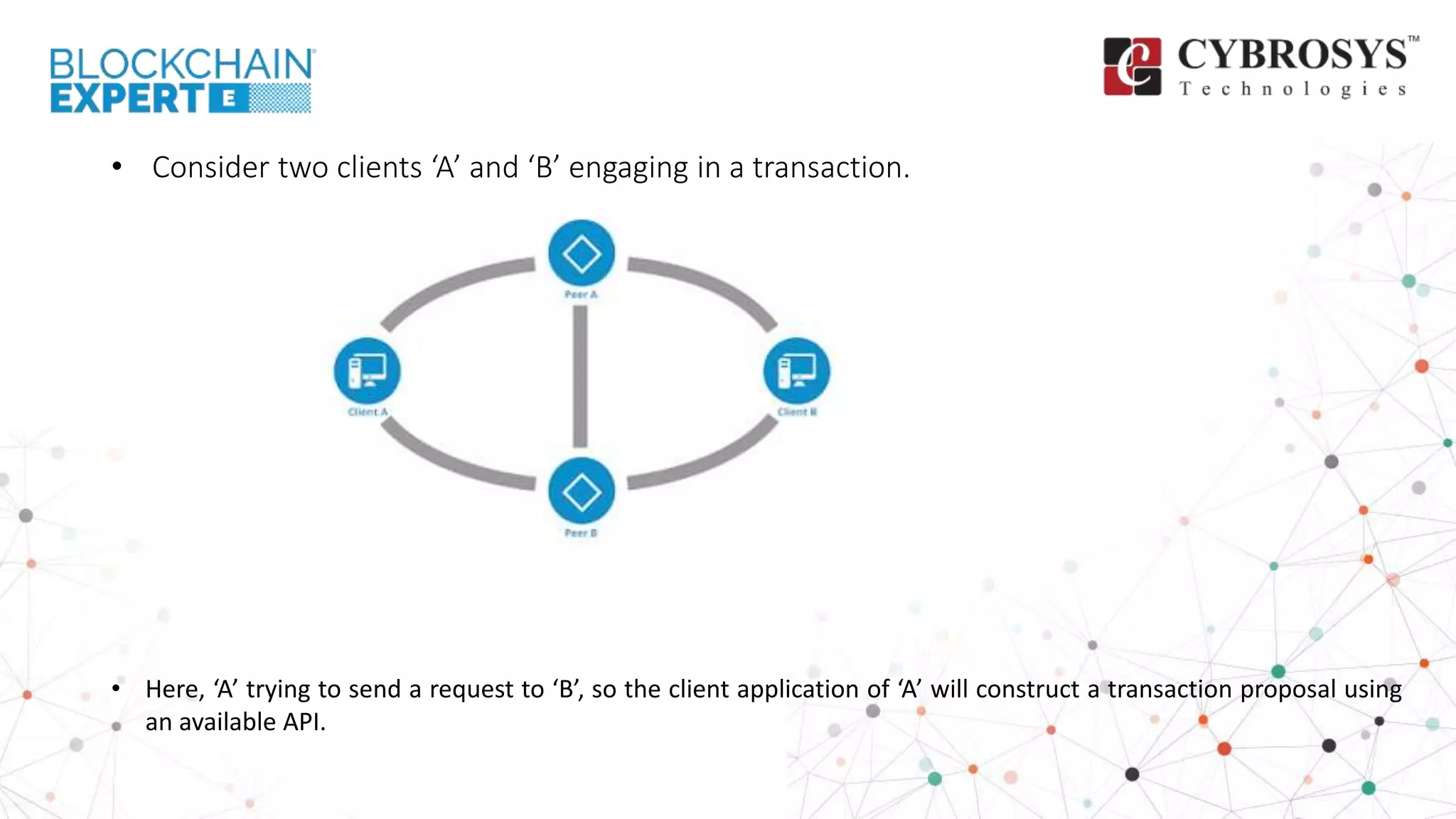
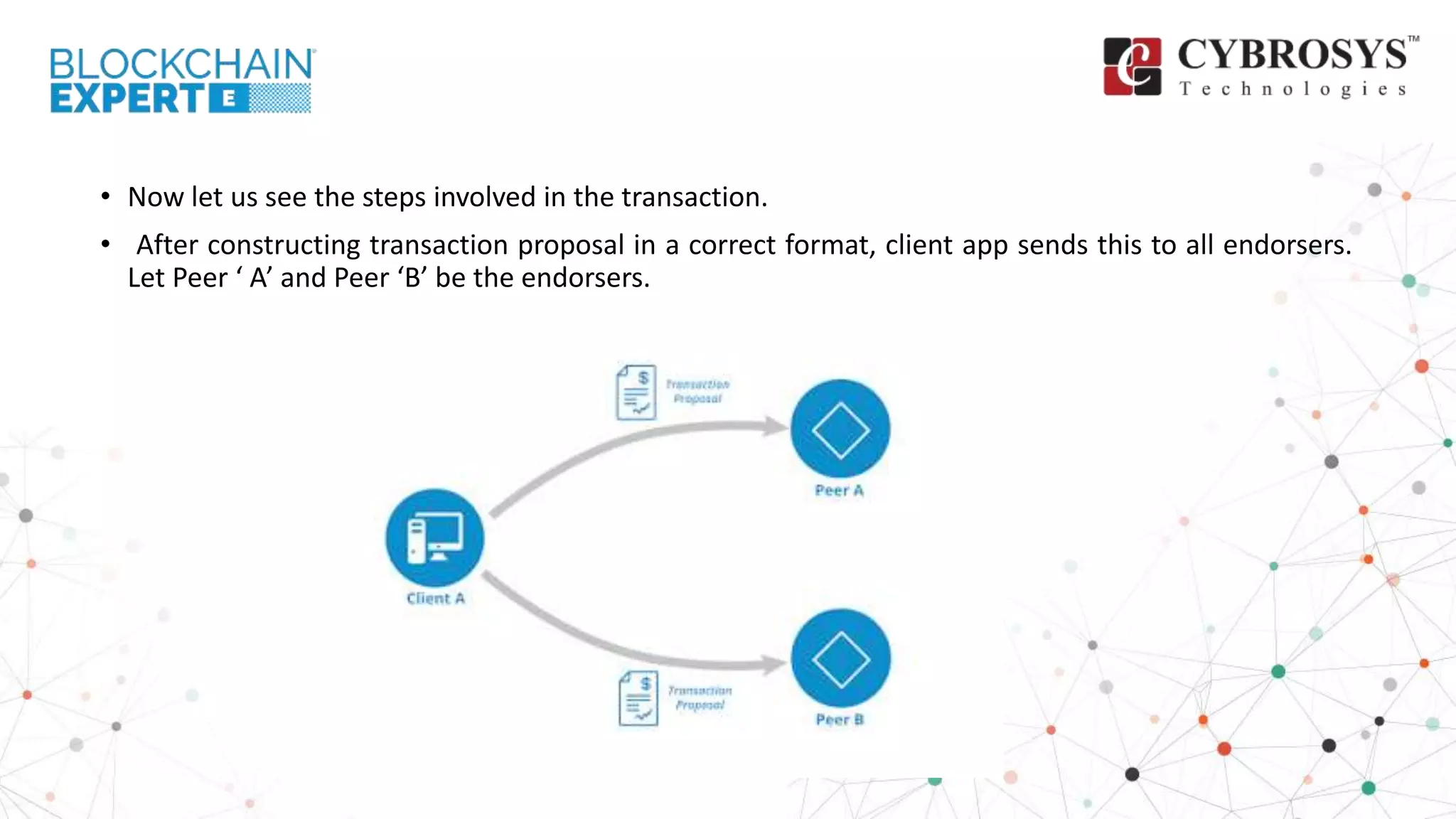
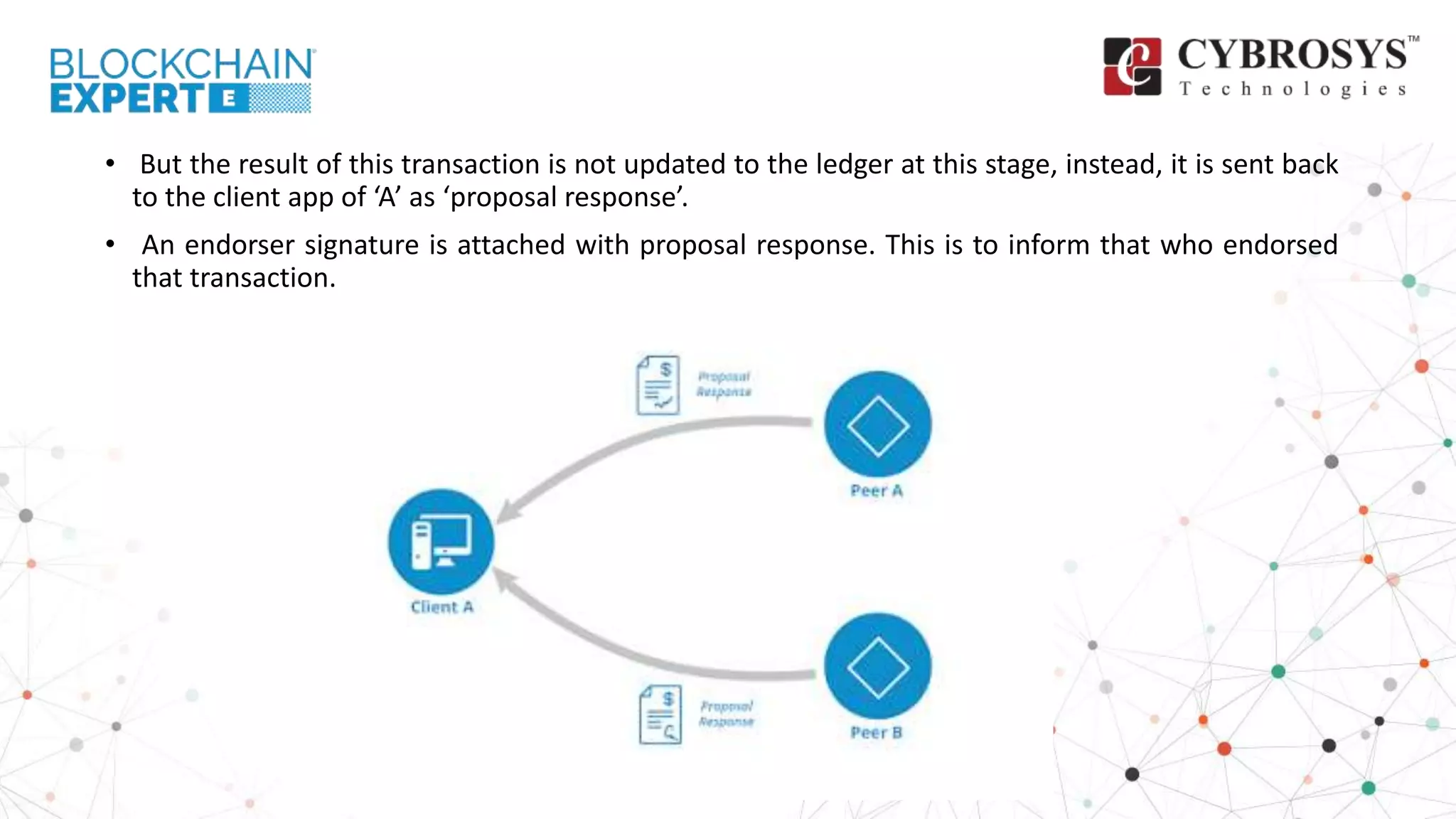
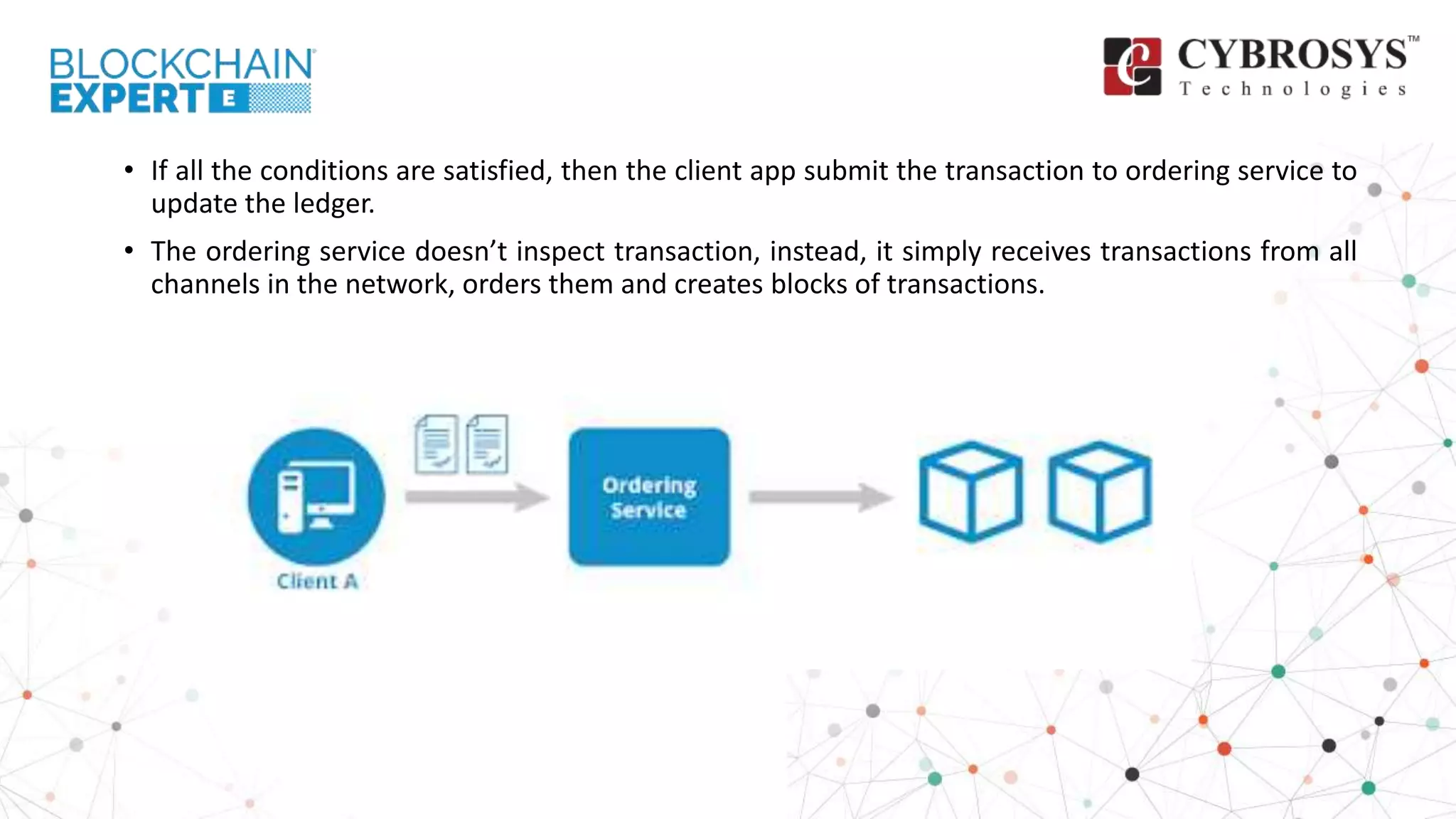
