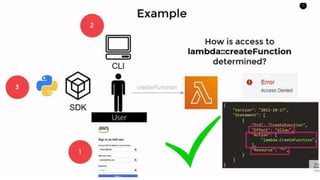
AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a web service that allows secure management of access to AWS resources by controlling user authentication and permissions. Key components include users, groups, policies, and roles, each facilitating organized and scalable access control. Best practices for IAM involve monitoring activities, strong password policies, and maintaining an understanding of AWS security features.









![Policy: AmazonS3ReadOnlyAccess
{
"Version": "2012-10-17", == This indicates the version of the policy language being used
"Statement": [ == This is an array of statements that define the permissions granted by the policy.
{
"Effect": "Allow", == This is the effect of the statement, which is set to "Allow." It means that this policy allows the
specified actions on the specified resources.
"Action": [ This is an array of actions that this policy allows.
"s3:Get*",
"s3:List*",
"s3:Describe*",
"s3-object-lambda:Get*",
"s3-object-lambda:List*"
],
"Resource": "*" == The asterisk (*) is a wildcard, meaning that this policy allows the specified actions on all S3
}
]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/identityaccessmanagement-240618070718-f8f2e98e/85/Identity-Access-Management-presented-by-Techserverglobal-10-320.jpg)