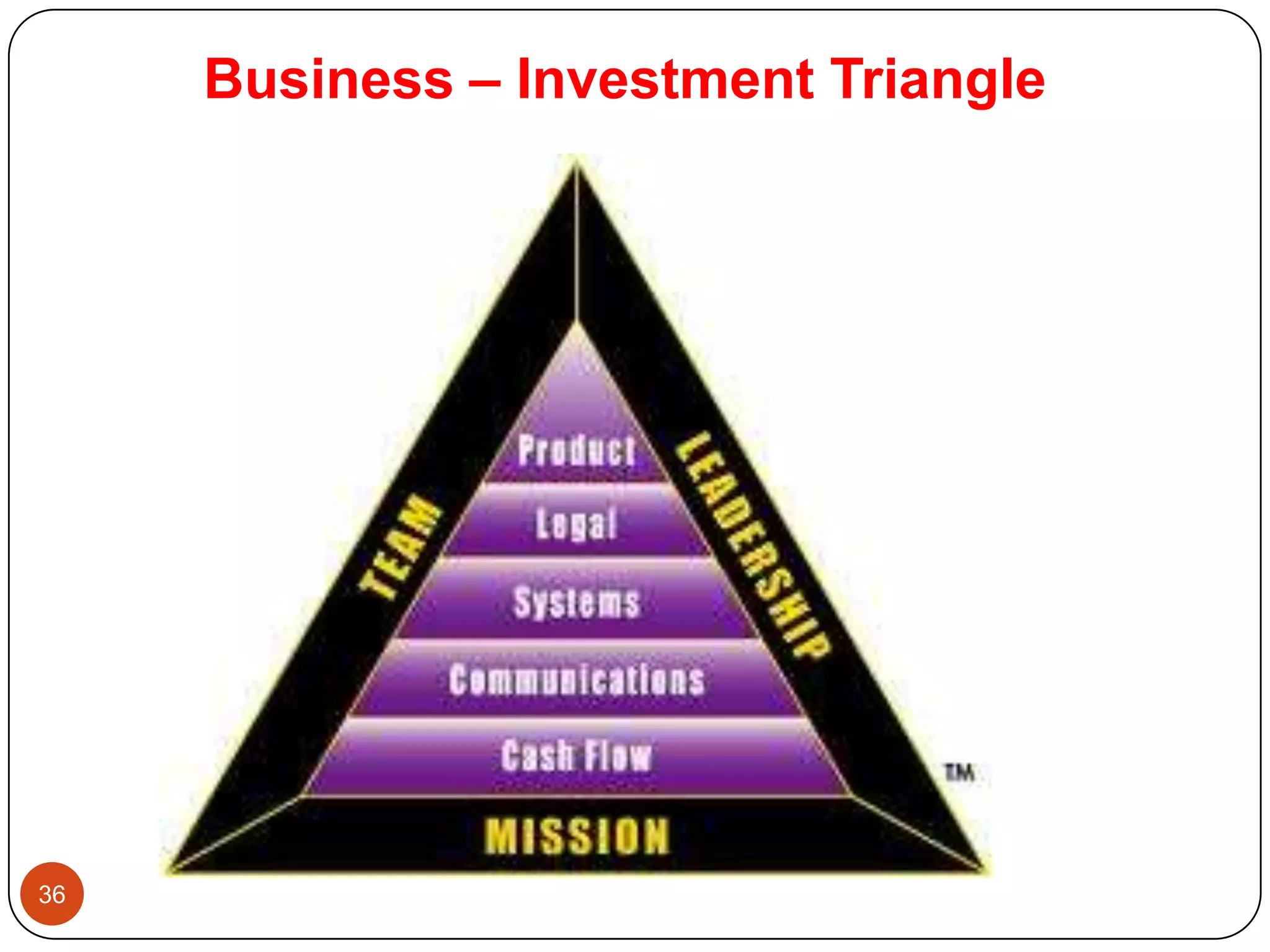
This document provides guidance on starting, growing, and sustaining a business. It discusses developing a vision and mission statement to guide business decisions. It emphasizes determining customer needs and defining the business's core competencies. The document advises segmenting the market and evaluating strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. It recommends setting goals and strategic options to achieve key success factors. Finally, it stresses the importance of developing a strategic plan and turning strategies into actionable projects.