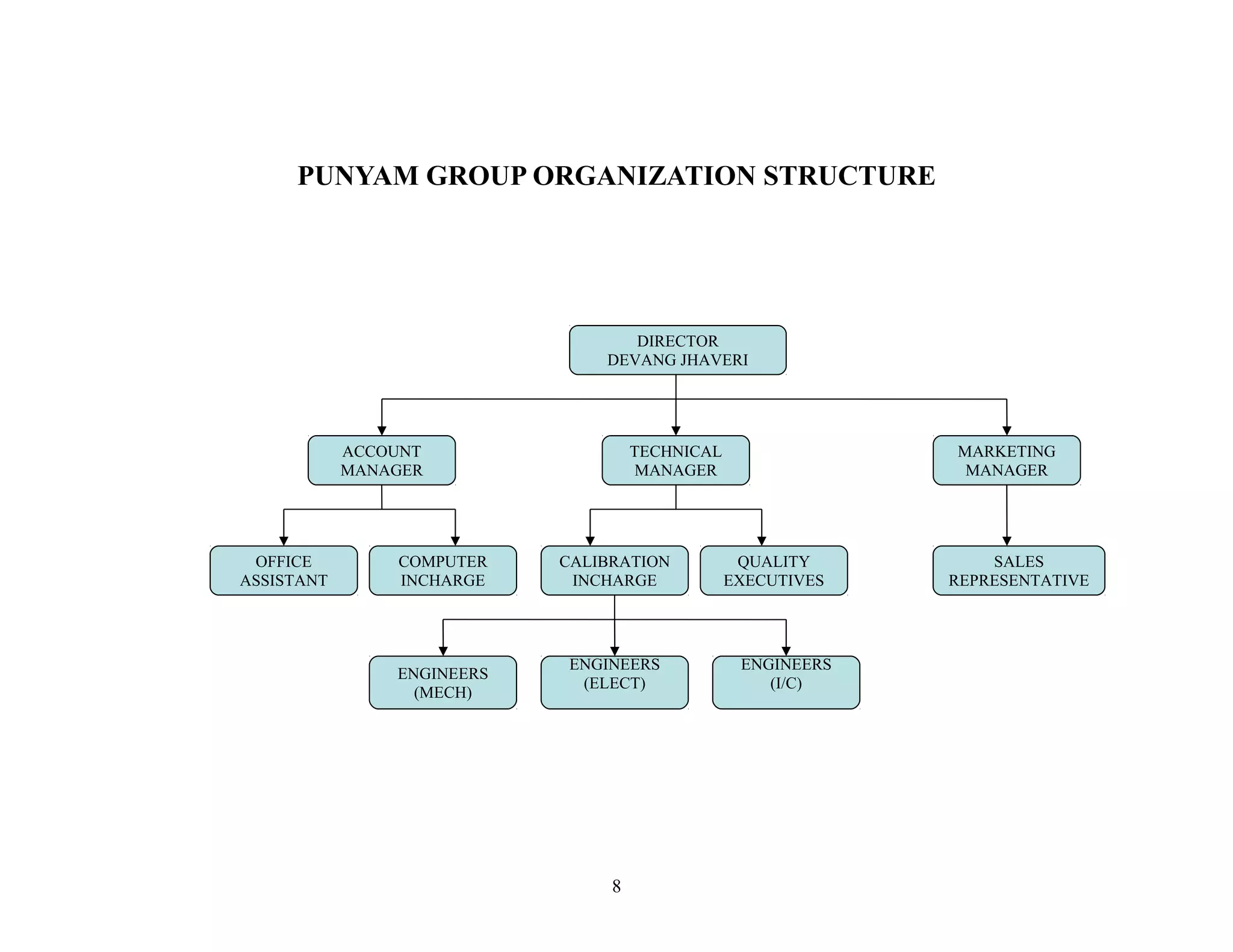
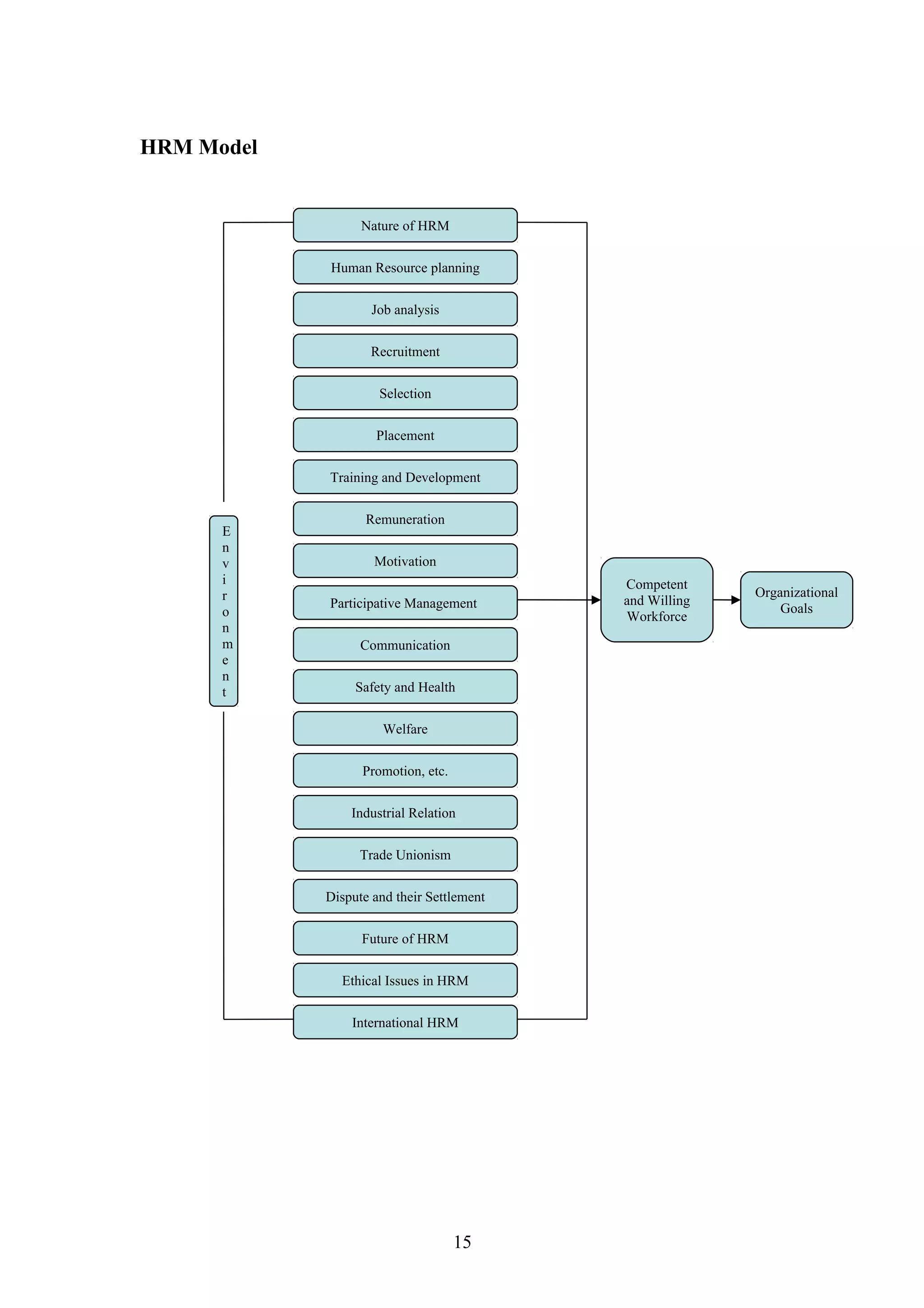
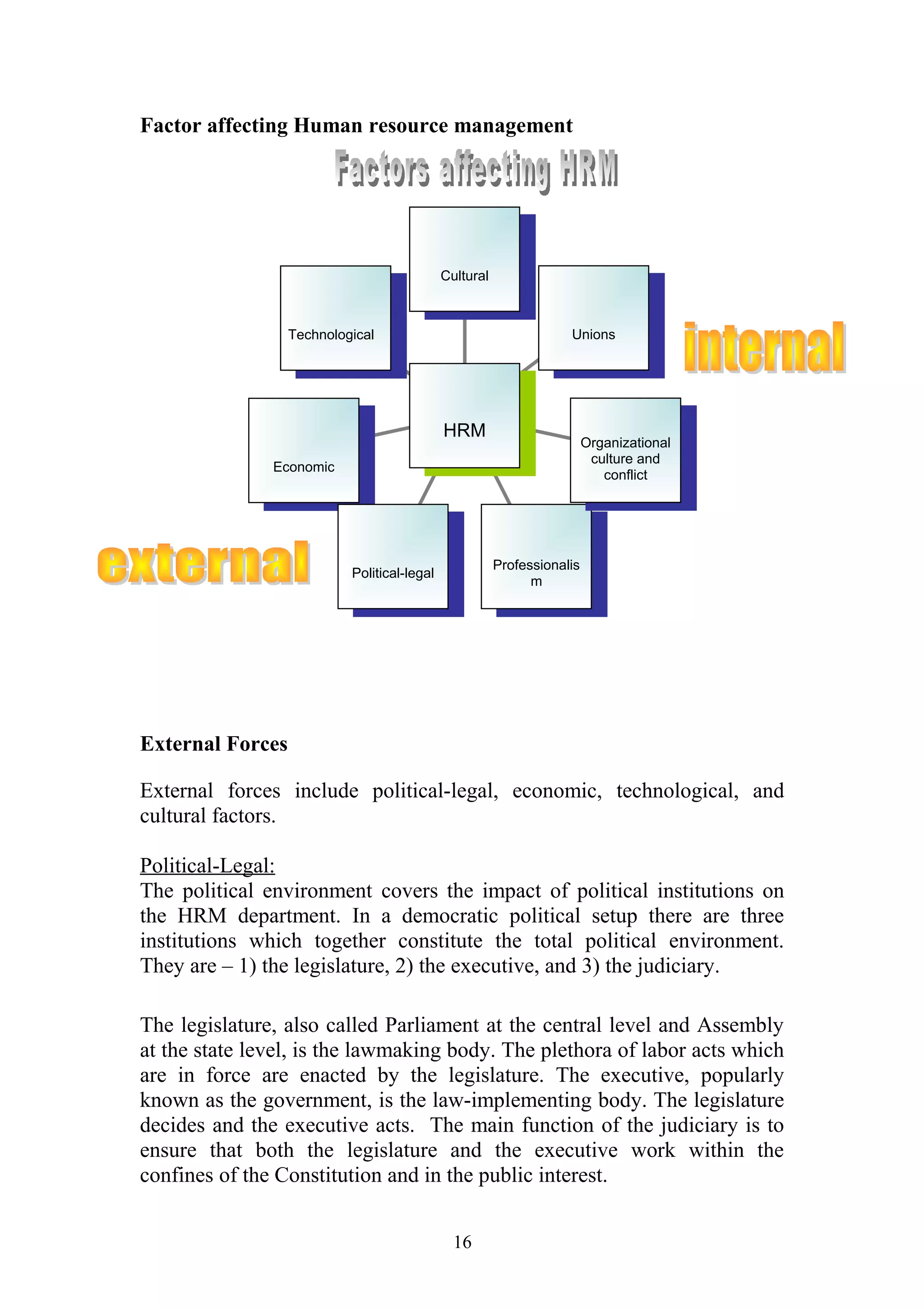
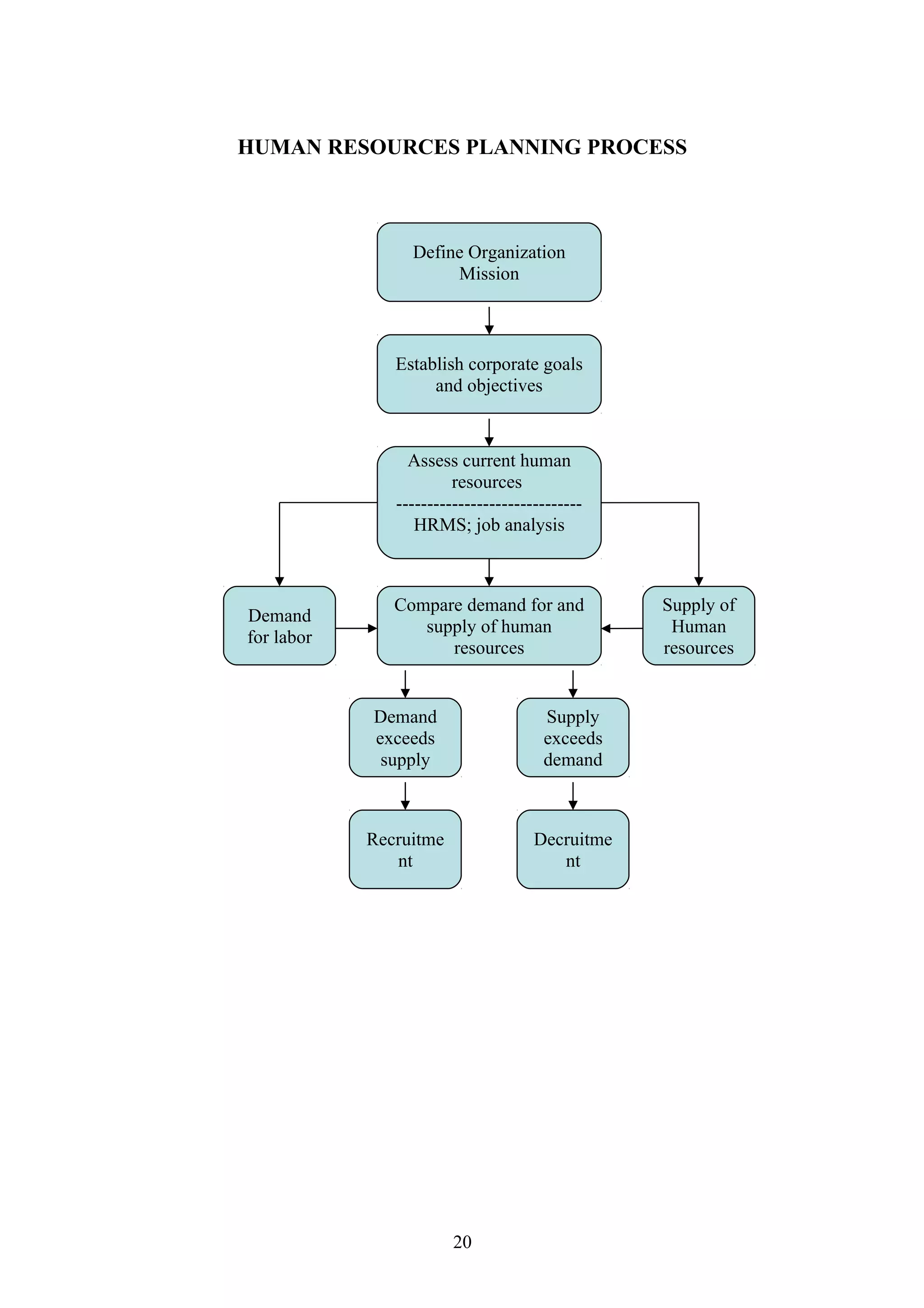
