This document discusses hyperuricemia, which is a high level of uric acid in the blood. It covers the following key points:
- Causes of hyperuricemia include overproduction of uric acid, underexcretion by the kidneys, or a combination of the two. Various medical conditions and medications can also cause hyperuricemia.
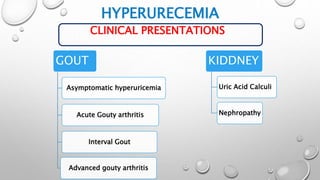
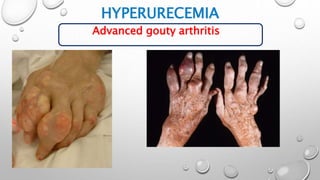
- Clinical presentations of hyperuricemia include gout (painful arthritis), uric acid kidney stones, and nephropathy. Gout typically starts as acute attacks of pain and swelling in joints like the big toe. Without treatment, gout can progress to chronic arthritis and tophi (hard lumps) under the skin.


![HYPERURECEMIA
URIC ACID : END PRODUCT OF PURINE METABOLISM.
HYPERURICEMIA: (SERUM URIC ACID LEVEL > 6.8 MG/DL [>
404.5 MCMOL/L]).
1 MG/DL =59.5 MCMOL/L.
INTRODUCTION](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hyperuricemia-190724133907/85/Hyperuricemia-3-320.jpg)