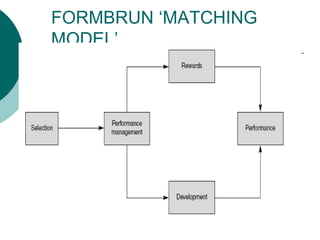
This document discusses human resource management and job analysis. It defines HRM as taking a strategic approach to managing an organization's employees. It outlines important HRM practices and roles like HR generalists and specialists. The document also defines job analysis as systematically investigating job tasks, duties, and responsibilities. It describes the purposes of job analysis including recruitment and training. Key parts of job analysis are the job description, which outlines job contents, and the job specification, which lists required qualifications. Various job analysis methods and tools are also outlined, including the Position Analysis Questionnaire. The document concludes with defining job design and common job design approaches.