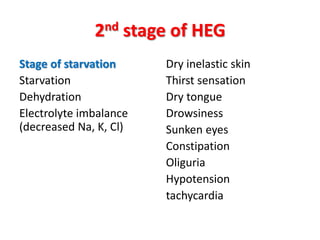
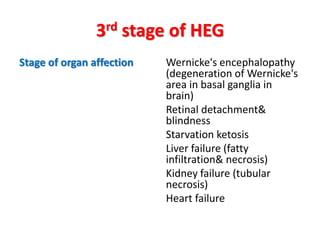
Hyperemesis gravidarum (HEG) is a severe form of vomiting in pregnancy that affects overall health, occurring in about 0.1 to 1% of pregnant women. Management involves hospitalization, reassessment of the patient's condition, dietary changes, and medication to control vomiting, with monitoring for complications such as dehydration and organ failure. While emesis is a common symptom of pregnancy, hyperemesis is serious and can lead to significant health risks for both the mother and fetus.