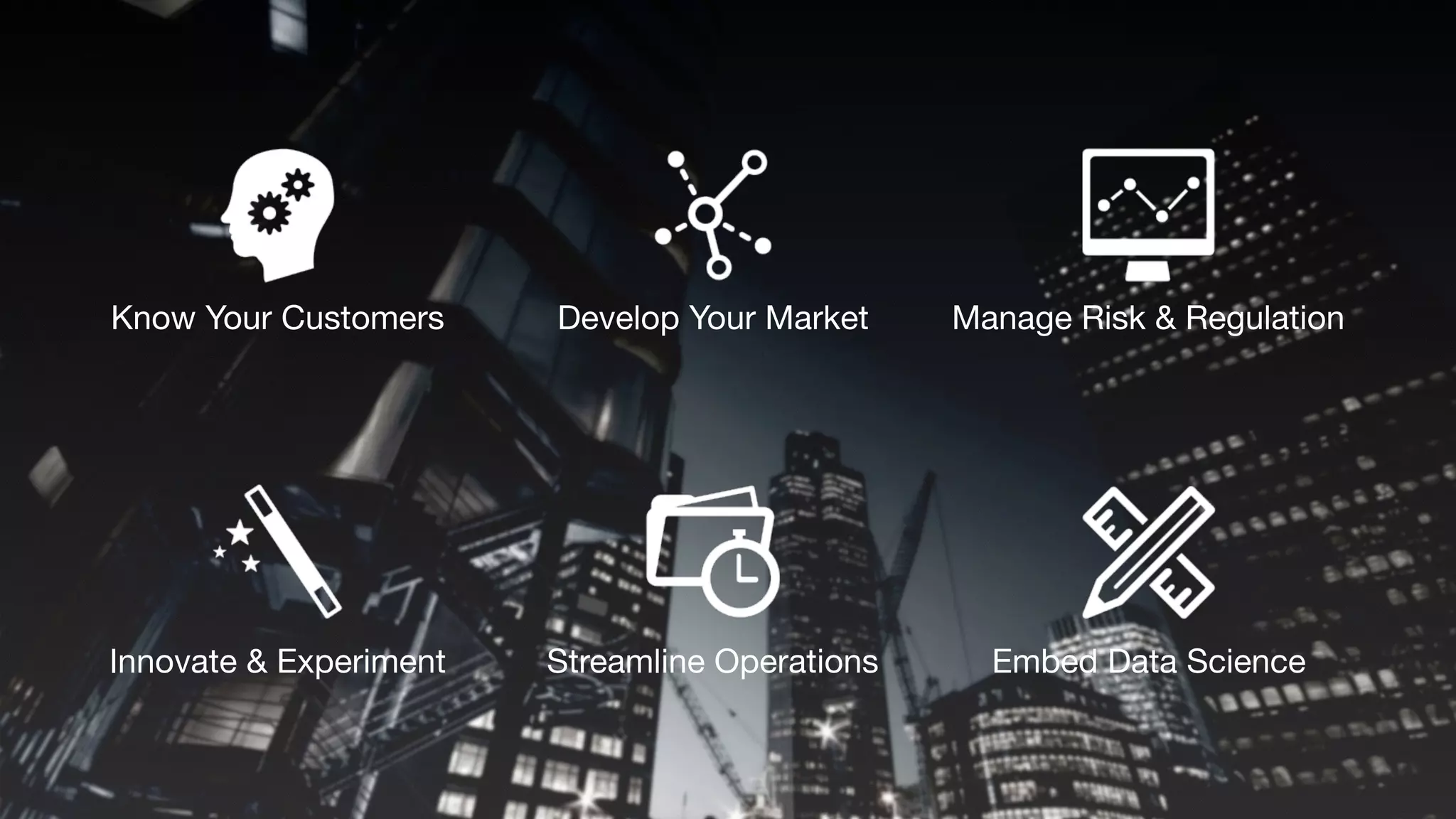
