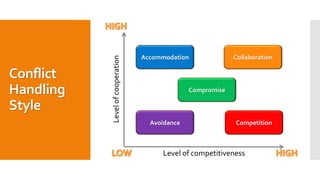
This document discusses various topics related to human relations skills and personality psychology. It covers personality traits and theories, attitudes, improving self-esteem, dealing with stress, effective communication, team dynamics, conflict handling styles, and goal setting. The key aspects covered include the Big Five personality traits, attitudes and how they shape behavior, techniques for improving self-esteem like positive self-talk, the impact of stress and methods for managing it, principles of effective teamwork and goal setting.