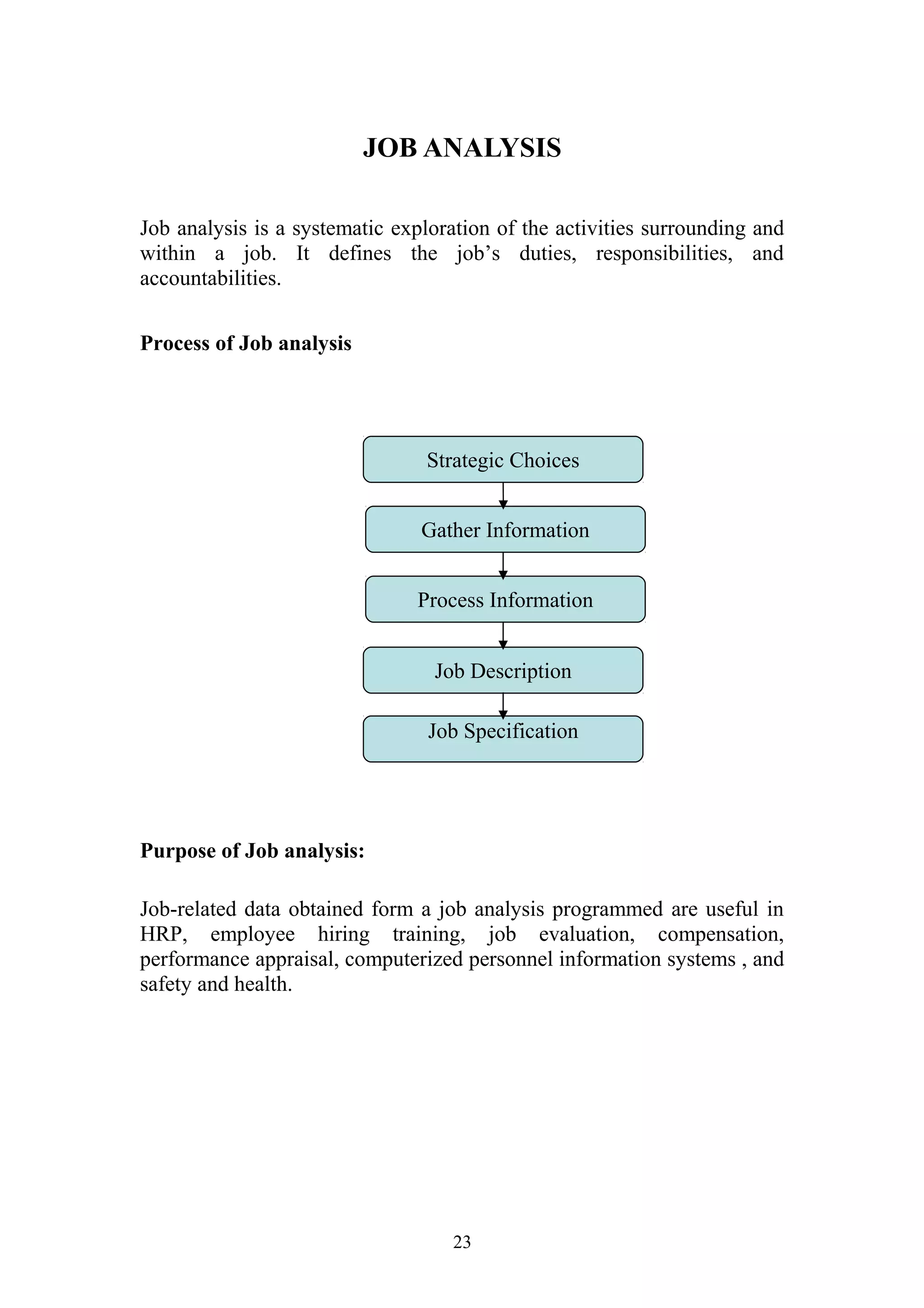
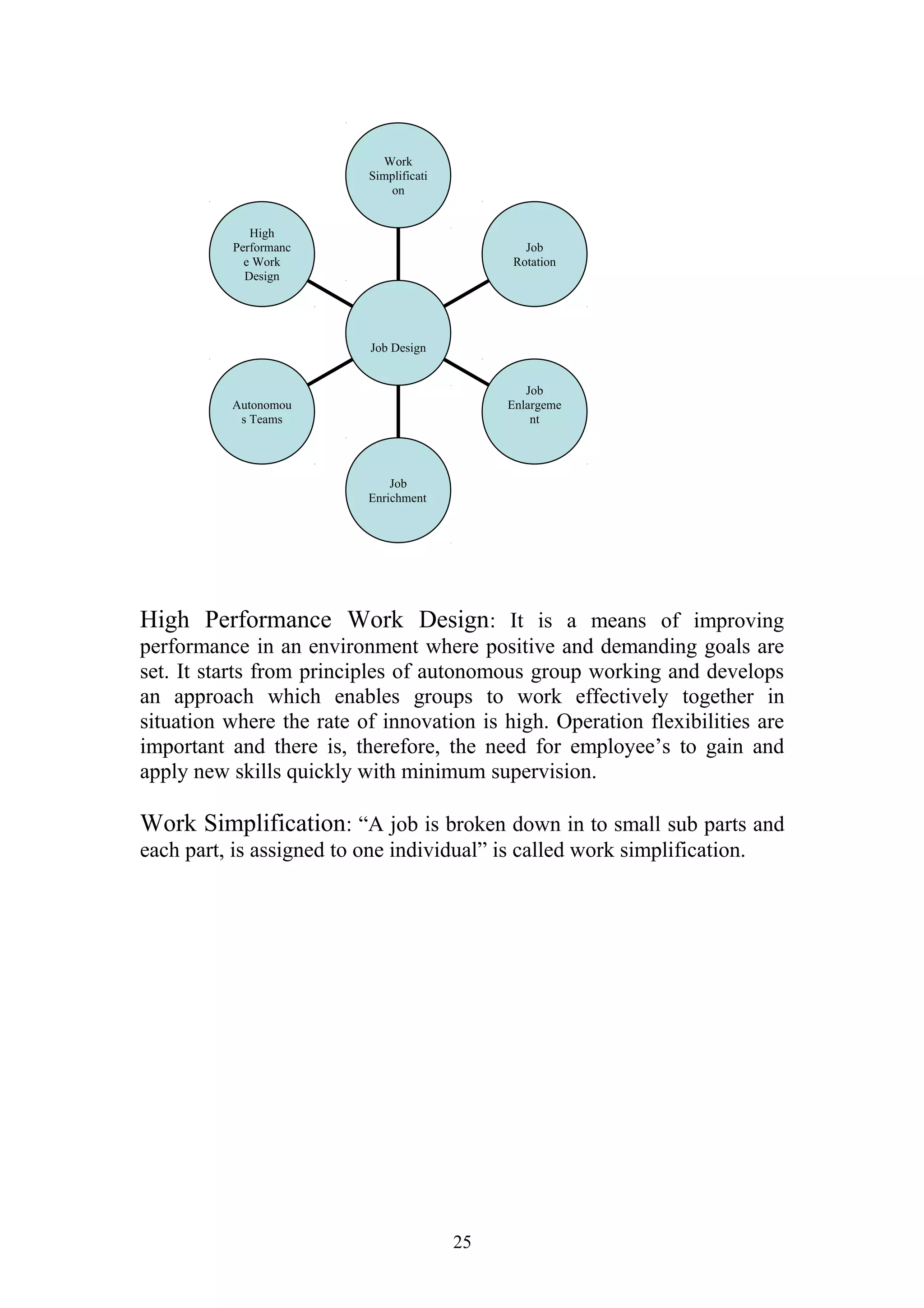
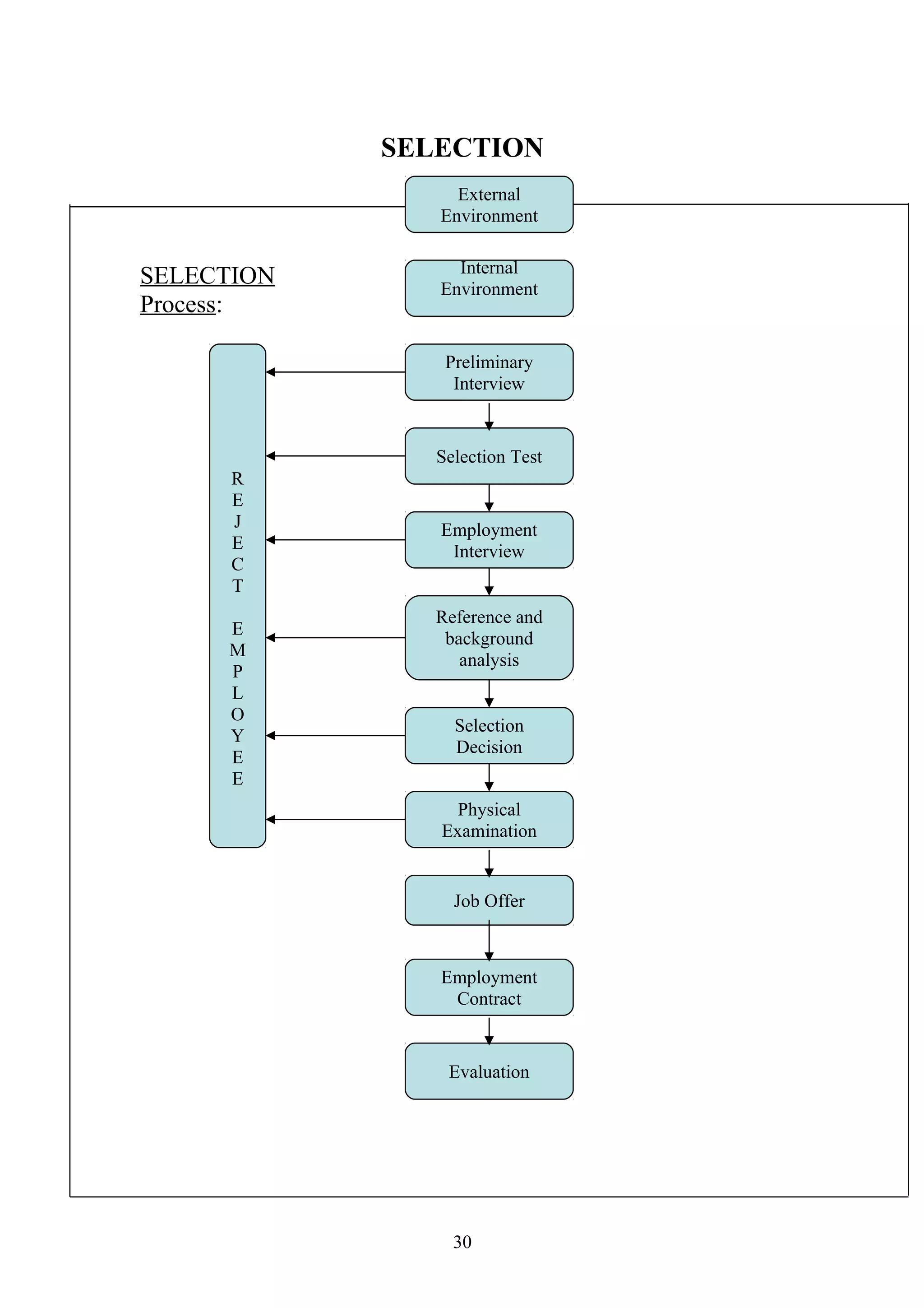
