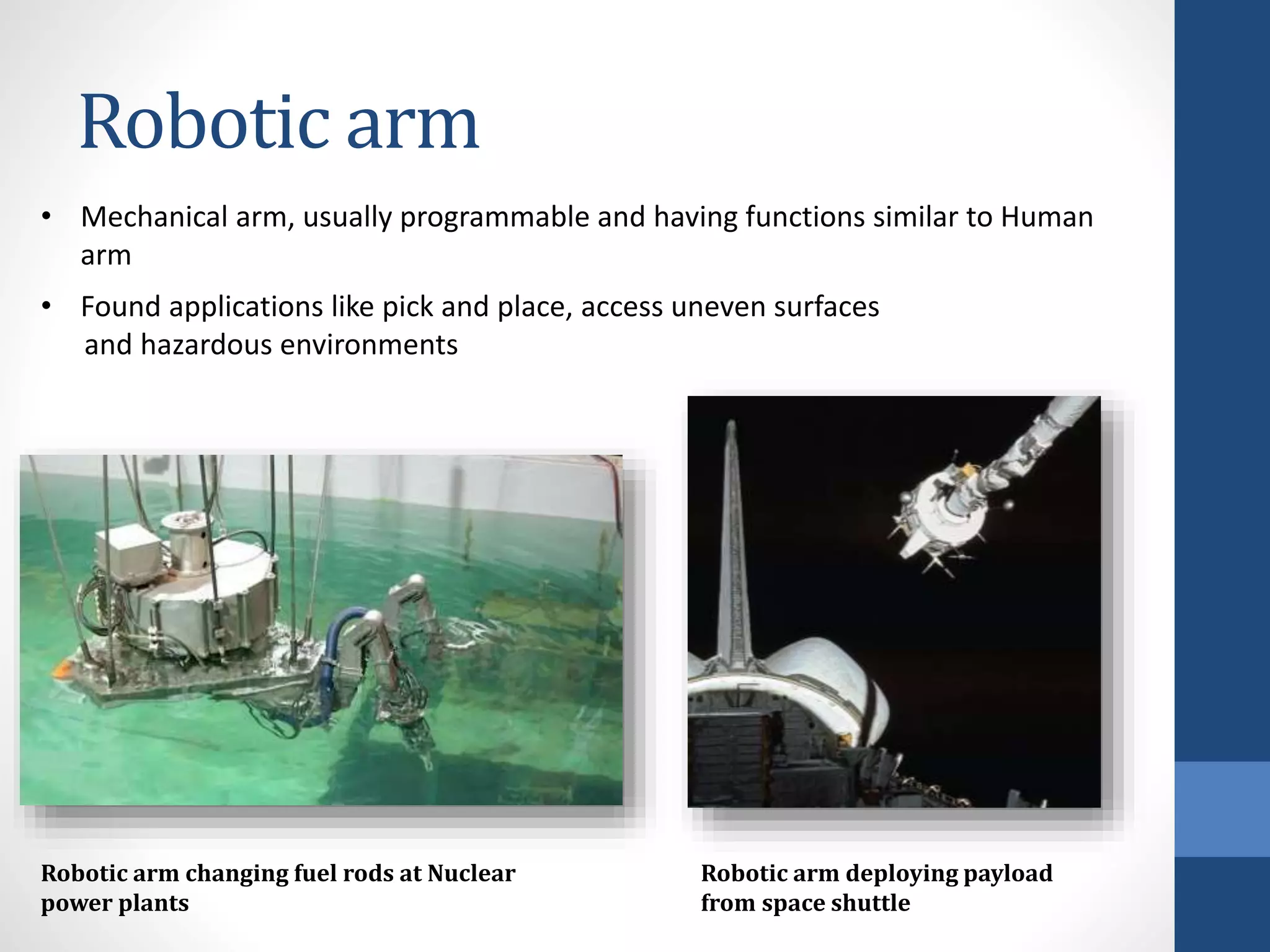
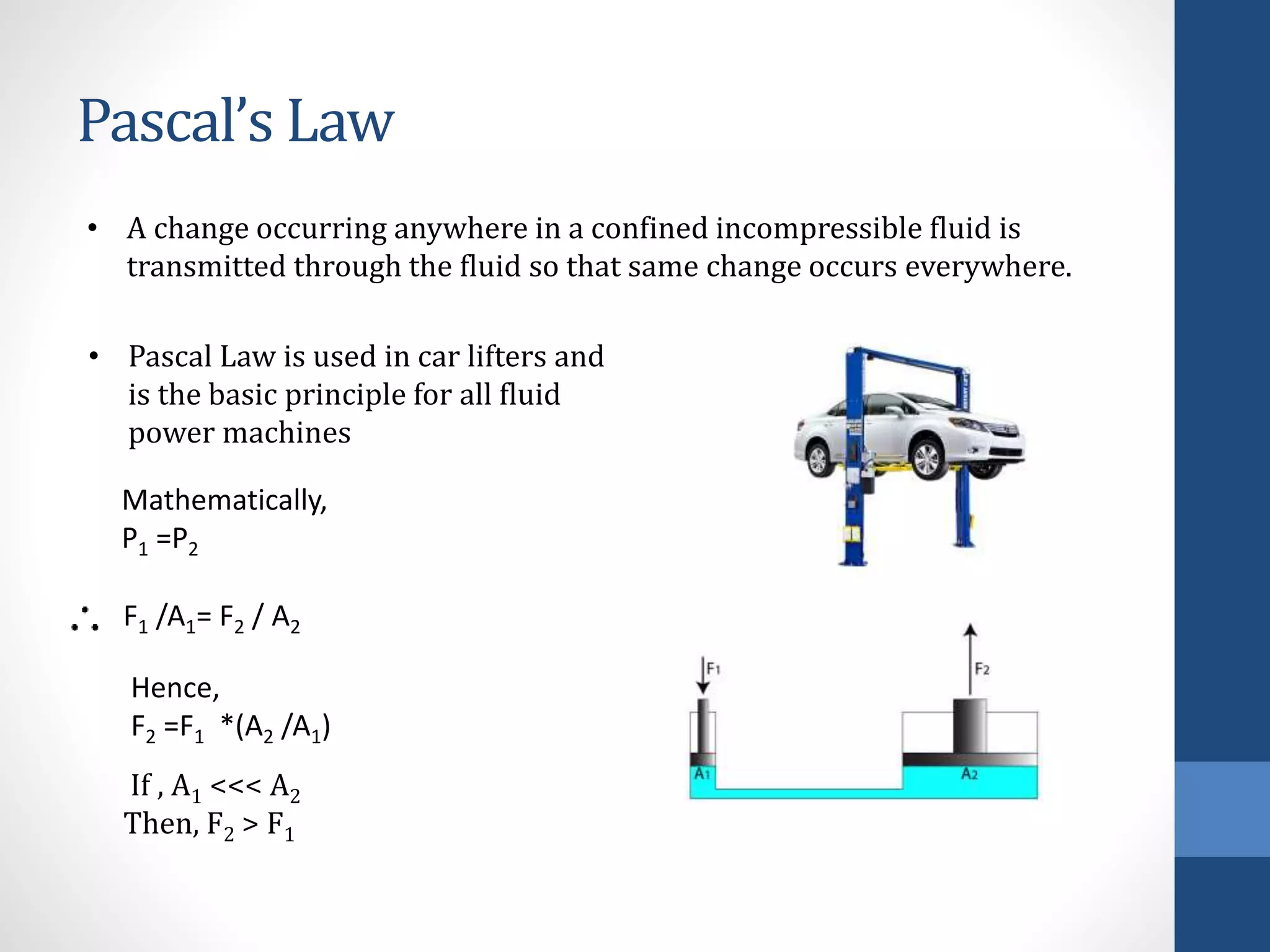
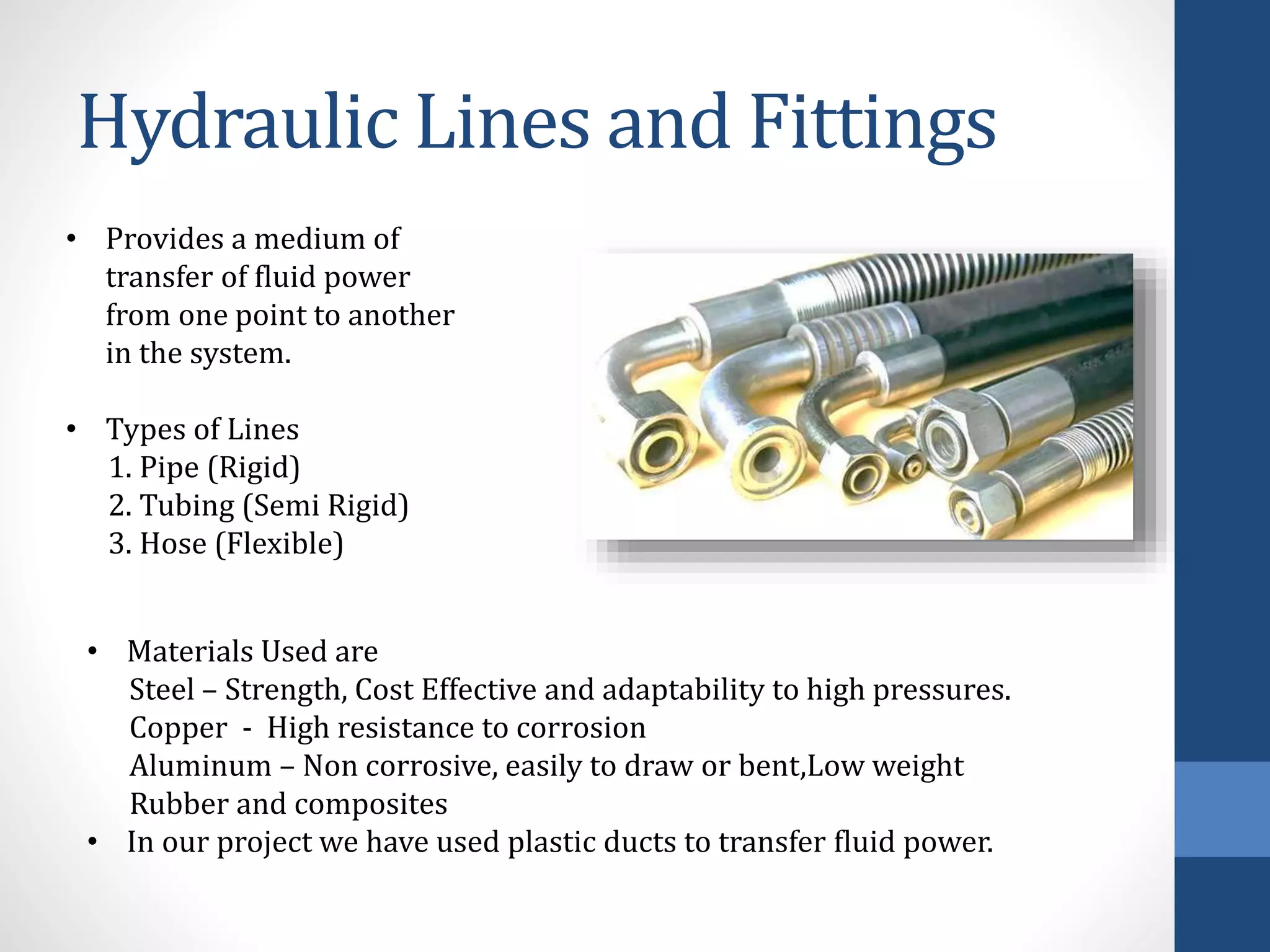
The document outlines a minor project focused on creating a hydraulic robotic arm, detailing its objectives, components, and applications within robotics. It covers essential topics such as fluid power, hydraulic systems, and the practical uses of robots in various fields. The project aims to fabricate a functional model while promoting further exploration in robotics through enhancements like automation and AI.