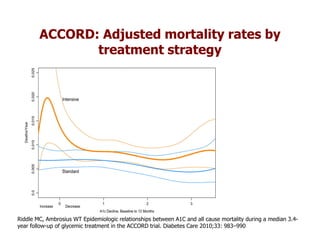
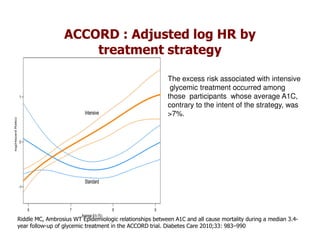
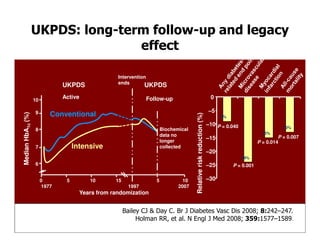
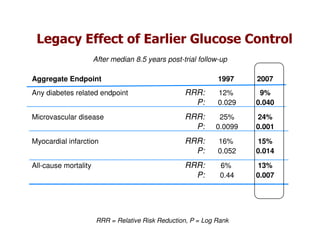
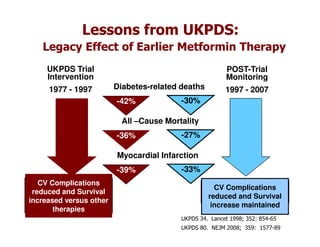
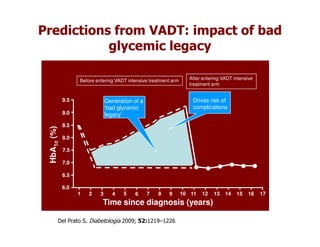
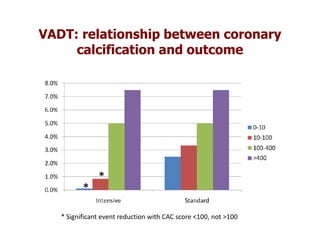
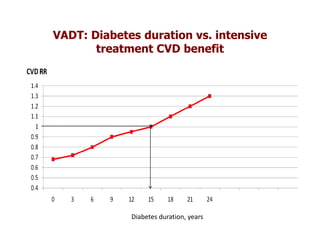
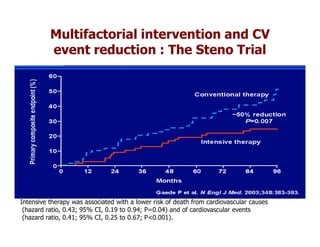
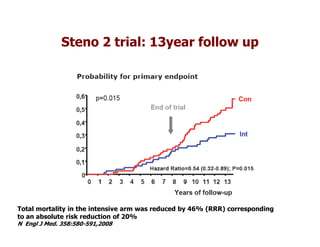
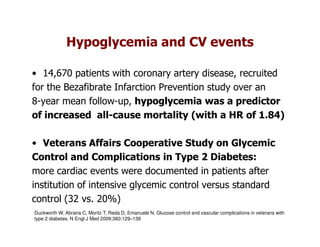
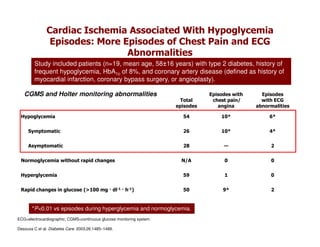
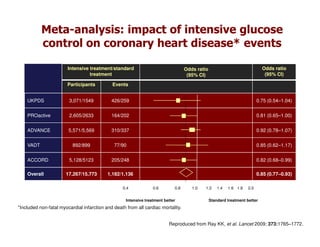
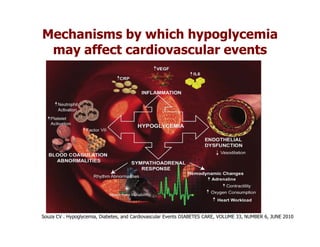
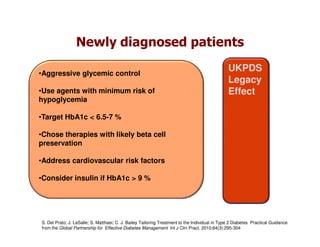
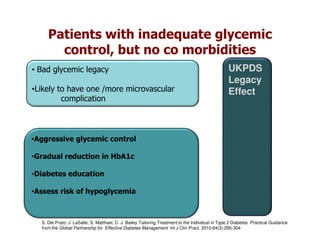
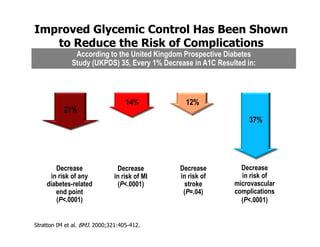
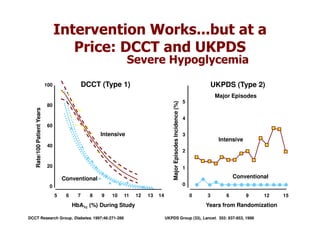
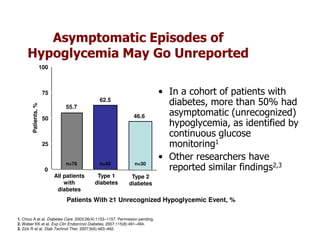
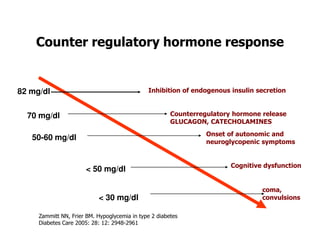
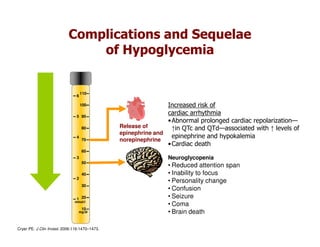
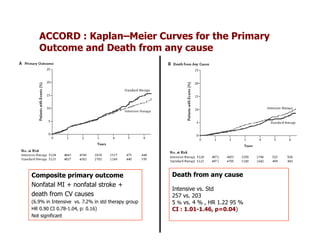
This document discusses evidence that intensive glycemic control can reduce cardiovascular risk for patients with type 2 diabetes, but that this risk reduction may come at the price of increased risk of hypoglycemia. Some key points discussed include: 1) trials like UKPDS and ACCORD showed glycemic control reduced microvascular and cardiovascular complications but increased risk of hypoglycemia; 2) hypoglycemia is associated with increased cardiovascular risk and mortality in some studies; and 3) the benefits of intensive control may depend on patient characteristics like age and diabetes duration, with shorter-duration patients experiencing more benefit. The document evaluates how best to fit treatment targets and medications to individual patients to maximize benefits and minimize hypoglycemia risk.



