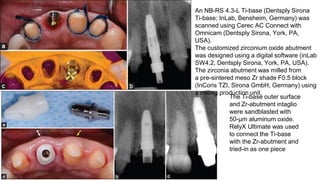
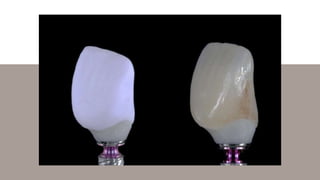
Titanium implant abutments are common due to their strength and biocompatibility, but they can compromise aesthetics, particularly in patients with thin mucosa. The introduction of hybrid abutments, combining titanium inserts with ceramics, aims to enhance aesthetics while maintaining mechanical integrity and minimizing complications, as shown by various studies. The document highlights advancements in materials and techniques, emphasizing the need for further clinical evaluations of hybrid abutments in implant restorations.















![Follow-up appointments at
1 week [Figure 3c] and 2
months [Figure 3d] showed
that the soft tissue responded
favorably, and bone
augmentation was left to heal
for 4 months.
Provisional crowns were
splinted and fabricated
from bis-acryl as a 4-unit
provisional fixed dental
prosthesis (FDP) [Figure
4a-c] modified per the
patient’s
Request.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hybridabutments-230206132414-cb1aa5b9/85/hybrid-abutments-pptx-16-320.jpg)