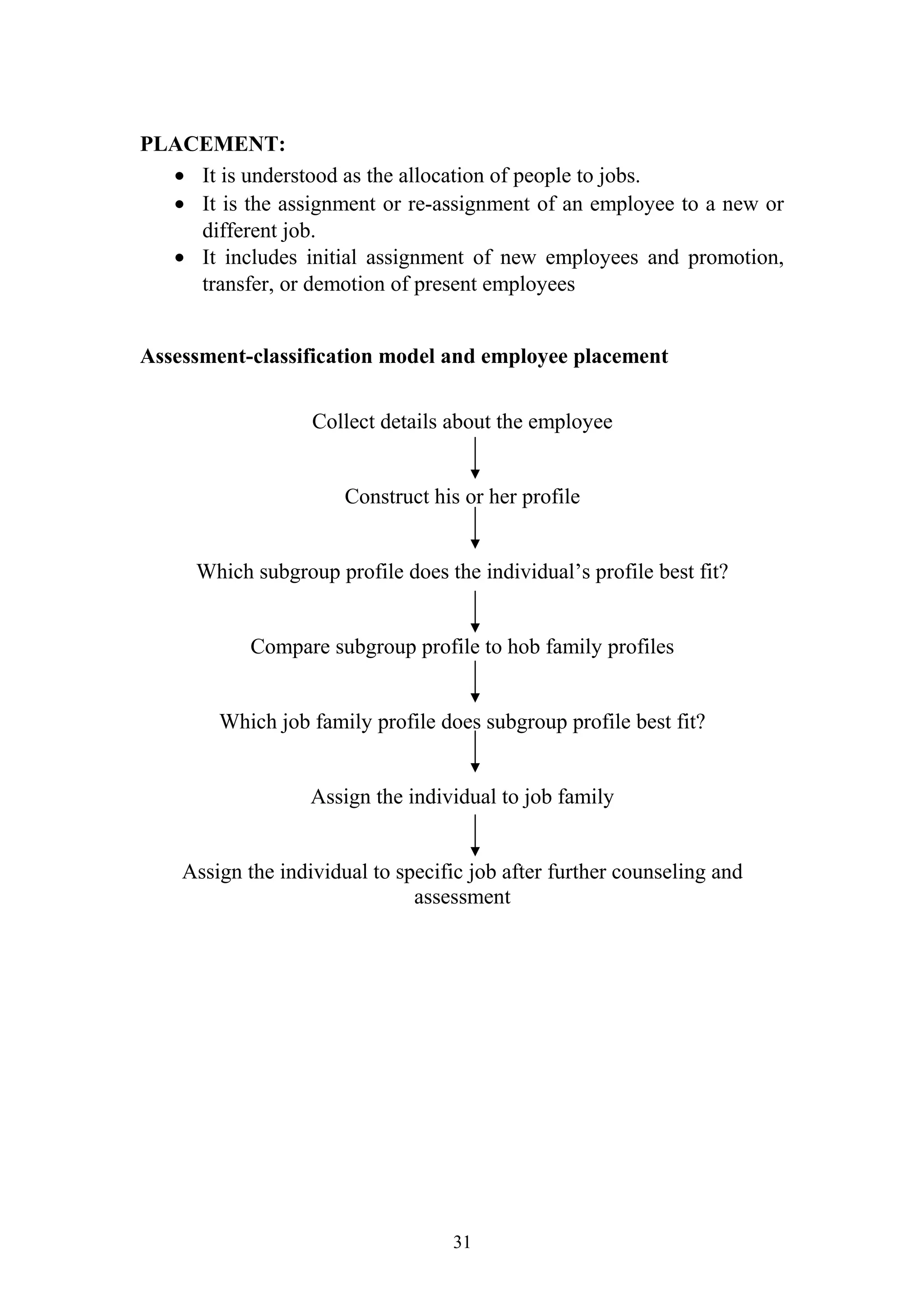
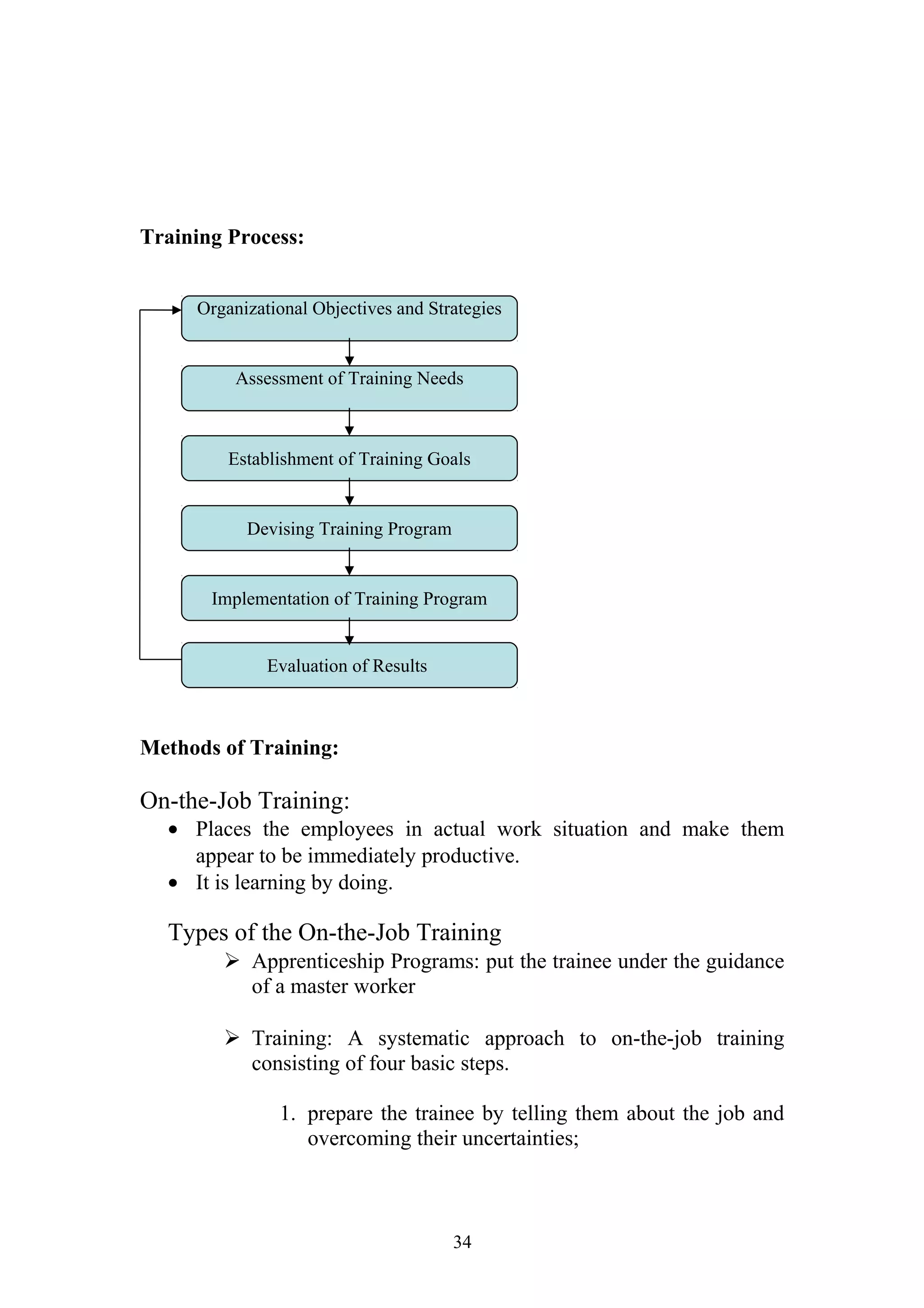
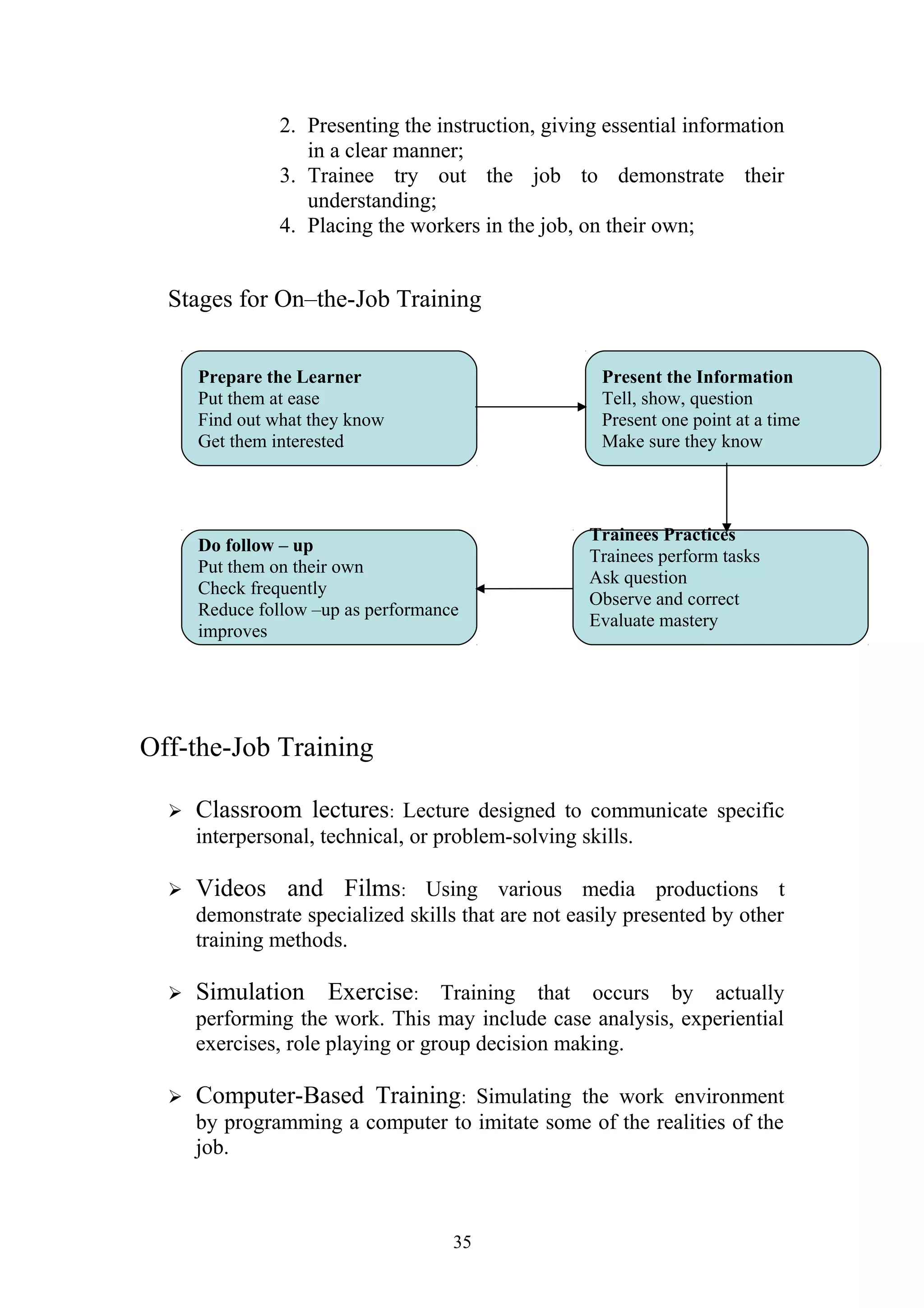
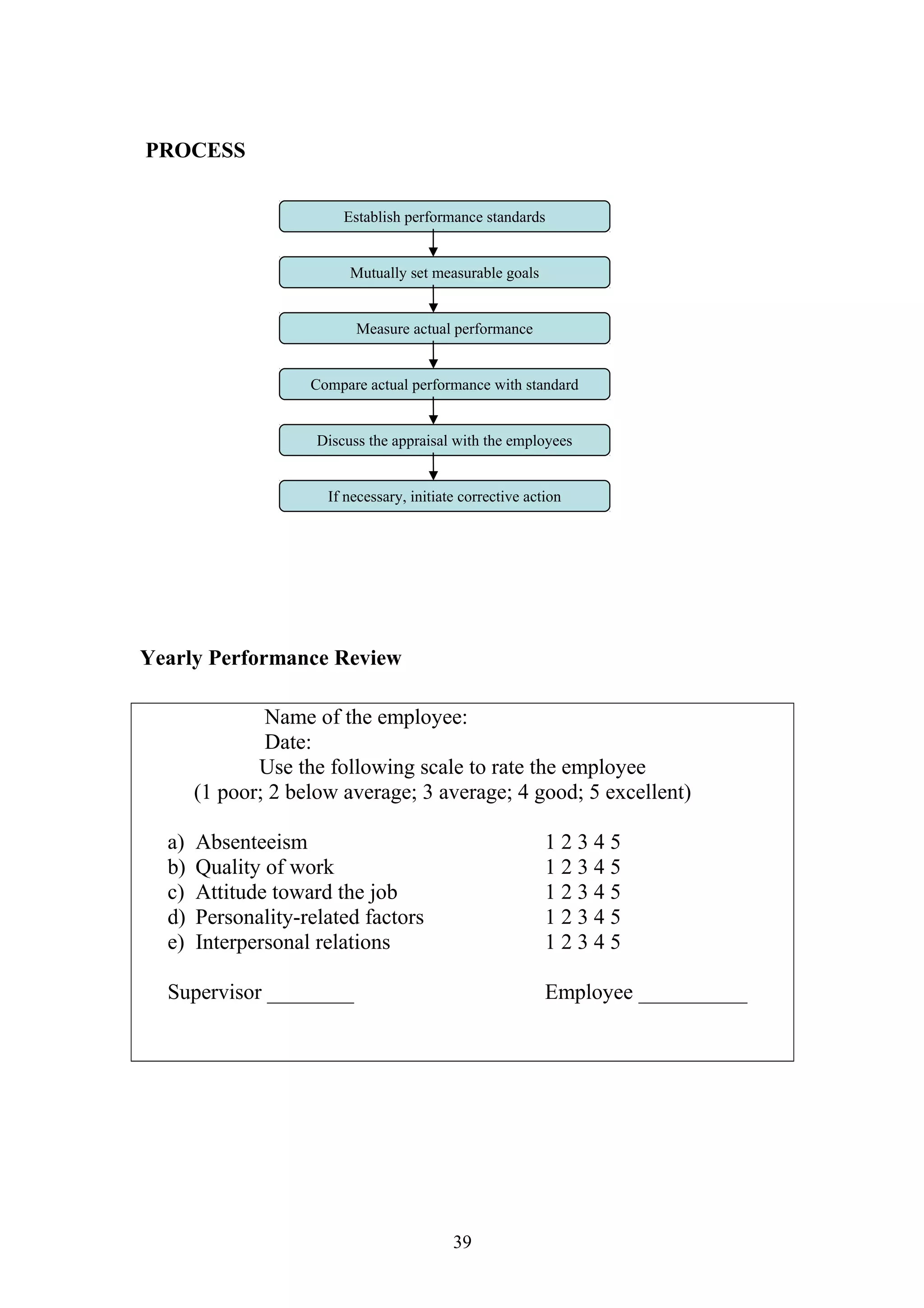
