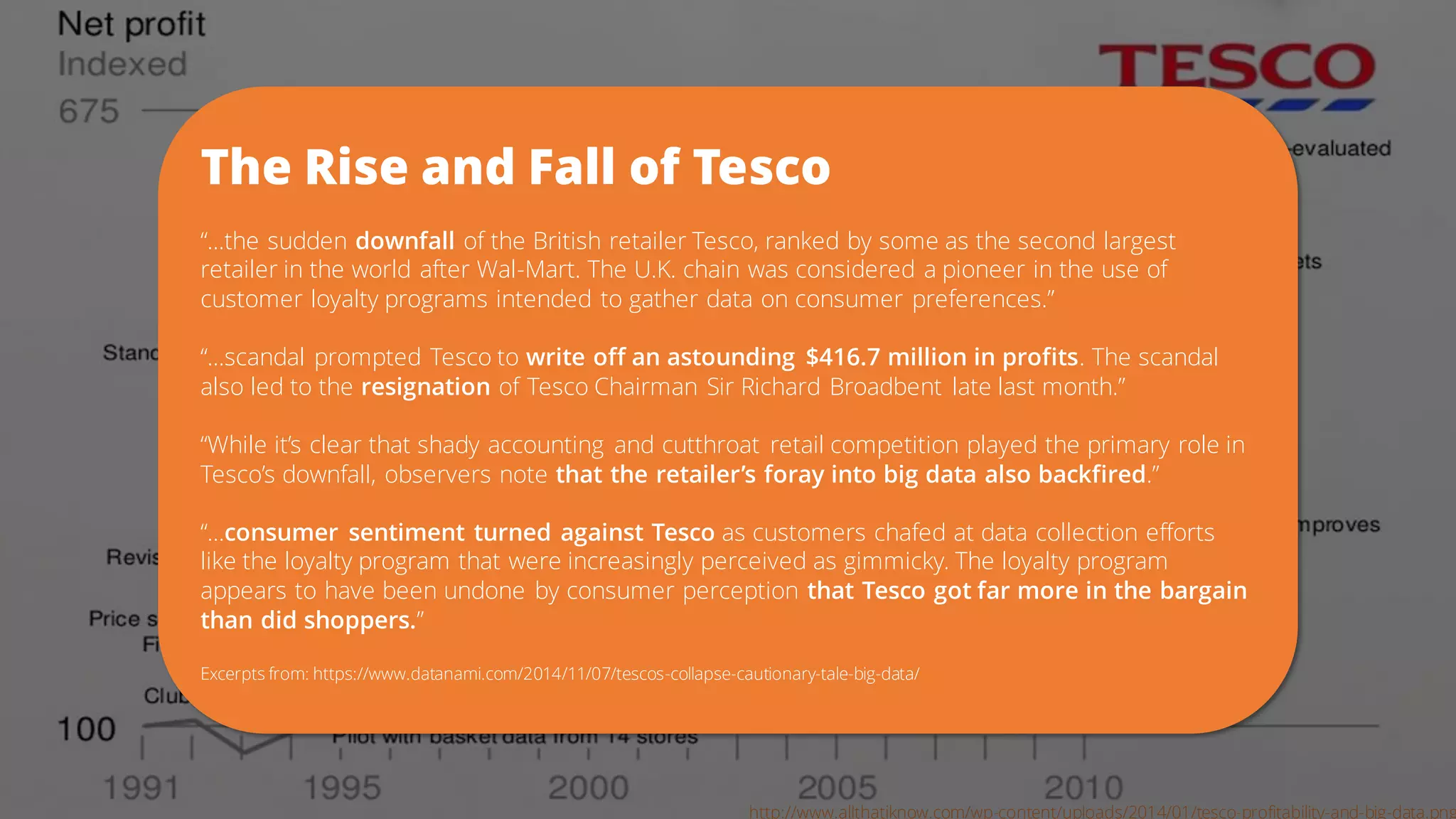
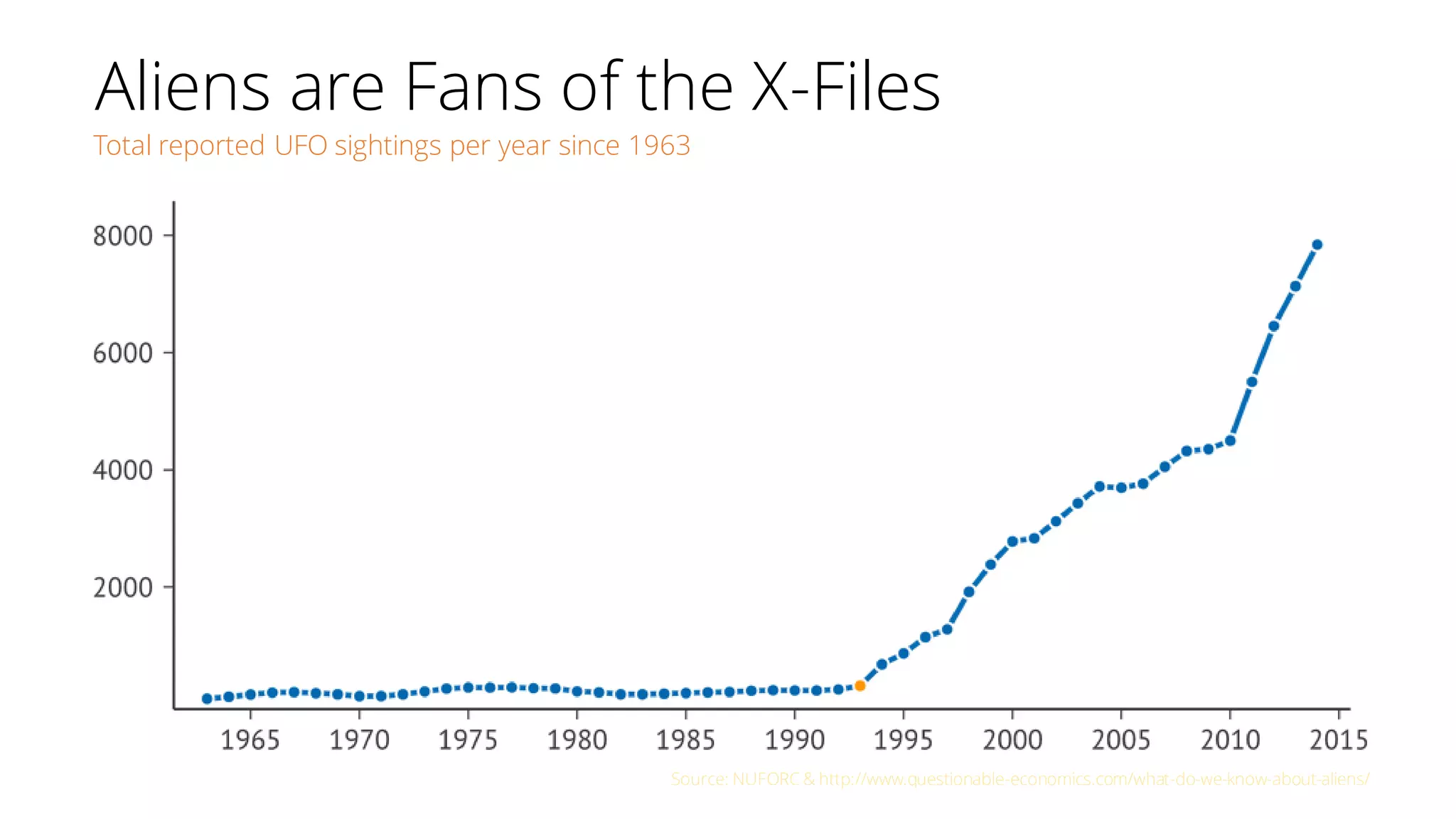
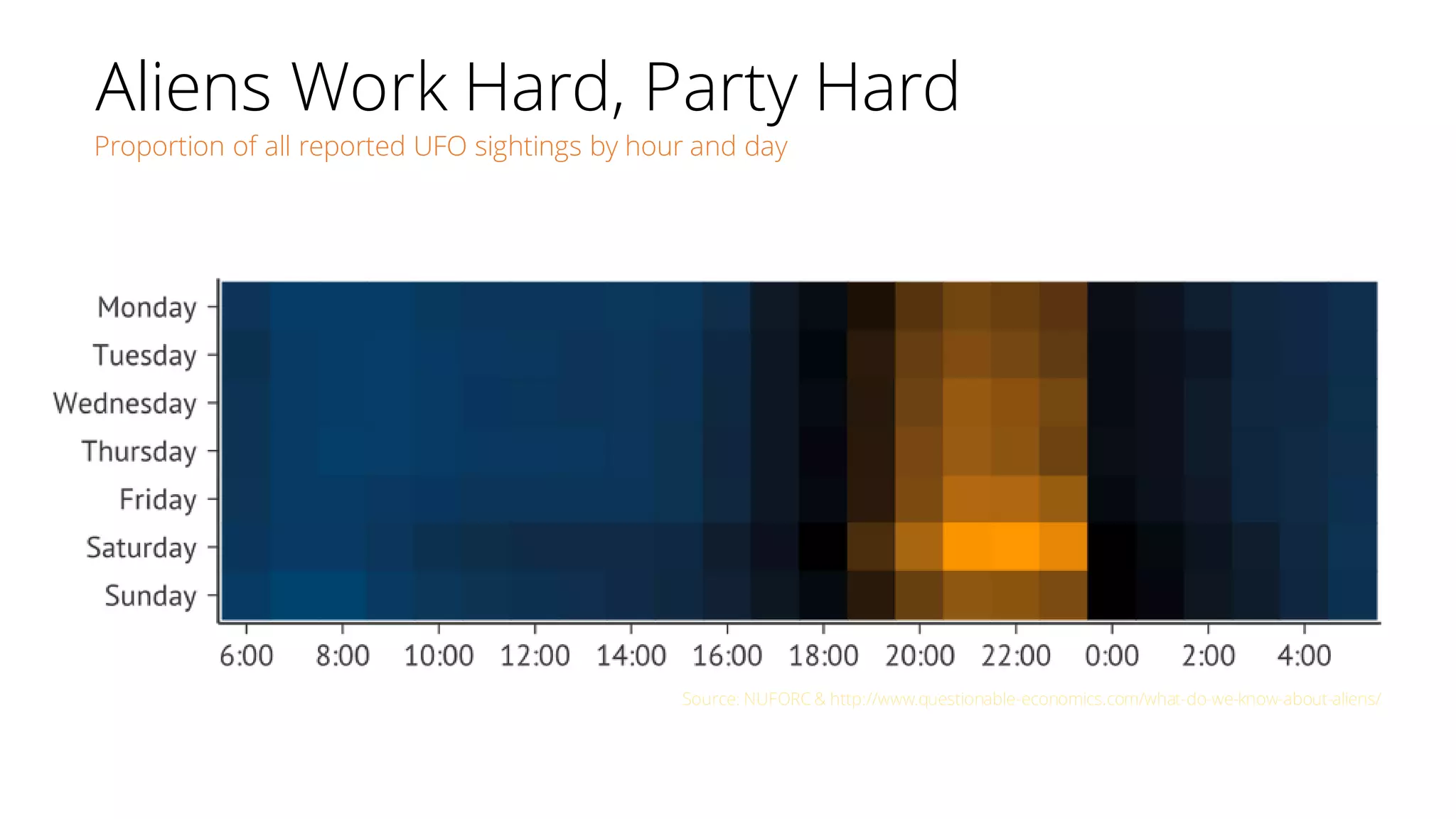
