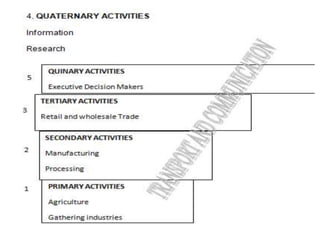
The document discusses human activities, emphasizing how they vary by physical environment, culture, technology, and economic factors. It categorizes human activities into primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary, and quinary sectors, detailing their roles in the economy. Additionally, it addresses spatial interactions and diffusion theories, highlighting how geographical factors and population influence economic activities and relationships between different areas.