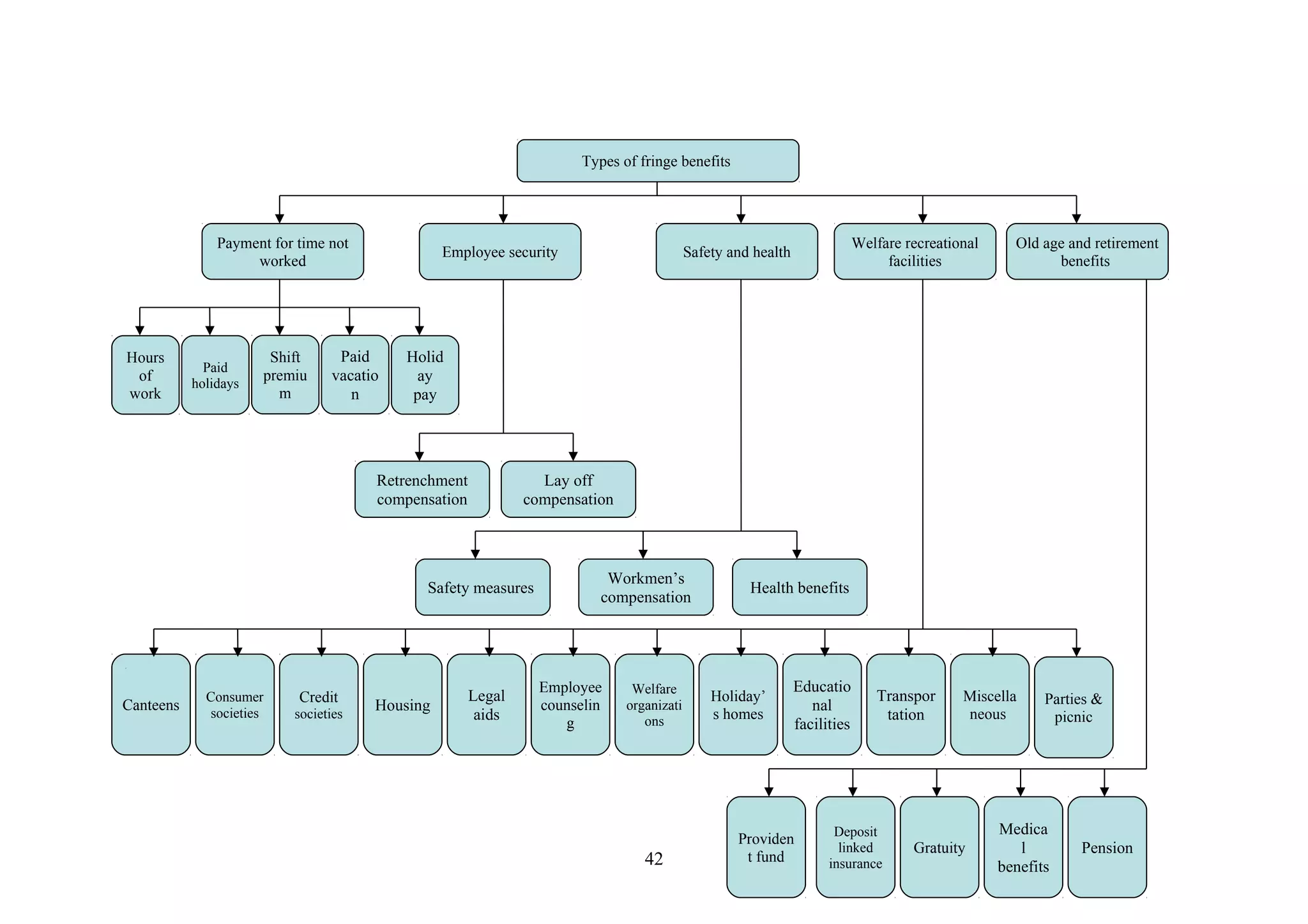
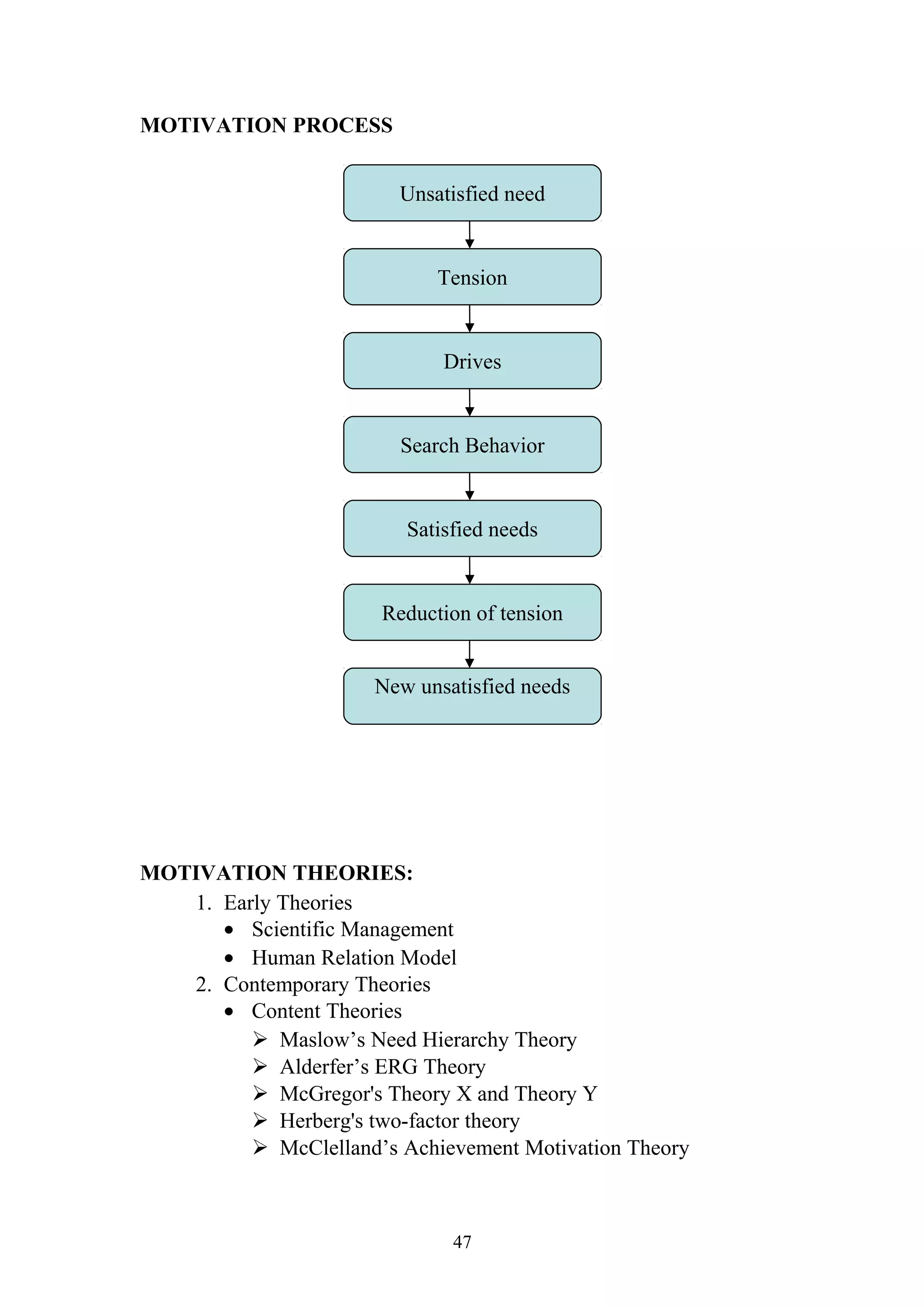
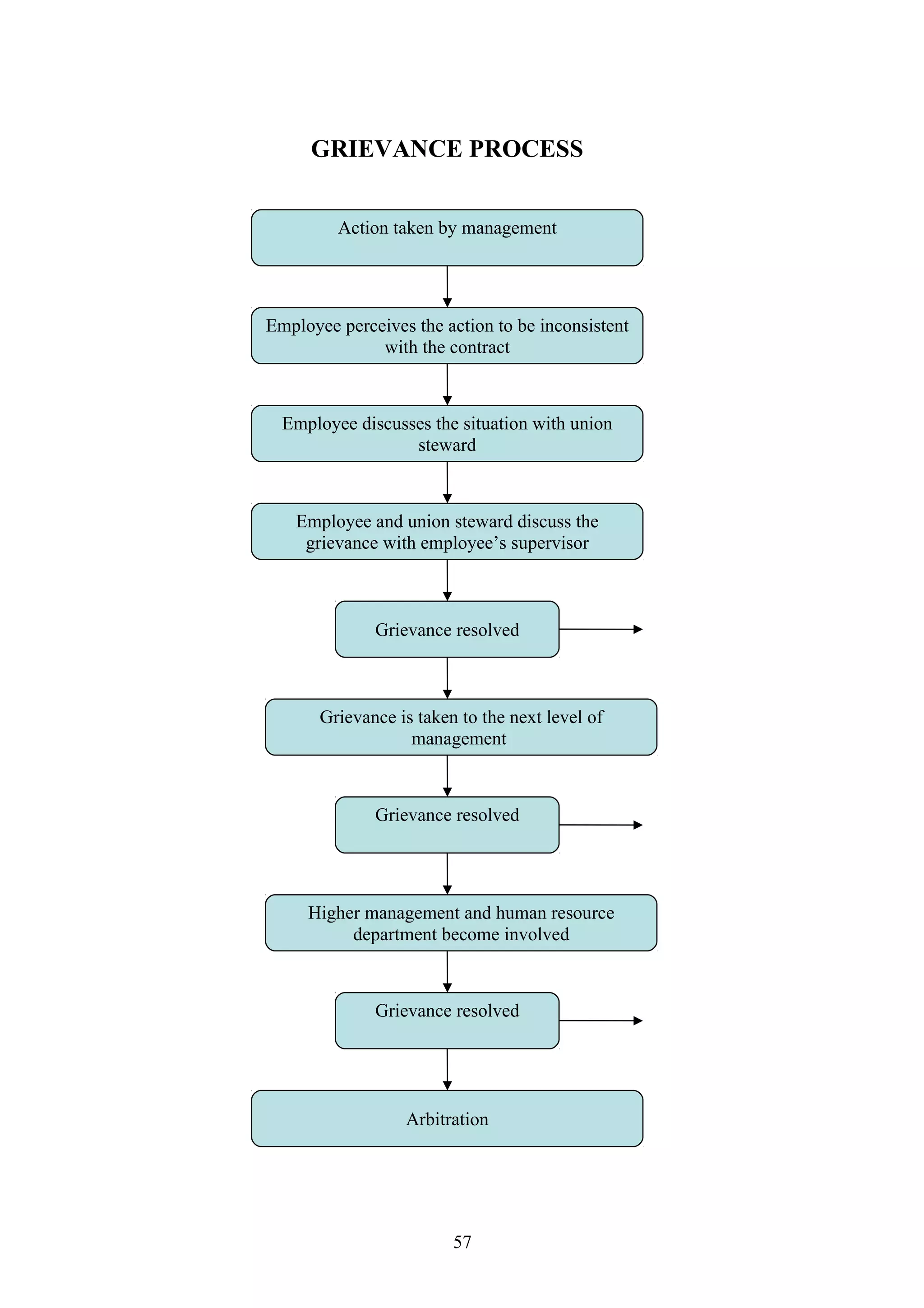
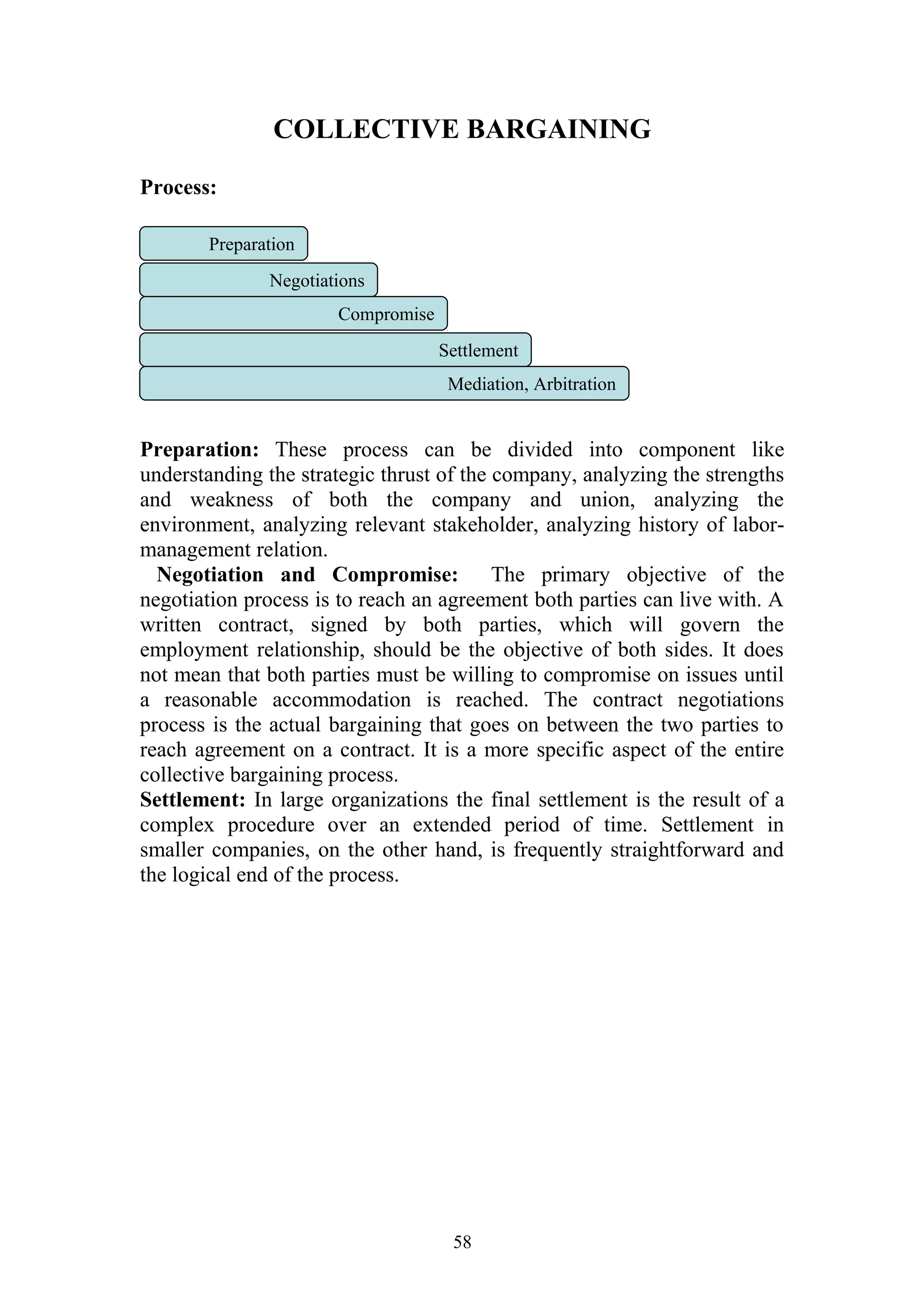
