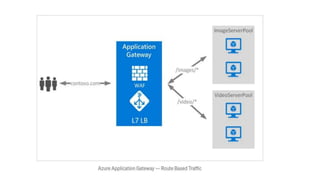
The Azure Application Gateway is a web traffic load balancer that operates at OSI layer 7, allowing for advanced routing based on URI paths and host headers, unlike traditional load balancers which work at layer 4. It supports TLS/SSL termination and end-to-end encryption, catering to varying security and compliance requirements. The key difference between an application gateway and a standard load balancer lies in the application's routing and security features, with the application gateway offering more specialized capabilities.