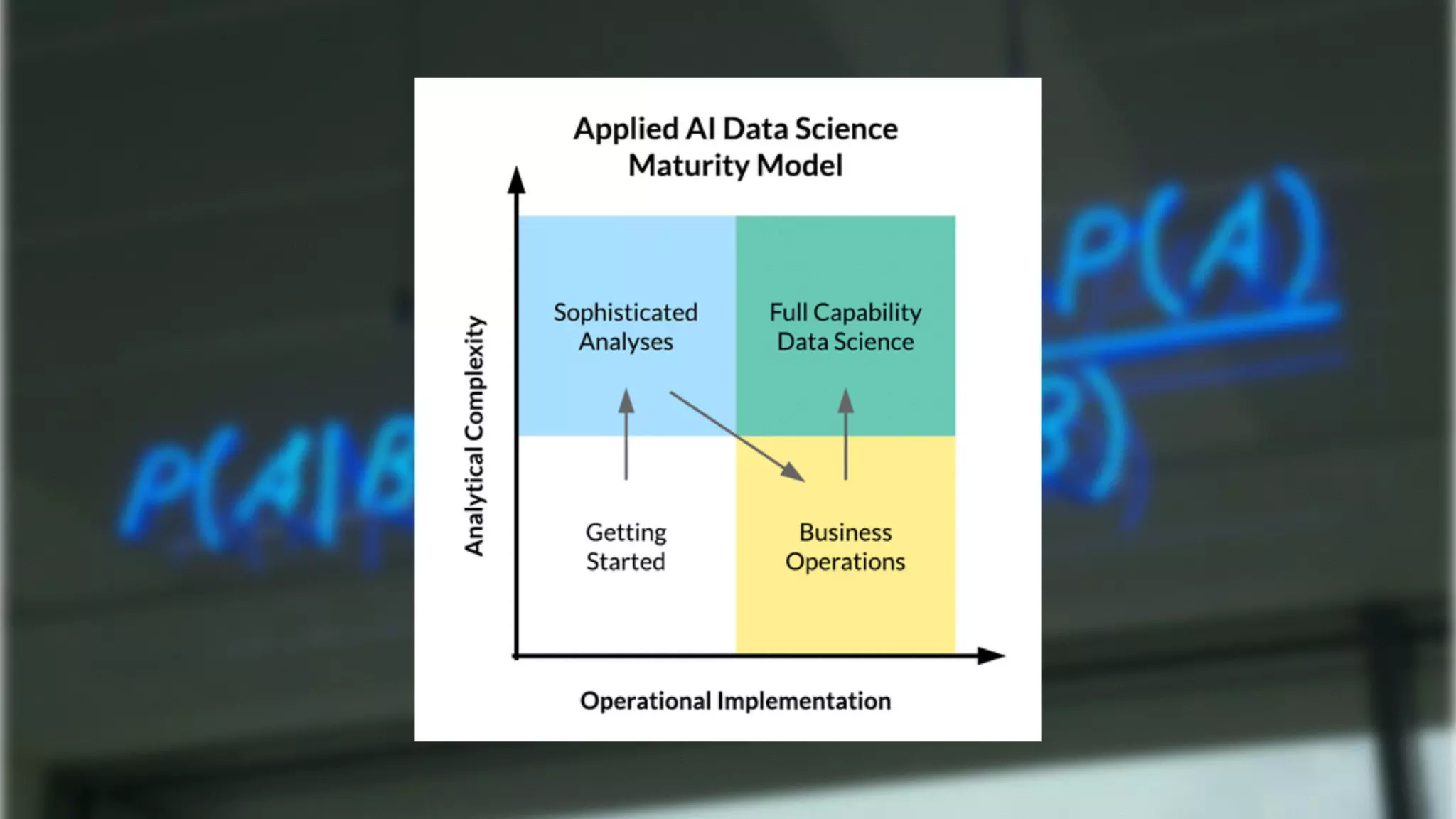