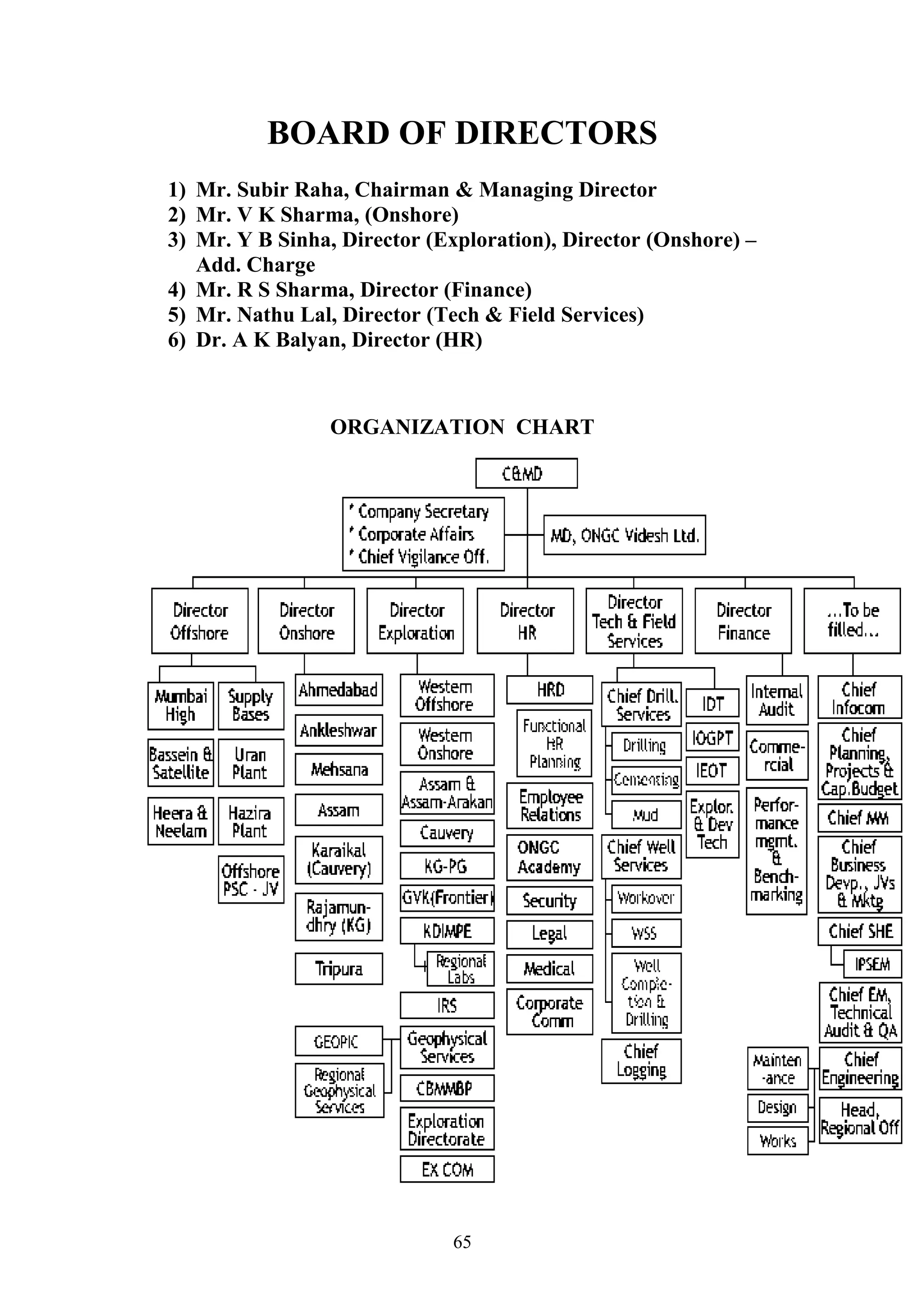
This document is a summer project report submitted by Virang B. Darji to fulfill requirements for an MBA program. It discusses work completed at Punyam Management Services Pvt. Ltd., where the student studied human resource management practices. The report includes sections on the company profile, organization structure, human resource planning, job analysis, recruitment, selection, training and development, performance appraisal, employee welfare, motivation, industrial relations, grievance procedures, collective bargaining, and a case study.