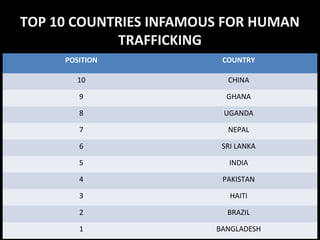
Human trafficking is defined as the recruitment, transportation, transfer, harboring, or receipt of humans for the purpose of exploitation through force, fraud, or coercion. It is the third largest international crime generating billions of dollars in profit each year. Victims are often lured with false promises of good jobs and better lives, and then forced into labor or commercial sex against their will. Common forms of human trafficking include sex trafficking, labor trafficking, and organ harvesting. Poverty, lack of economic opportunities, and demand for cheap labor or commercial sex are key drivers. The top countries for human trafficking globally are Bangladesh, Brazil, Haiti, Pakistan, India, and Nepal. In India, trafficking is prevalent with victims sourced from