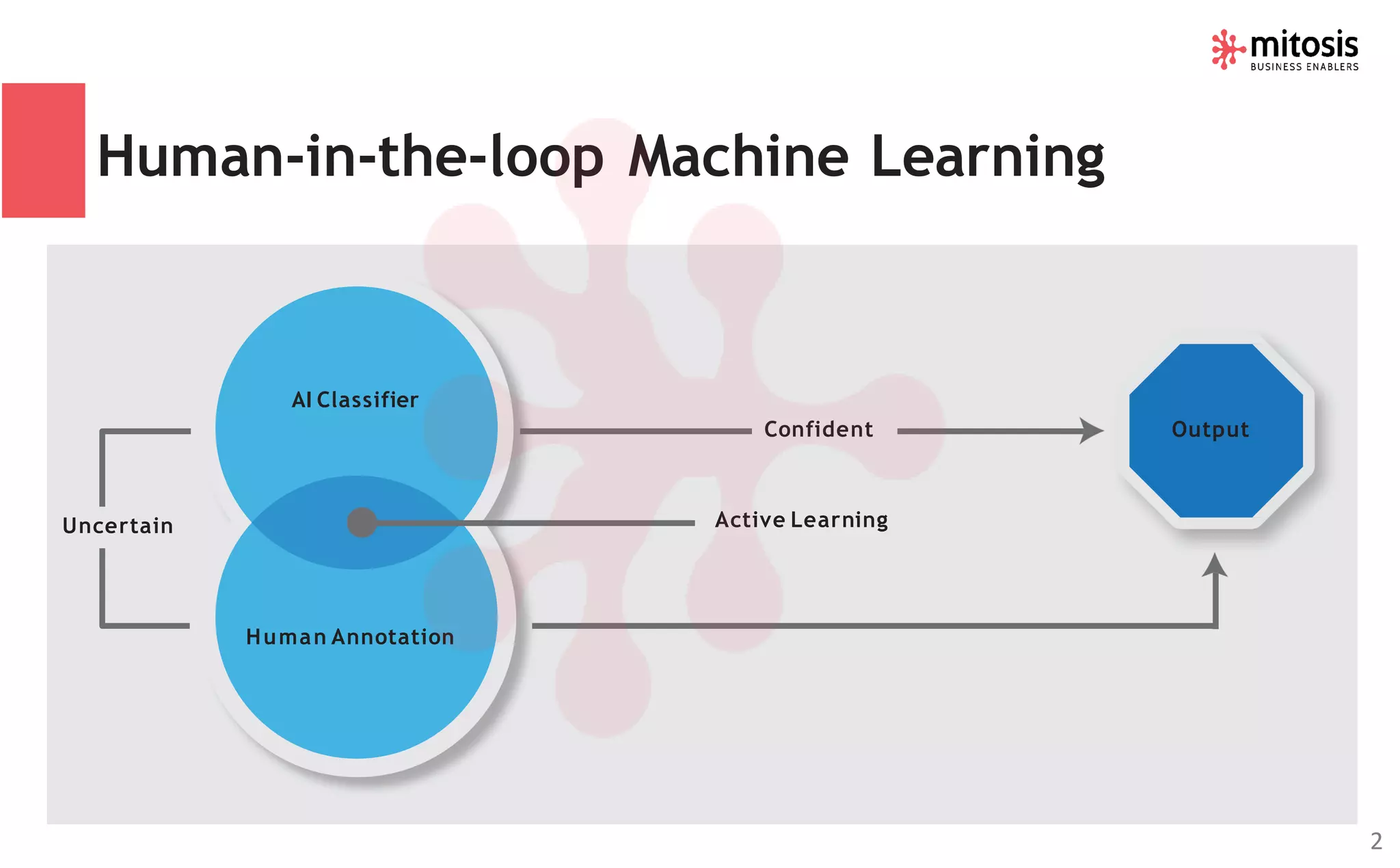
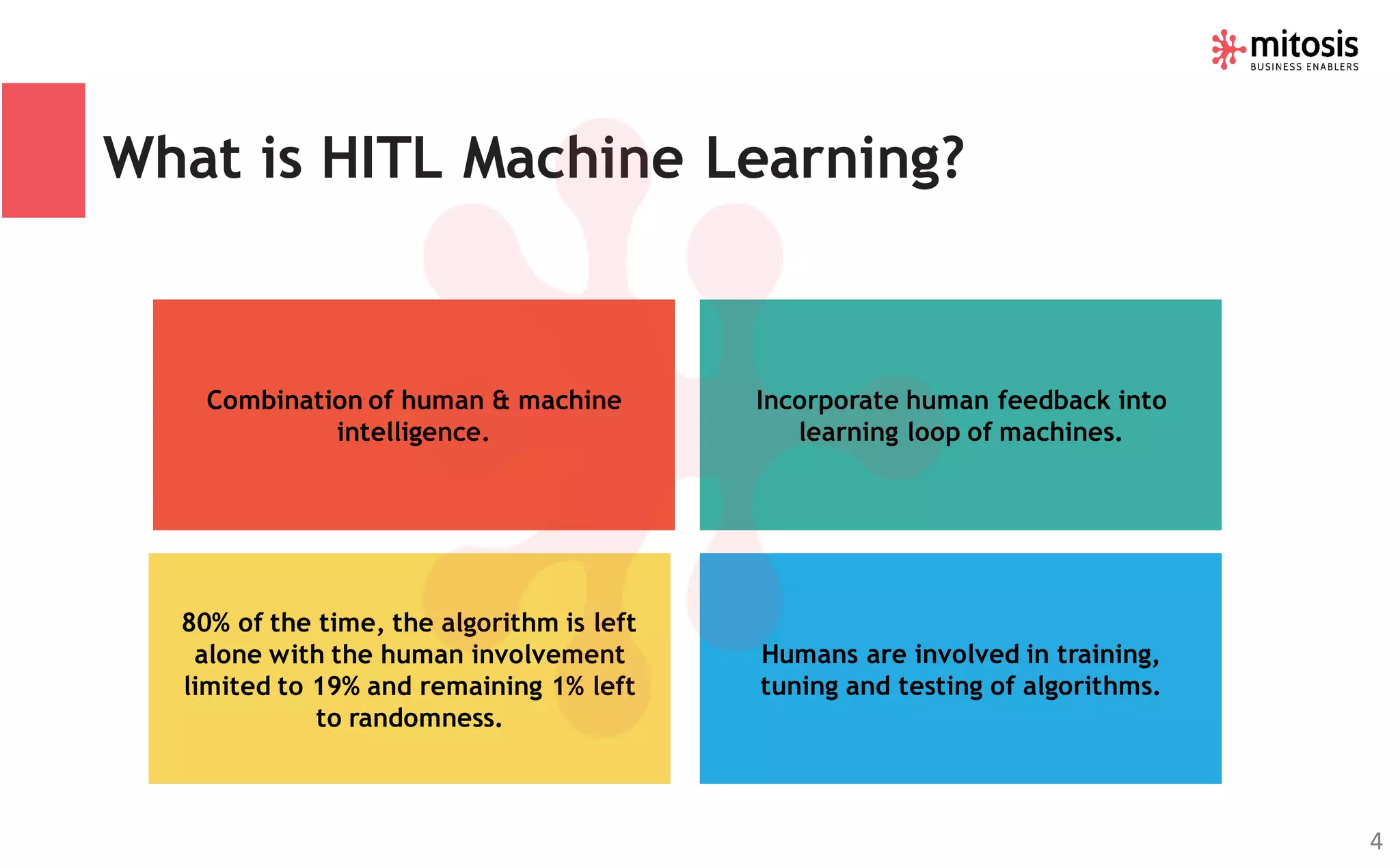
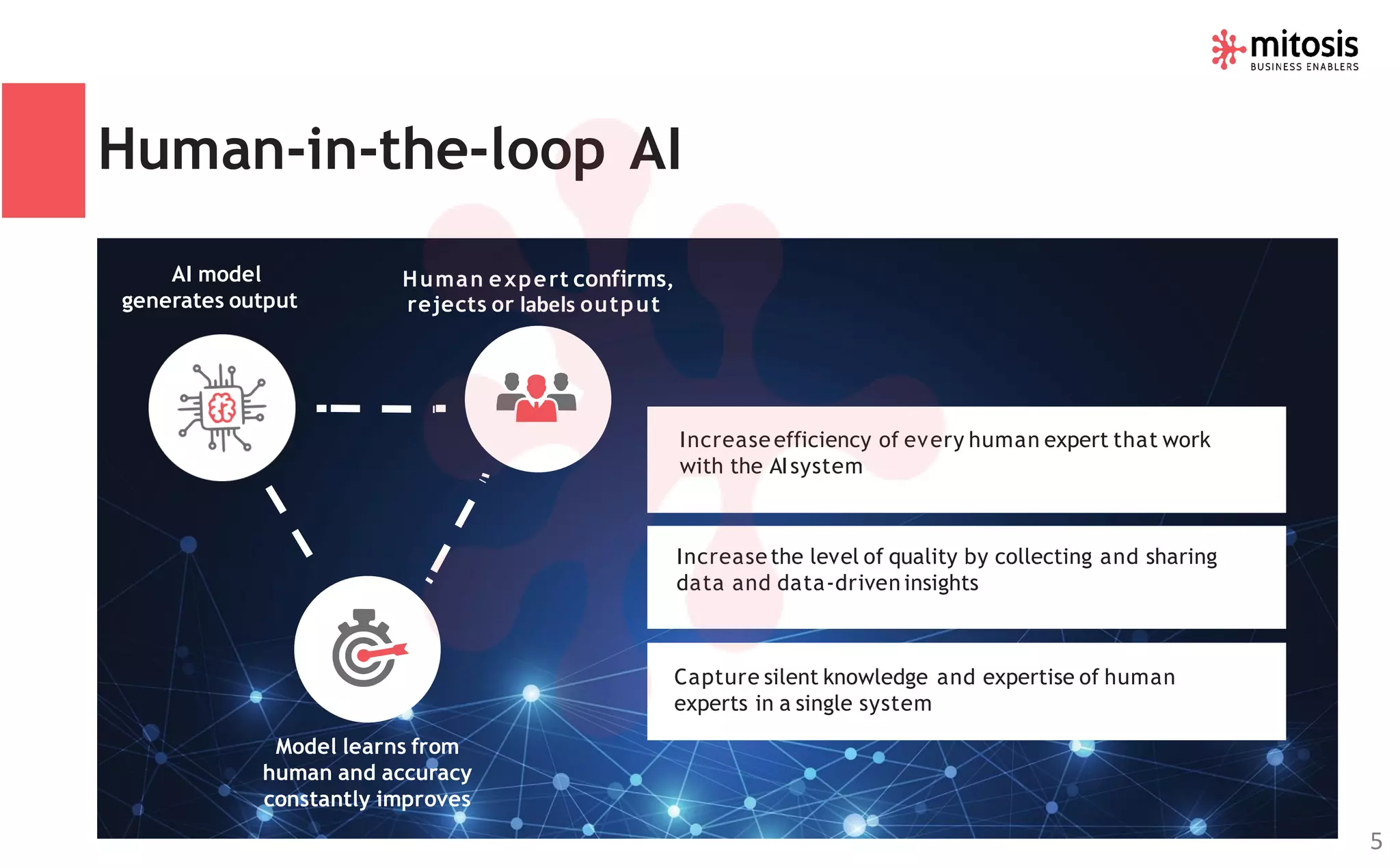