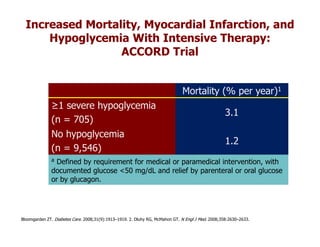
![Severe hypoglycemia : definition in
ACCORD
Requiring medical or paramedical attention in which
there was either a documented capillary glucose level 50
mg/dL (2.8 mmol/L) or in which prompt recovery was
achieved with oral carbohydrate, intravenous glucose, or
glucagons
Severe Hypoglycemia Monitoring and Risk Management Procedures in the Action to Control Cardiovascular
Risk in Diabetes (ACCORD) Trial . Am J Cardiol 2007;99[suppl]:80i–89i)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cvhypoglycemia-100901113411-phpapp02/85/Cardiovascular-events-Hypoglycemia-7-320.jpg)



![ACCORD
• Rate of 1-year change in A1c showed that a greater
decline in A1c was associated with a lower risk of death
• 20% higher risk of death for every 1% higher A1c level
above 6%, suggesting that lower blood glucose levels
may be a worthy target in some patients
• Patients with the [consistently] lowest A1c levels had
the lowest risk. The excess mortality risk was in
those patients who failed to achieve and sustain
A1c levels between 6% and 7%.
Update on ACCORD. International Diabetes Federation 2009 World Diabetes
Congress. October 22, 2009; Montreal, QC. American Diabetes Association (ADA) 69th Scientific Sessions:
Abstract 468-P. Presented June 9, 2009](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cvhypoglycemia-100901113411-phpapp02/85/Cardiovascular-events-Hypoglycemia-15-320.jpg)