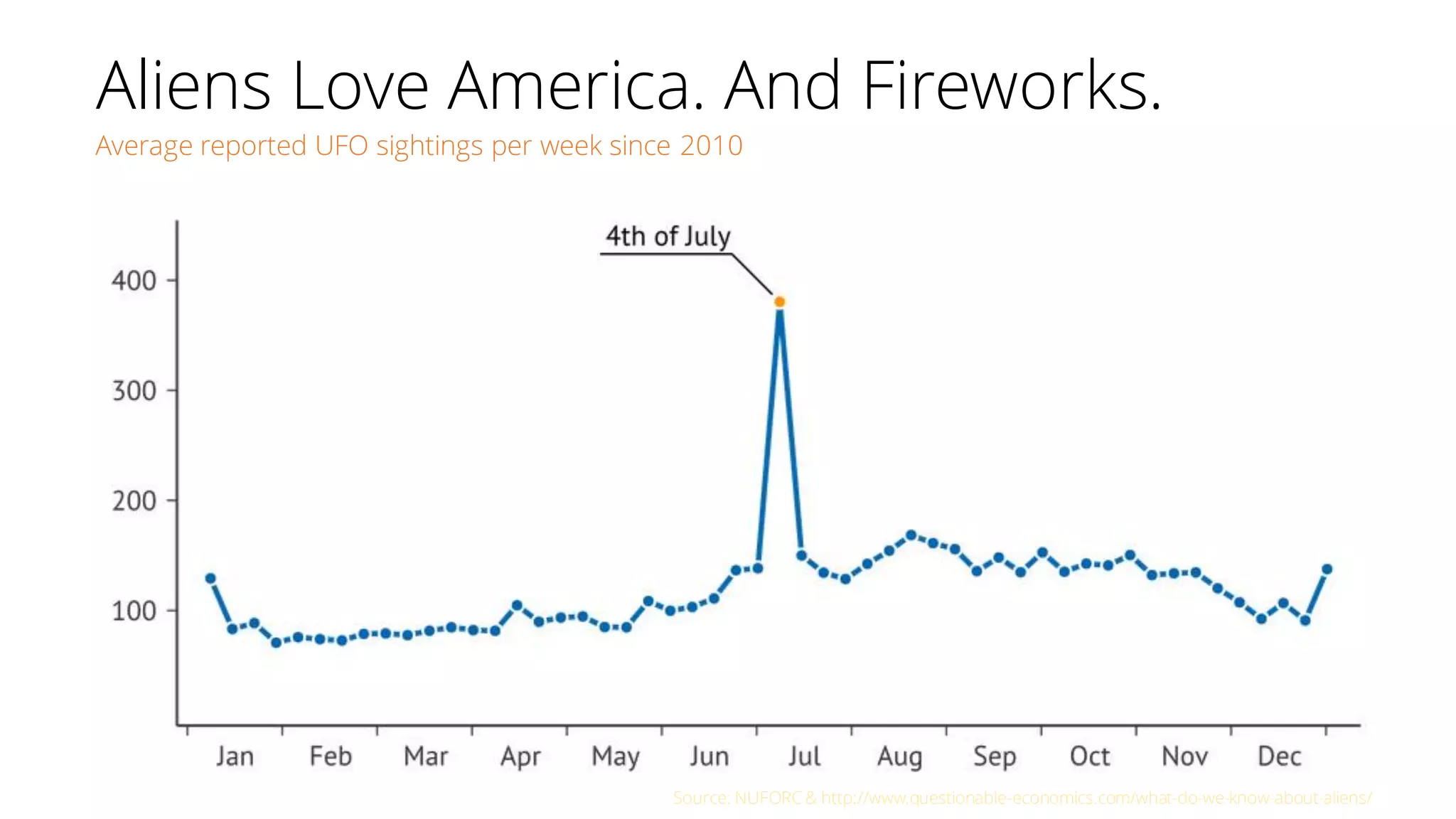
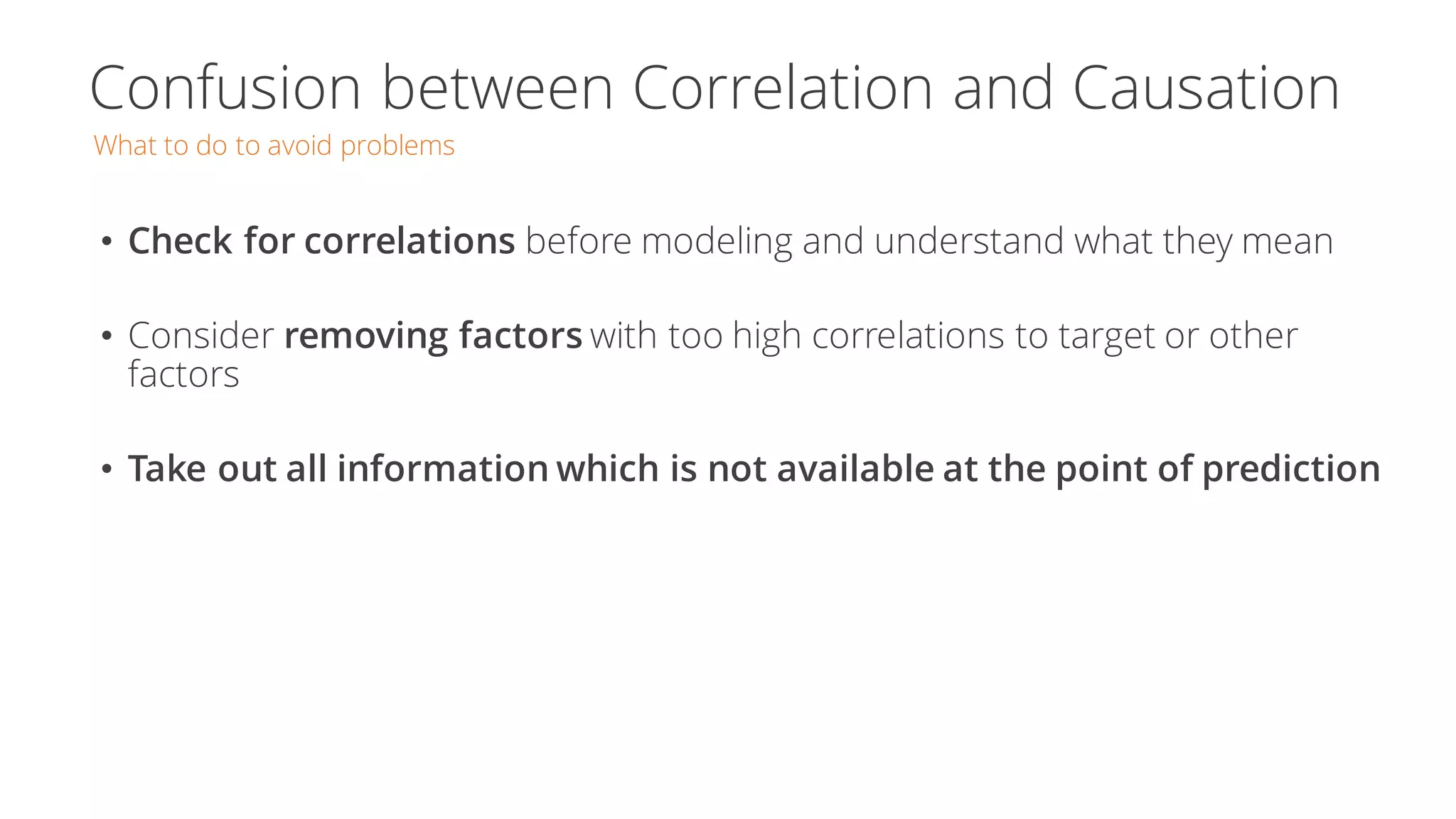
