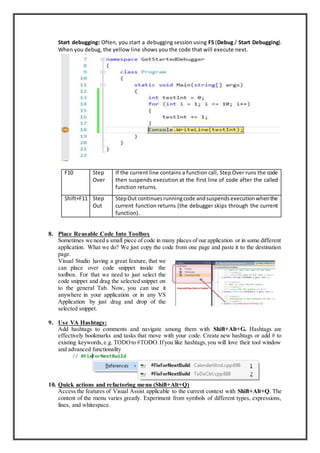
Visual Studio, Eclipse, and NetBeans are three popular IDEs. Visual Studio features include automatic indentation, side-by-side editing, IntelliSense, debugging tools, and reusable code snippets. Eclipse features include file encoding settings, automatic saving, type filters, launch configurations, and code formatting options. NetBeans provides a full-featured Java EE environment out of the box and strong support for HTML5, JavaScript, and CSS development.