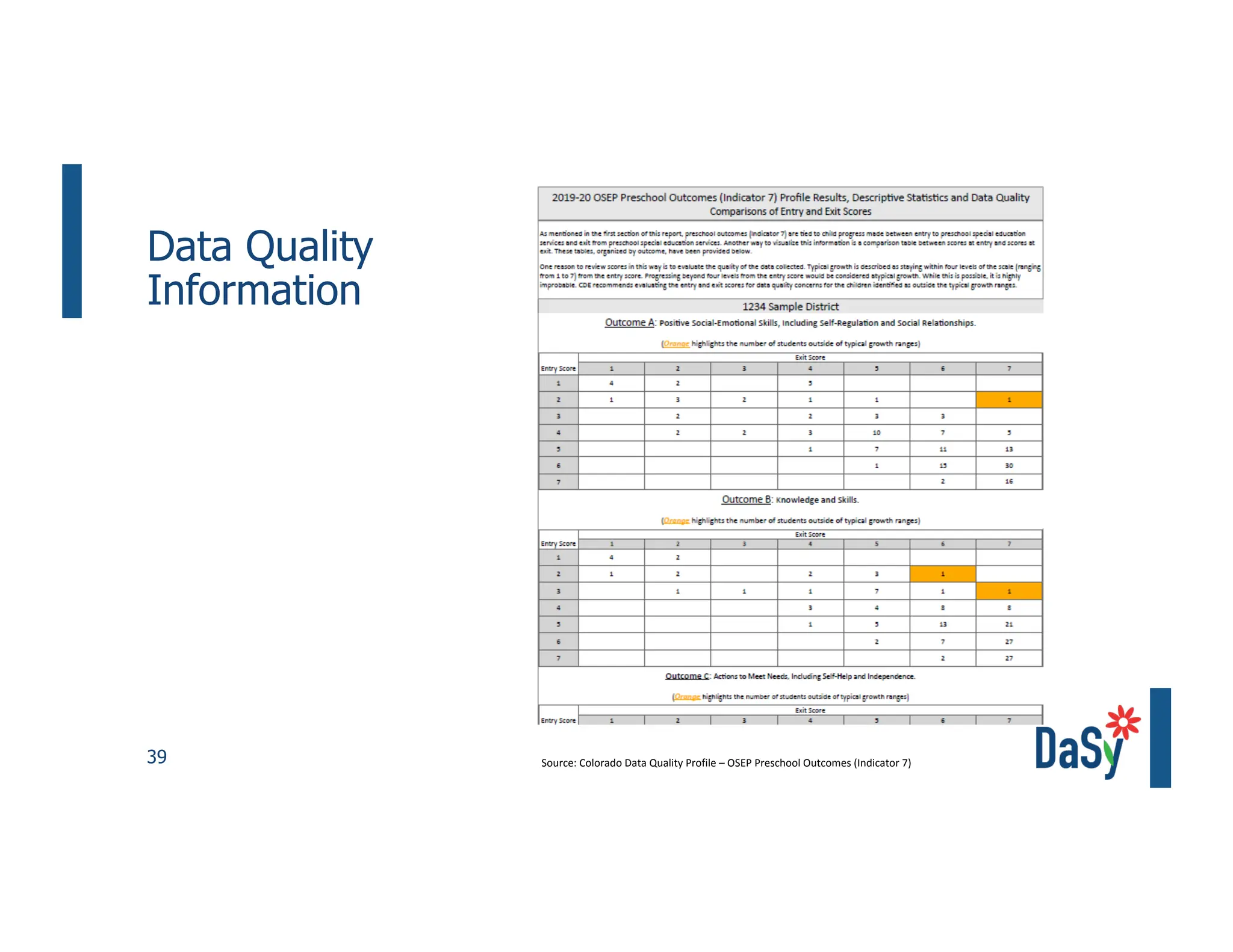
This document summarizes a presentation on unlocking the power of qualitative data through visualization. It discusses defining qualitative data and its benefits, frameworks for qualitative visualization like word clouds and matrices, and tools for sharing qualitative insights. Examples from Humans of New York and Colorado's early childhood outcomes data are provided. The presentation aims to help audiences better understand and communicate qualitative information.