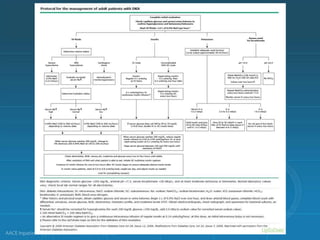
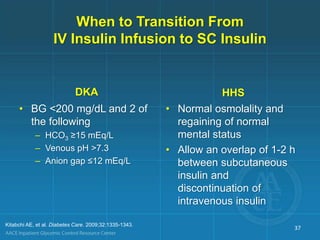
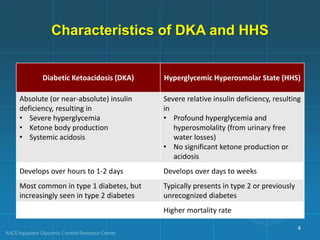
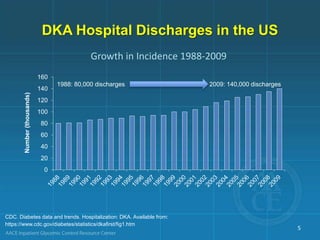
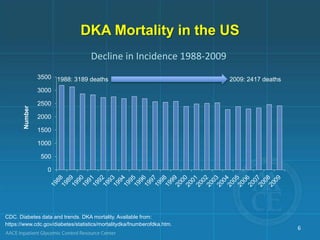
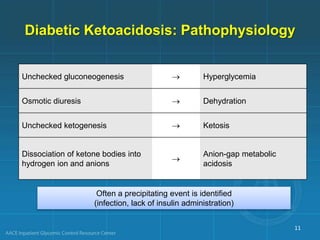
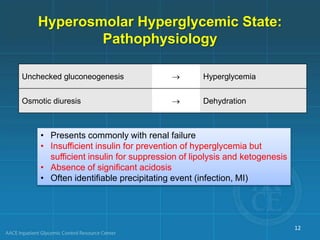
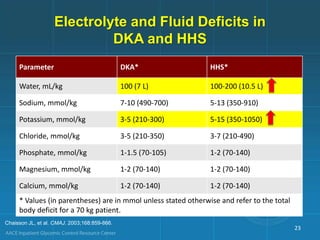
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state (HHS) are life-threatening emergencies characterized by severe hyperglycemia and electrolyte abnormalities. DKA is defined by blood glucose over 250 mg/dL, venous pH below 7.3, bicarbonate below 15 mEq/L, and ketonemia or ketonuria. HHS involves blood glucose over 600 mg/dL, venous pH above 7.3, and minimal ketone production. Treatment involves fluid resuscitation, insulin therapy to lower blood glucose, electrolyte replacement, and identifying/treating precipitating causes. Transition to subcutaneous insulin can occur when blood glucose is below







![Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis
• The normal anion gap in mEq/L is calculated as:
[Na] - [Cl + HCO3]
• The normal gap is <12 mEq/L
• Causes of anion gap acidosis (unmeasured anions)
include:
– Ketoacidosis (diabetic, alcoholic)
– Lactic acidosis (lactate [underperfusion, sepsis])
– Uremia (phosphates, sulfates)
– Poisonings/overdoses (methanol, ethanol, ethylene glycol,
aspirin, paraldehyde)
• In ketoacidosis, the “delta” of the anion gap above
12 mEq/L is composed of anions derived from keto-
acids
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hyperglycemic-emergencies-180204203905/85/Hyperglycemic-emergencies-15-320.jpg)








![Laboratory Diagnostic Criteria of
DKA and HHS
Parameter Normal range DKA HHS
Plasma glucose, mg/dL 76-115 ≥250* ≥600
Arterial pH† 7.35-7.45 ≤7.30 >7.30
-Hydroxybutyrate, mg/dL 4.2-5.2
≥31 (children)
≥40 (adults)
Serum bicarbonate, mmol/L‡ 22-28 ≤18 >15
Effective serum osmolality, mmol/kg 275-295 ≤320 >320
Anion gap,§ mmol/L 8-12 >12 Variable
Serum ketones¶ Negative Positive None or trace
Urine ketones‡ Negative Moderate to high None or trace
*May occur at lower glucose values, especially under physiologically stressful conditions.
† If venous pH is used, a correction of 0.03 must be made.
‡ Suggestive but not diagnostic of DKA.
§ Calculation: (Na+) – [Cl- + HCO3
- (mEq/L)].
¶ Nitroprusside reaction method.
Chaisson JL, et al. CMAJ. 2003;168:859-866. Handelsman Y, et al. Endocr Pract. 2016;22:753-762. Haw SJ, et al.
In: Managing Diabetes and Hyperglycemia in the Hospital Setting: A Clinician’s Guide. Draznin B, ed. Alexandria,
VA: American Diabetes Association; 2016;284-297.
25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hyperglycemic-emergencies-180204203905/85/Hyperglycemic-emergencies-25-320.jpg)
![ADA Diagnostic Criteria for
DKA and HHS
Parameter
DKA
HHSMild Moderate Severe
Plasma glucose, mg/dL >250 >250 >250 >600
Arterial pH 7.25-7.3 7.0-7.24 <7.0 >7.30
Serum bicarbonate, mmol/L 15-18 10 to <15 <10 >15
Serum ketones† Positive Positive Positive Small
Urine ketones† Positive Positive Positive Small
Effective serum osmolality,*
mOsm/kg
Variable Variable Variable >320
Anion gap >10 >12 >12 Variable
Alteration in sensoria or mental
obtundation
Alert Alert/drowsy Stupor/coma Stupor/coma
*Calculation: 2[measured Na+ (mEq/L)] + glucose (mg/dL)/18.
† Nitroprusside reaction method.
26
ADA. Diabetes Care. 2009;26:S109-S117.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hyperglycemic-emergencies-180204203905/85/Hyperglycemic-emergencies-26-320.jpg)