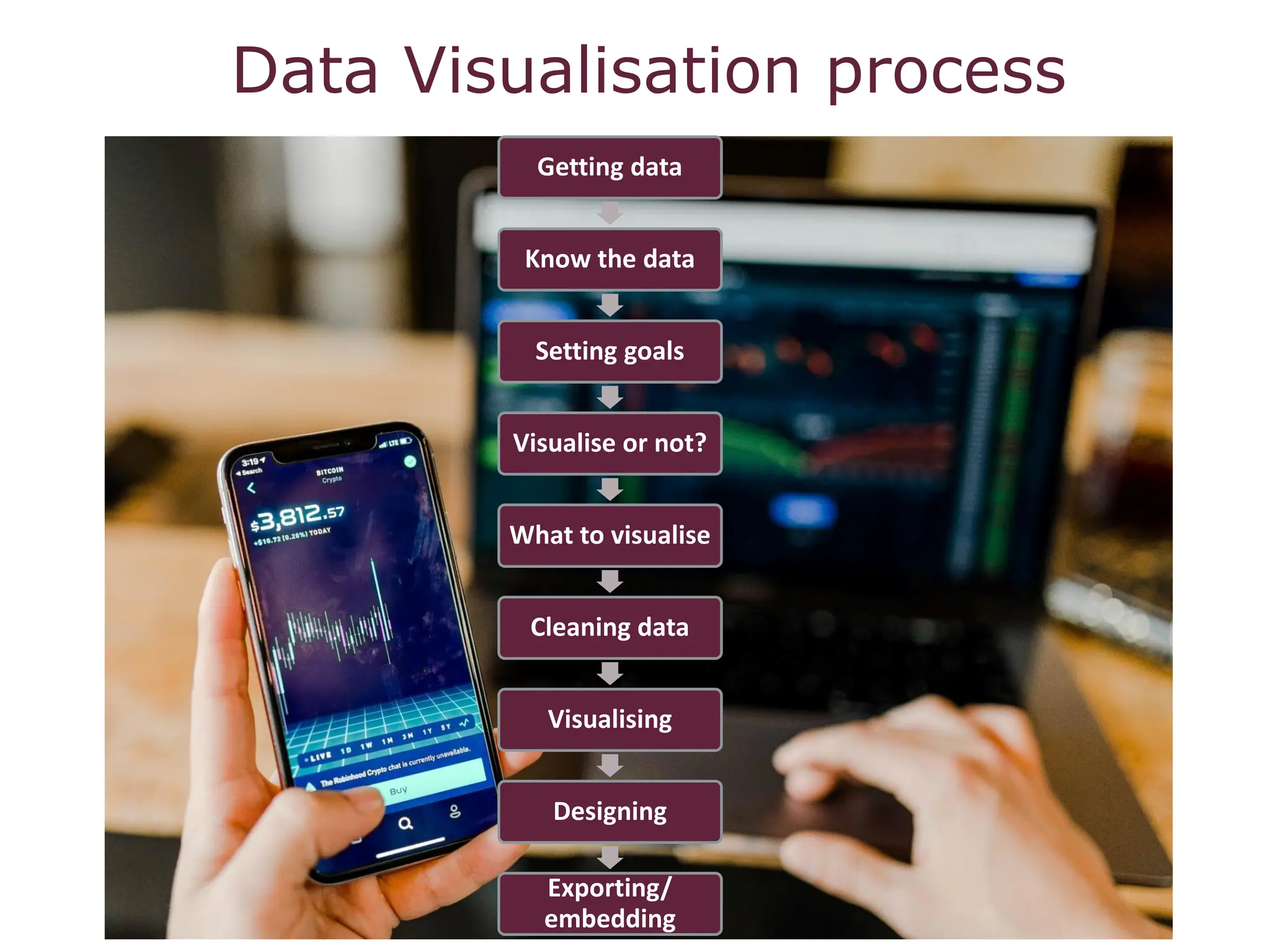
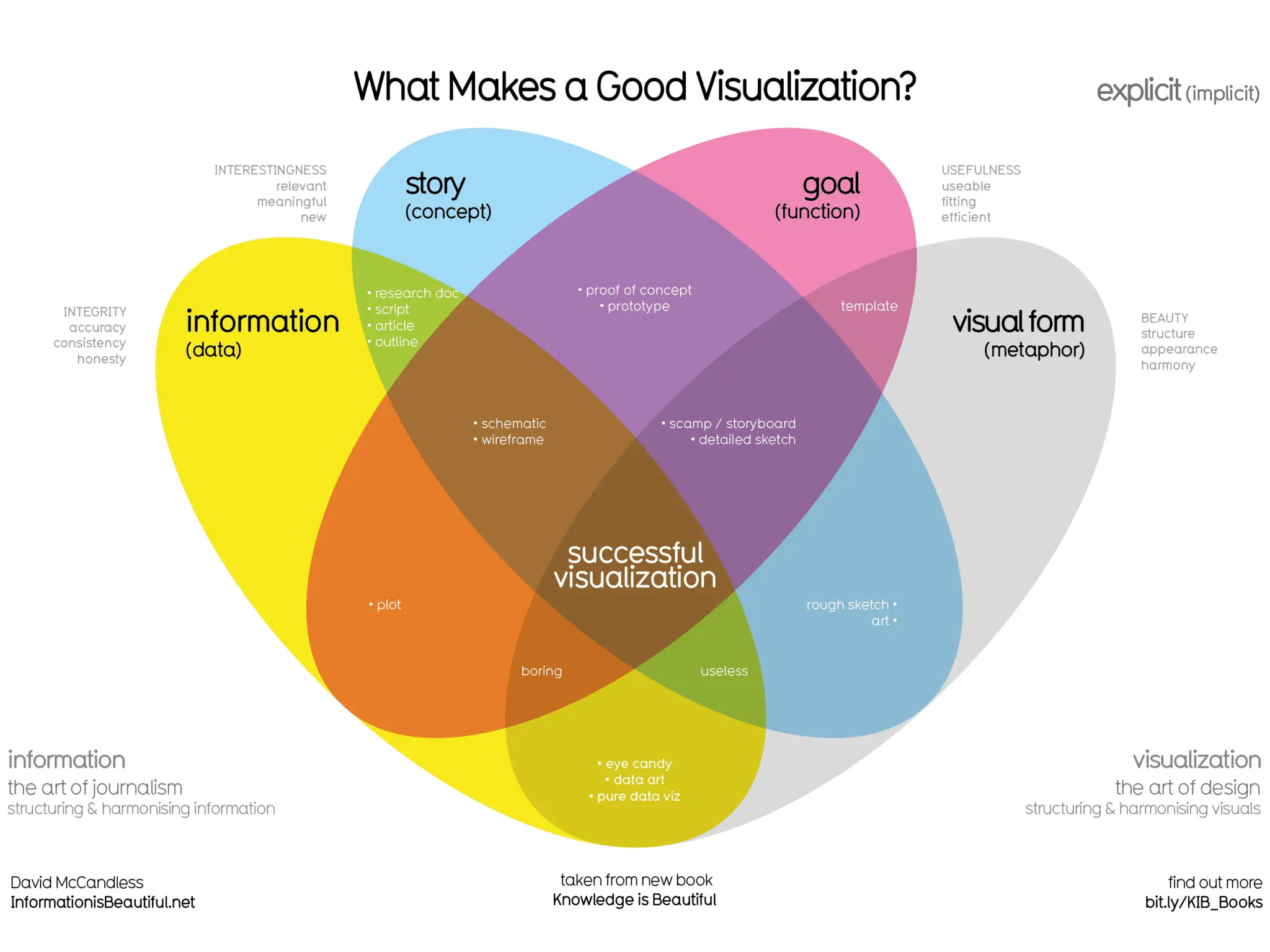
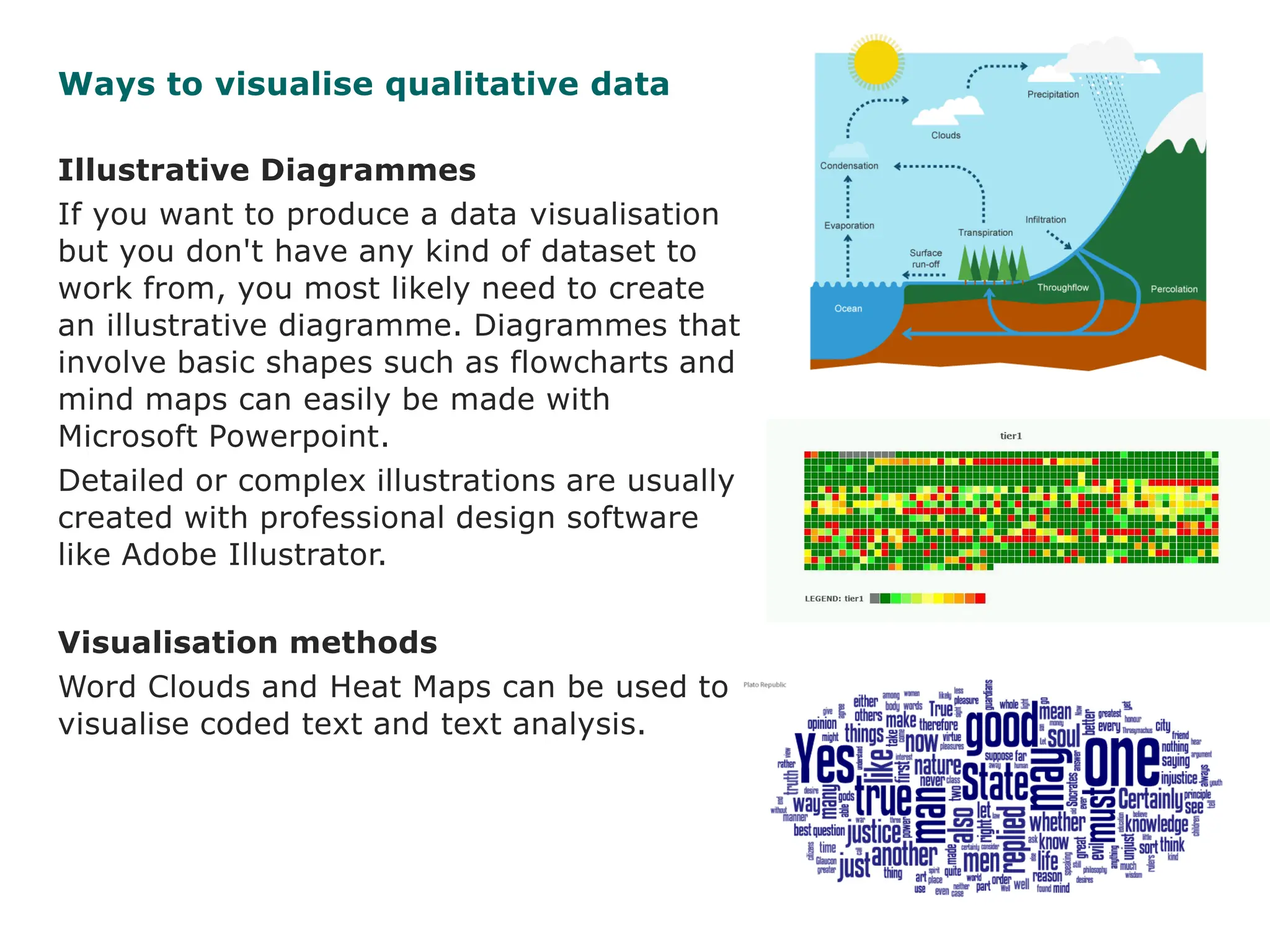
Visualizing data tells compelling stories that increase research impact. It is important to know the audience and find the key story or message in the data. The type of visualization should be chosen based on the data, goals, and audience. Effective use of color, choosing the right visualization type, and understanding visual literacy principles are important for communicating with visualizations.