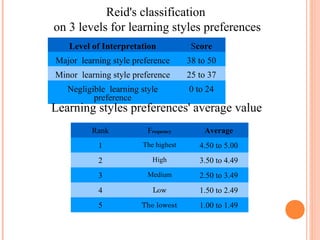
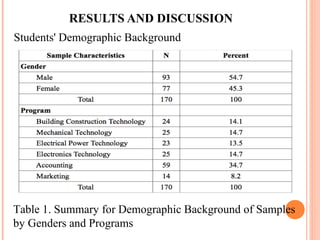
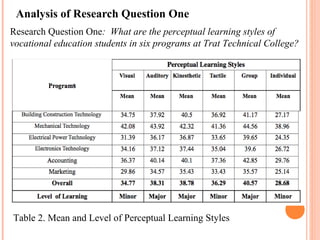
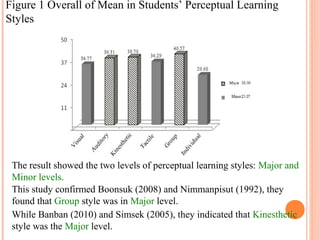
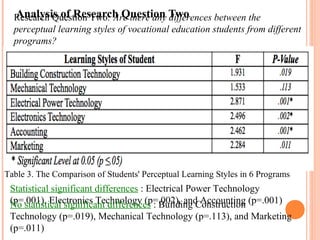
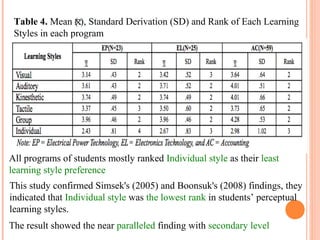
This document summarizes a study on the perceptual learning styles of vocational education students at Trat Technical College in Thailand. The study surveyed 170 students across 6 programs to determine their preferences on a scale for visual, auditory, kinesthetic, tactile, group, and individual learning styles. The results showed that group, kinesthetic, and auditory styles were the major preferred learning styles, while visual, tactile, and individual styles were minor preferences. There were also statistically significant differences found in the learning style preferences between students in the Electrical Power Technology, Electronics Technology, and Accounting programs compared to the other programs. The study concludes that understanding students' learning styles can help teachers design their lessons and activities to be more