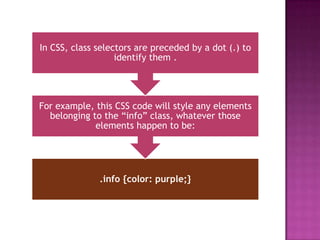
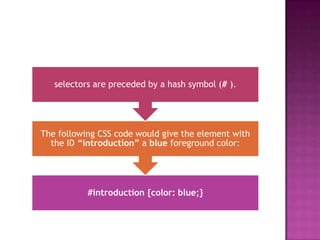
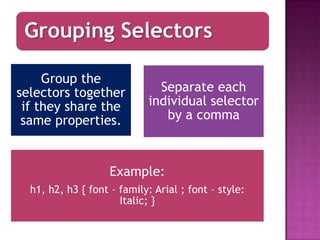
ID selectors target individual elements by ID, preceded by #, and IDs must be unique. Class selectors target elements of the same class, preceded by a dot, and the same class can be applied to multiple elements. They were differentiated - IDs target unique elements while classes can target multiple. An example was given combining ID and class selectors in HTML and applying CSS styles.