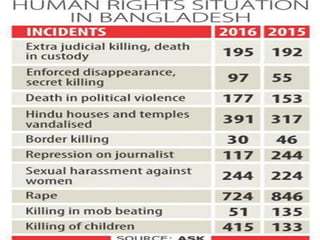
The document discusses human rights and provides examples of violations. It defines human rights as those inherent to human dignity. The Universal Declaration of Human Rights established international standards in 1948. Examples of violations include over 400 children dying from lead poisoning in Nigeria, over 1,000 Rohingya homes burned in Myanmar, and the death of Syrian refugee Aylan Kurdi attempting to reach Canada. The conclusion calls for more effective protection of rights through United Nations organizations and other advocates.