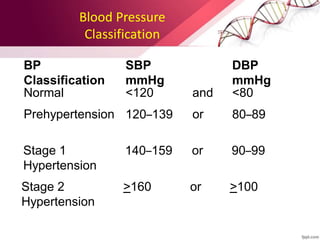
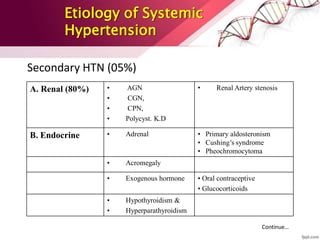
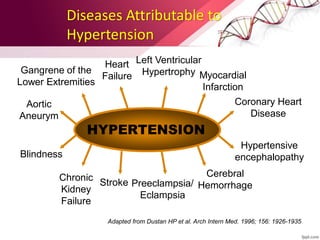
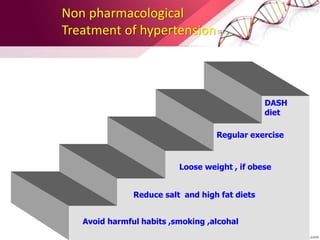
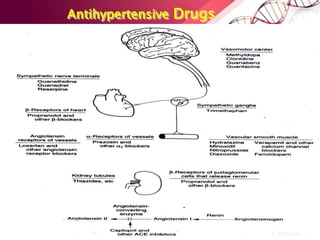
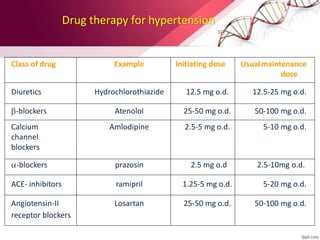
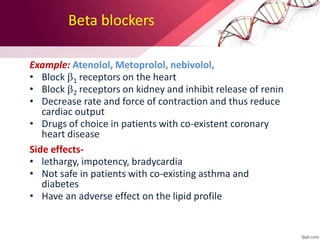
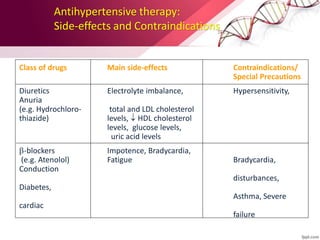
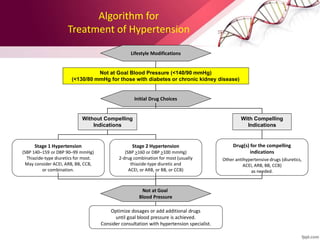
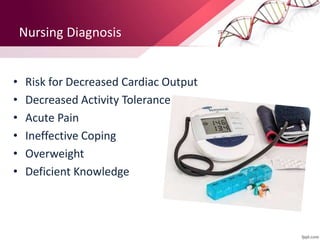
This document provides information on the diagnosis and management of hypertension. It defines hypertension as blood pressure greater than 140/90 mmHg. It describes the types and causes of hypertension, including essential (95% of cases, no identifiable cause) and secondary (underlying cause such as renal or endocrine issues). Target organ damage from uncontrolled hypertension includes effects on the heart, brain, kidneys, and retina. Lifestyle modifications and medication are used to treat hypertension with the goals of reducing blood pressure below 140/90 mmHg to prevent cardiovascular events. Common classes of antihypertensive medications discussed include diuretics, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, calcium channel blockers, and angiotensin receptor blockers.