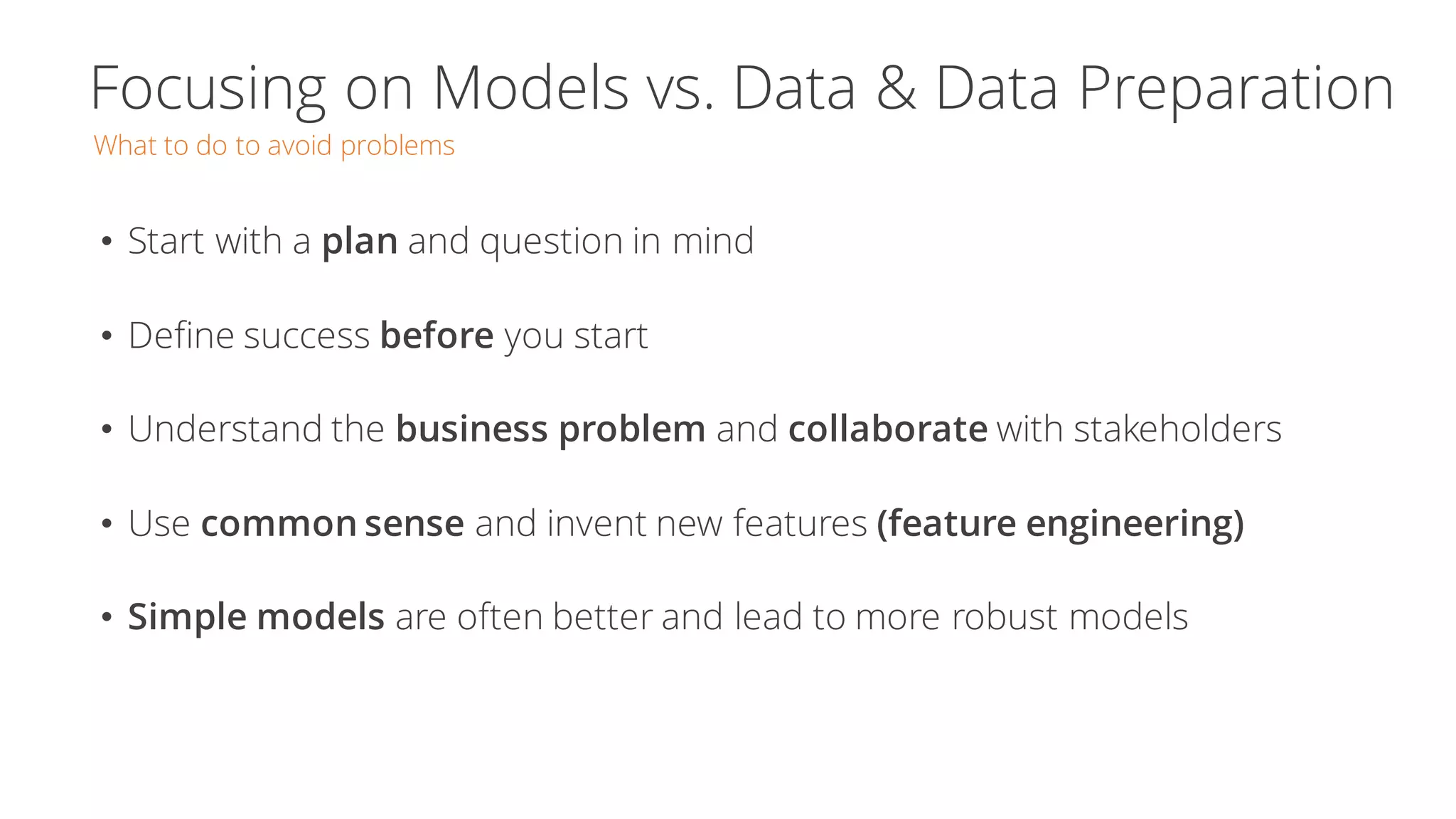
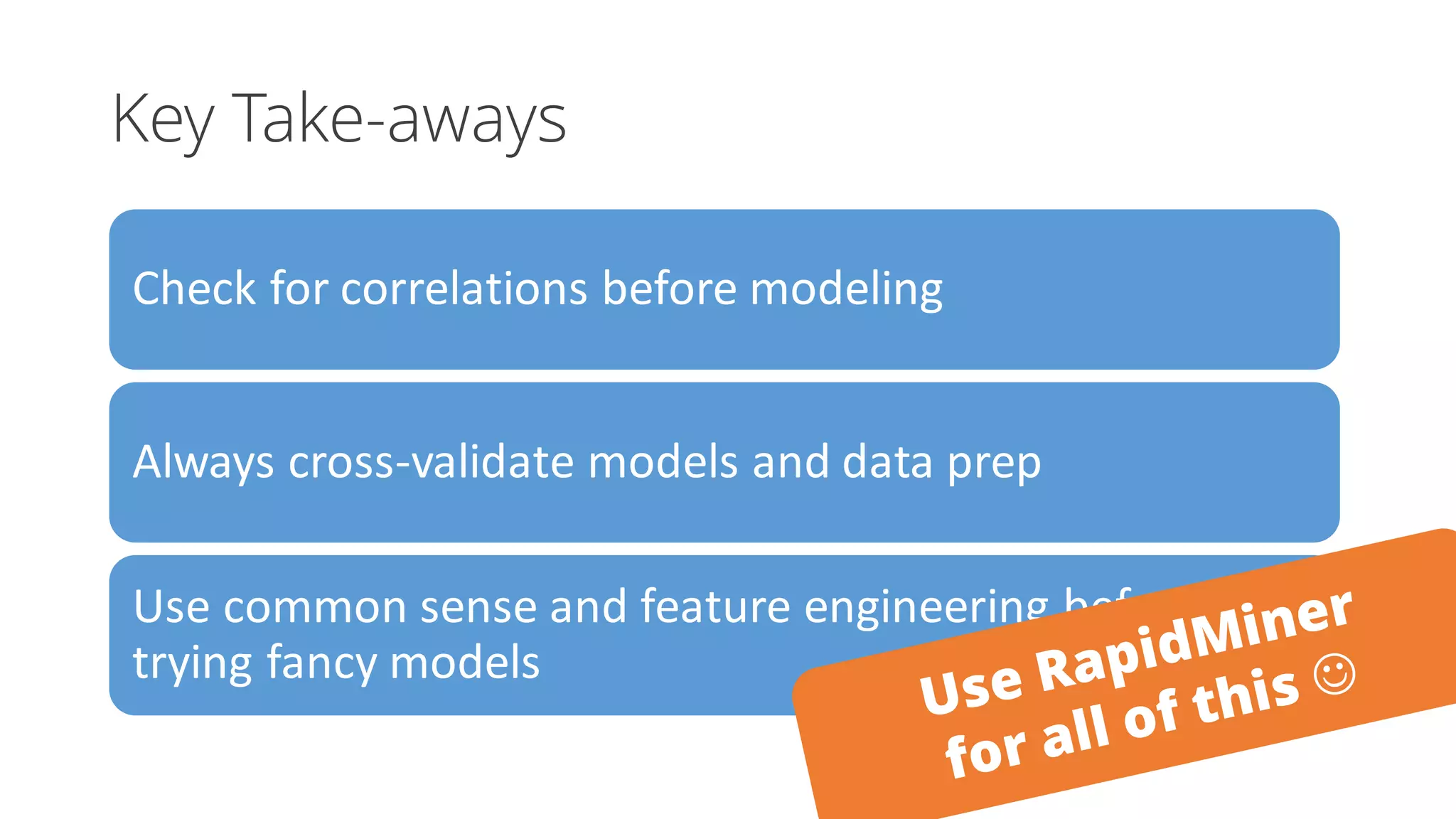
The document discusses the pitfalls of data science through the lens of Tesco's downfall, highlighting how improper data practices and negative consumer perceptions can lead to significant losses. It emphasizes the importance of proper model validation and correlation analysis to avoid costly mistakes in data-driven decision-making. Additionally, it offers strategies for successful data science practices, urging a focus on understanding business problems and engaging with stakeholders.