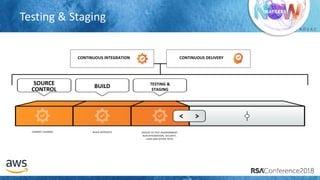
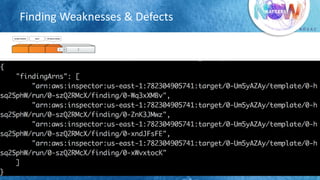
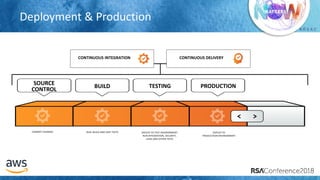
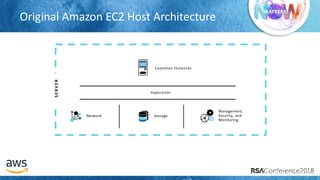
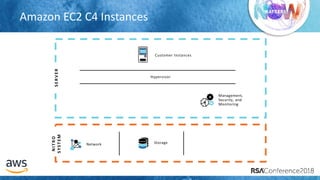
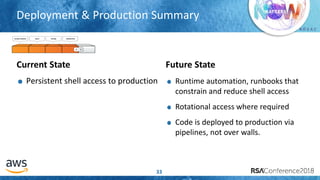
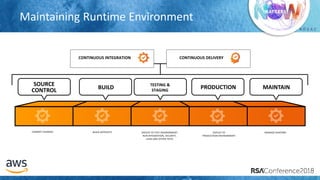
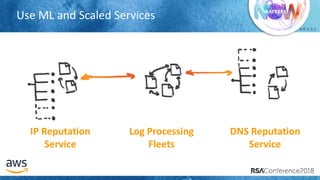
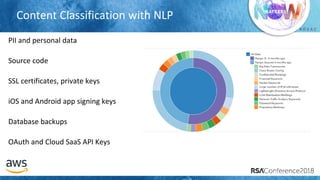
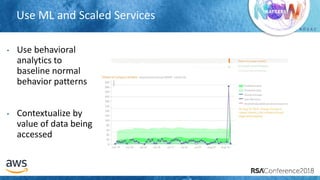
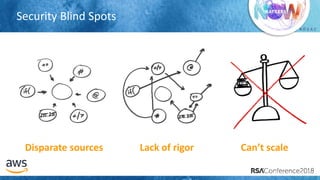
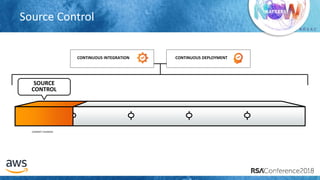
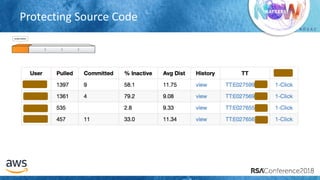
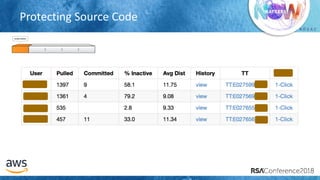
The document outlines best practices for securing cloud environments, emphasizing the need to minimize human interaction with data through automation and robust security measures. It advocates for continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD) processes, automation of security assessments, and the effective use of machine learning for data classification and anomaly detection. A call to action is made for organizations to involve security teams closely with development teams and to document and reduce human access to systems that handle sensitive data.





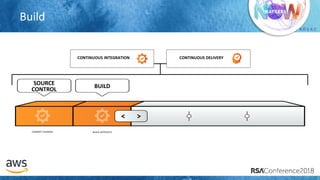
![# R S A C
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "sns:*",
"Resource": "*”
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"NotAction":"sns:Delete*",
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "sns:*",
"Resource": "*”
},
{
"Effect": ”Deny",
"Action": "sns:Delete*",
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
Policy A Policy B
Is Policy A more permissive than Policy B?
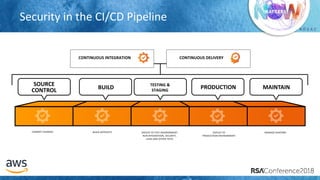
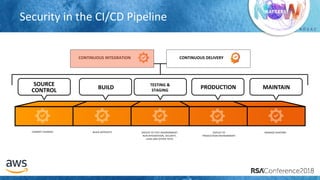
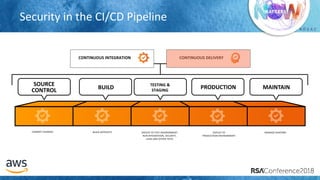
SOURCE CONTROL BUILD](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csv-t08-humans-and-data-dont-mix04102018draftv4-180425100131/85/Humans-and-Data-Don-t-Mix-Best-Practices-to-Secure-Your-Cloud-20-320.jpg)