This document discusses HTTP caching in web applications, emphasizing its benefits such as reduced latency, lower server costs, and improved response times. It outlines how HTTP works including client and origin interactions, request and response headers, and various caching techniques like conditional requests. Additionally, it suggests best practices for implementing caching, such as managing cache headers and considering cache invalidation strategies.





![HTTP CACHING IN WEB APPLICATIONS
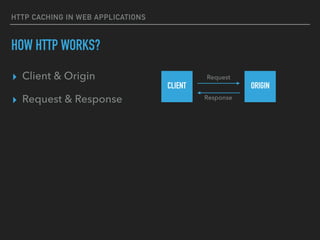
HOW HTTP WORKS?
▸ Client & Origin
▸ Request & Response
▸ HTTP Headers
CLIENT ORIGIN
Request
Response
$ curl -v https://example.com > /dev/null
> GET / HTTP/1.1
> Host: example.com
> Accept: */*
>
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< Server: nginx
< Date: Wed, 25 Feb 2016 16:45:00 GMT
<
[1024 bytes data]
{
{
Request headers
Response headers
Curl command
Response data](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/http-caching-devclub-lv-160227075728/85/HTTP-Caching-in-Web-Application-9-320.jpg)






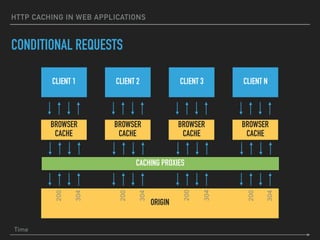
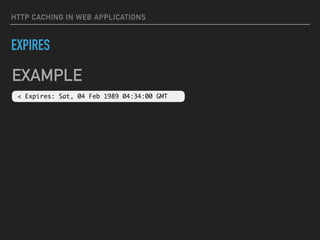
![HTTP CACHING IN WEB APPLICATIONS
CONDITIONAL REQUESTS: CODE
<?php
$ts = 1456419010; // Comes from DB or memory cache
$last_modified = gmdate('r', $ts);
header('Last-Modified: ' . $last_modified);
if (
isset($_SERVER['HTTP_IF_MODIFIED_SINCE'])
&& $ts <= strtotime($_SERVER['HTTP_IF_MODIFIED_SINCE'])
) {
header('HTTP/1.1 304 Not Modified');
exit(0);
}
sleep(5); // Do something very hard](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/http-caching-devclub-lv-160227075728/85/HTTP-Caching-in-Web-Application-21-320.jpg)
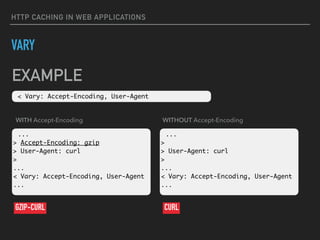
![HTTP CACHING IN WEB APPLICATIONS
CONDITIONAL REQUESTS: FIRST REQUEST
$ time curl -v https://example.com > /dev/null
> GET / HTTP/1.1
> Host: example.com
>
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< Server: nginx
< Date: Thu, 25 Feb 2016 16:50:10 GMT
< Last-Modified: Thu, 25 Feb 2016 16:50:10 GMT
<
[data not shown]
real 0m5.020s
user 0m0.005s
sys 0m0.006s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/http-caching-devclub-lv-160227075728/85/HTTP-Caching-in-Web-Application-22-320.jpg)
![HTTP CACHING IN WEB APPLICATIONS
CONDITIONAL REQUESTS: SUBSEQUENT REQUEST
$ time curl -v https://example.com
-H "If-Modified-Since: Thu, 25 Feb 2016 16:50:10 GMT" > /dev/null
> GET / HTTP/1.1
> Host: example.com
> If-Modified-Since: Thu, 25 Feb 2016 16:50:10 GMT
>
< HTTP/1.1 304 Not Modified
< Server: nginx
< Date: Thu, 25 Feb 2016 16:51:10 GMT
< Last-Modified: Thu, 25 Feb 2016 16:50:10 GMT
<
[data not shown]
real 0m0.019s
user 0m0.005s
sys 0m0.005s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/http-caching-devclub-lv-160227075728/85/HTTP-Caching-in-Web-Application-23-320.jpg)





![HTTP CACHING IN WEB APPLICATIONS
CONDITIONAL REQUESTS: CODE
<?php
$last_mod = 1456419010; // Comes from DB or memory cache
$last_mod_of_linked_resource = 1456419010; // Comes from DB or memory cache
$etag = md5($last_mod . $last_mod_of_linked_resource);
header('ETag: ' . $etag);
if (
isset($_SERVER['HTTP_IF_NONE_MATCH'])
&& $_SERVER['HTTP_IF_NONE_MATCH'] === $etag
) {
header('HTTP/1.1 304 Not Modified');
exit(0);
}
sleep(5); // Do something very hard](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/http-caching-devclub-lv-160227075728/85/HTTP-Caching-in-Web-Application-29-320.jpg)
![HTTP CACHING IN WEB APPLICATIONS
CONDITIONAL REQUESTS: FIRST REQUEST
$ time curl -v https://example.com > /dev/null
> GET / HTTP/1.1
> Host: example.com
>
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< Server: nginx
< Date: Thu, 25 Feb 2016 16:50:10 GMT
< ETag: 228c662b04e31dc303d380ad03c2bc0b
<
[data not shown]
real 0m5.020s
user 0m0.005s
sys 0m0.006s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/http-caching-devclub-lv-160227075728/85/HTTP-Caching-in-Web-Application-30-320.jpg)
![HTTP CACHING IN WEB APPLICATIONS
CONDITIONAL REQUESTS: SUBSEQUENT REQUEST
$ time curl -v https://example.com
-H "If-None-Match: 228c662b04e31dc303d380ad03c2bc0b" > /dev/null
> GET / HTTP/1.1
> Host: example.com
> If-None-Match: 228c662b04e31dc303d380ad03c2bc0b
>
< HTTP/1.1 304 Not Modified
< Server: nginx
< Date: Thu, 25 Feb 2016 16:51:10 GMT
< ETag: 228c662b04e31dc303d380ad03c2bc0b
<
[data not shown]
real 0m0.019s
user 0m0.005s
sys 0m0.005s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/http-caching-devclub-lv-160227075728/85/HTTP-Caching-in-Web-Application-31-320.jpg)