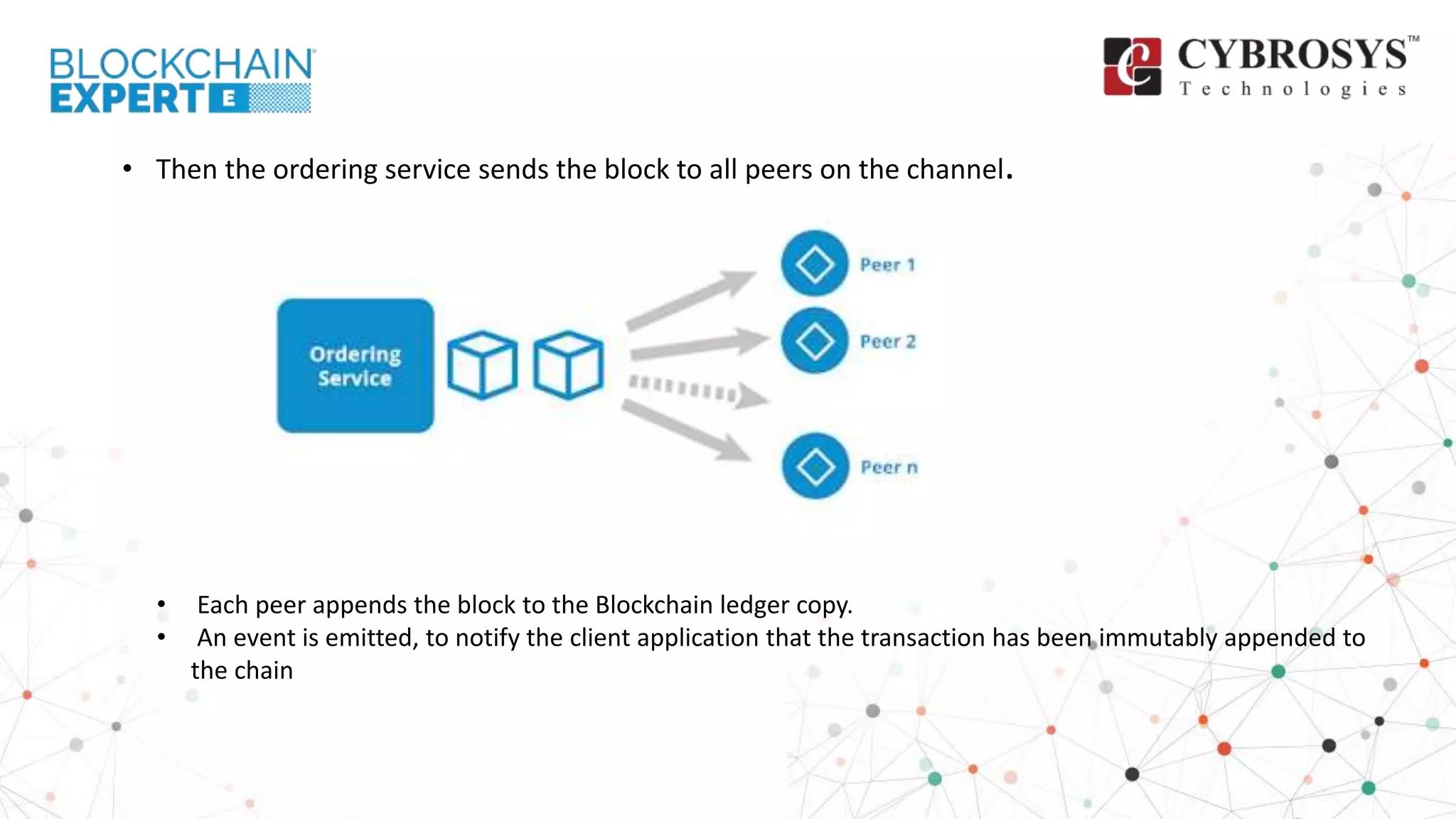
This document provides an overview of how transactions are conducted in the Hyperledger Fabric architecture, emphasizing the construction of transaction proposals by clients. It outlines the process involving endorsers who validate proposals before responses are generated and submitted to an ordering service, which organizes transactions into blocks for updating the ledger. The overview highlights key components such as proposal verification, endorsement policies, and the final appending of transactions to the blockchain.