Embed presentation
Download to read offline



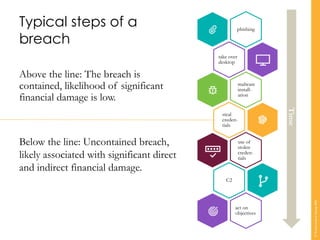
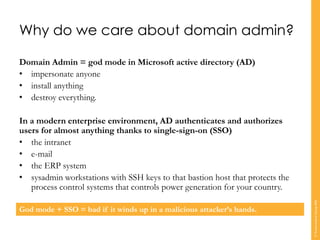







Carsten Maartmann-Moe, a white hat hacker and penetration tester, gave a presentation about how attackers gain domain admin privileges after an initial breach. He explained that domain admin is like "god mode" since it allows impersonating anyone, installing anything, and destroying everything due to single sign-on. He then showed that domain admin is often obtained through default passwords, poorly configured middleware/platforms, vulnerabilities in internal web apps, password sweeping, Oracle/SQL databases, GPOs, Linux systems, and legacy software. Maartmann-Moe demonstrated how an attacker could use an Oracle database, weak passwords, or JBoss to obtain domain admin privileges. His key recommendation was to focus on patching, configuration