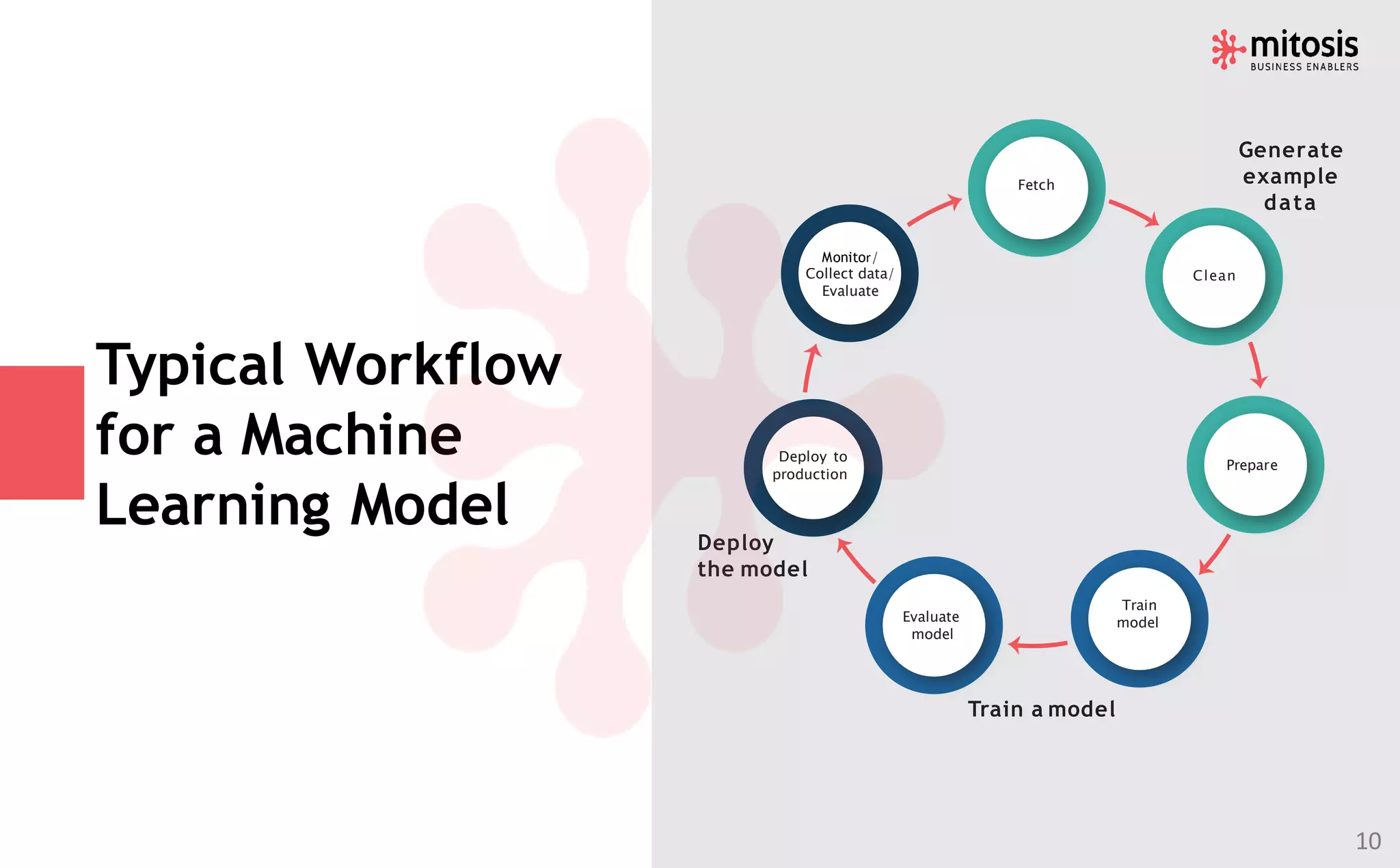
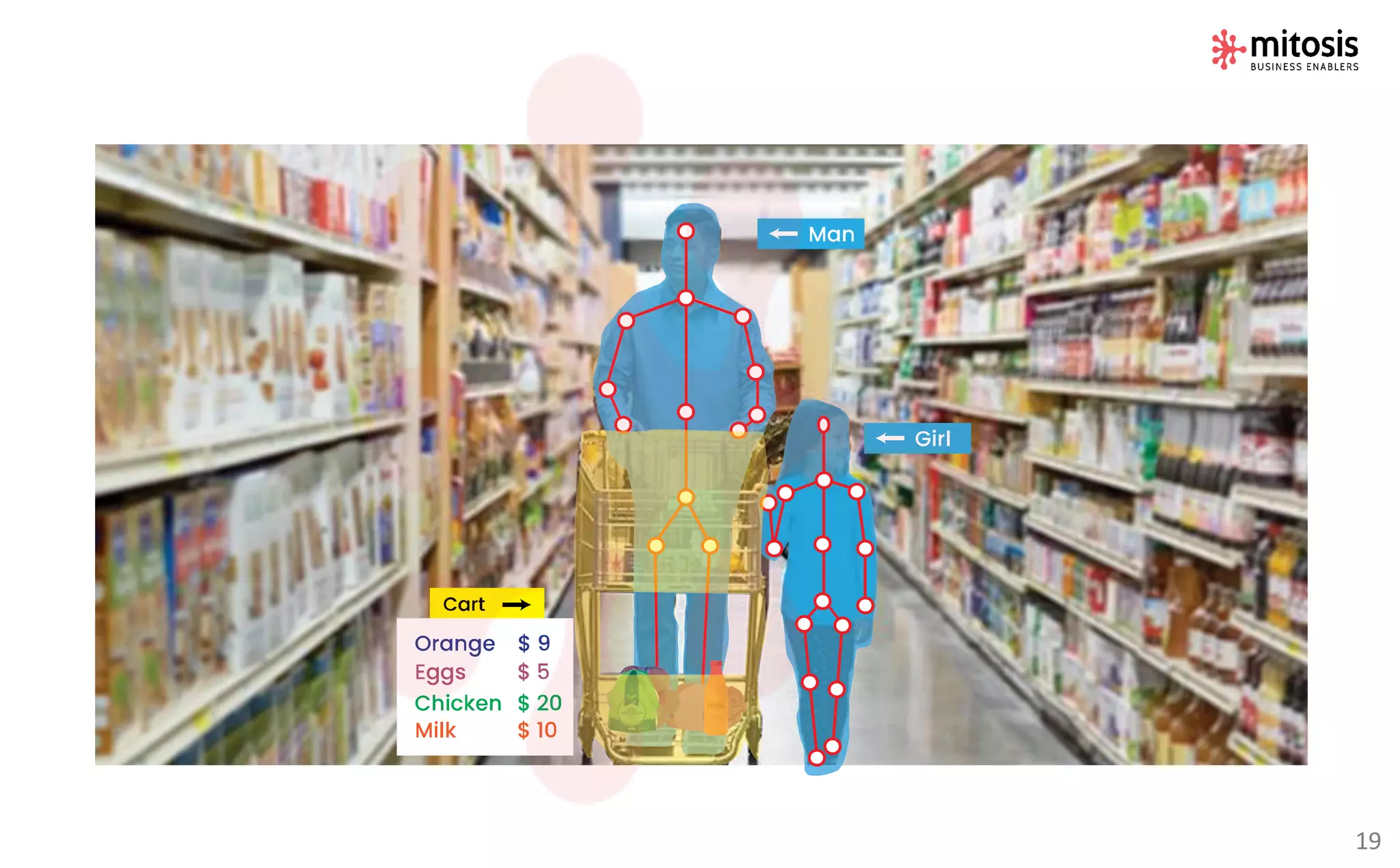
Human-in-the-loop (HITL) machine learning integrates human and machine intelligence to enhance algorithm training and testing, allowing for continuous improvement through human feedback. It involves various data labeling techniques to develop AI models for applications like natural language processing and computer vision. The HITL approach is evolving towards automation while ensuring human oversight, significantly impacting business workflows in the future.