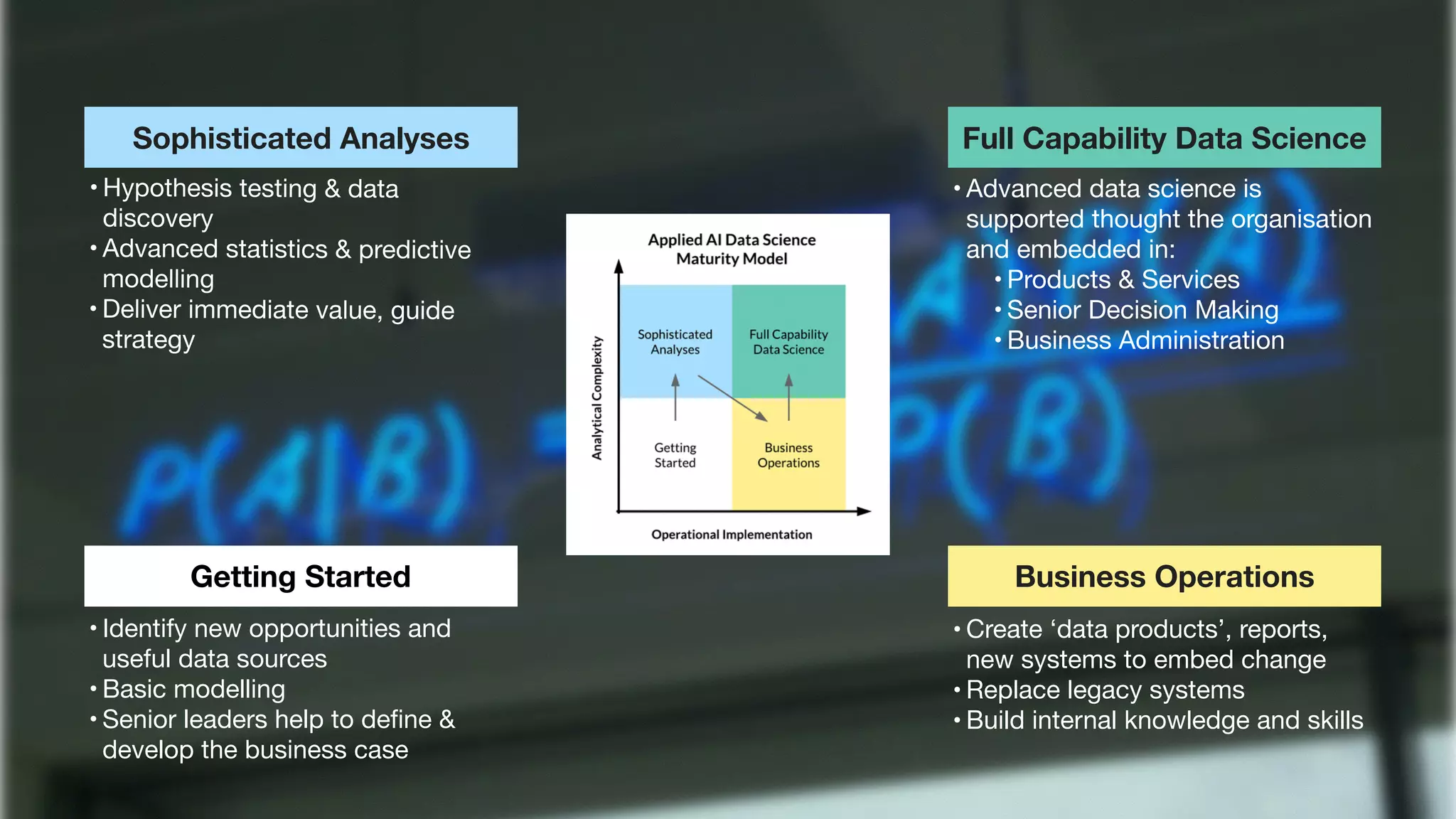
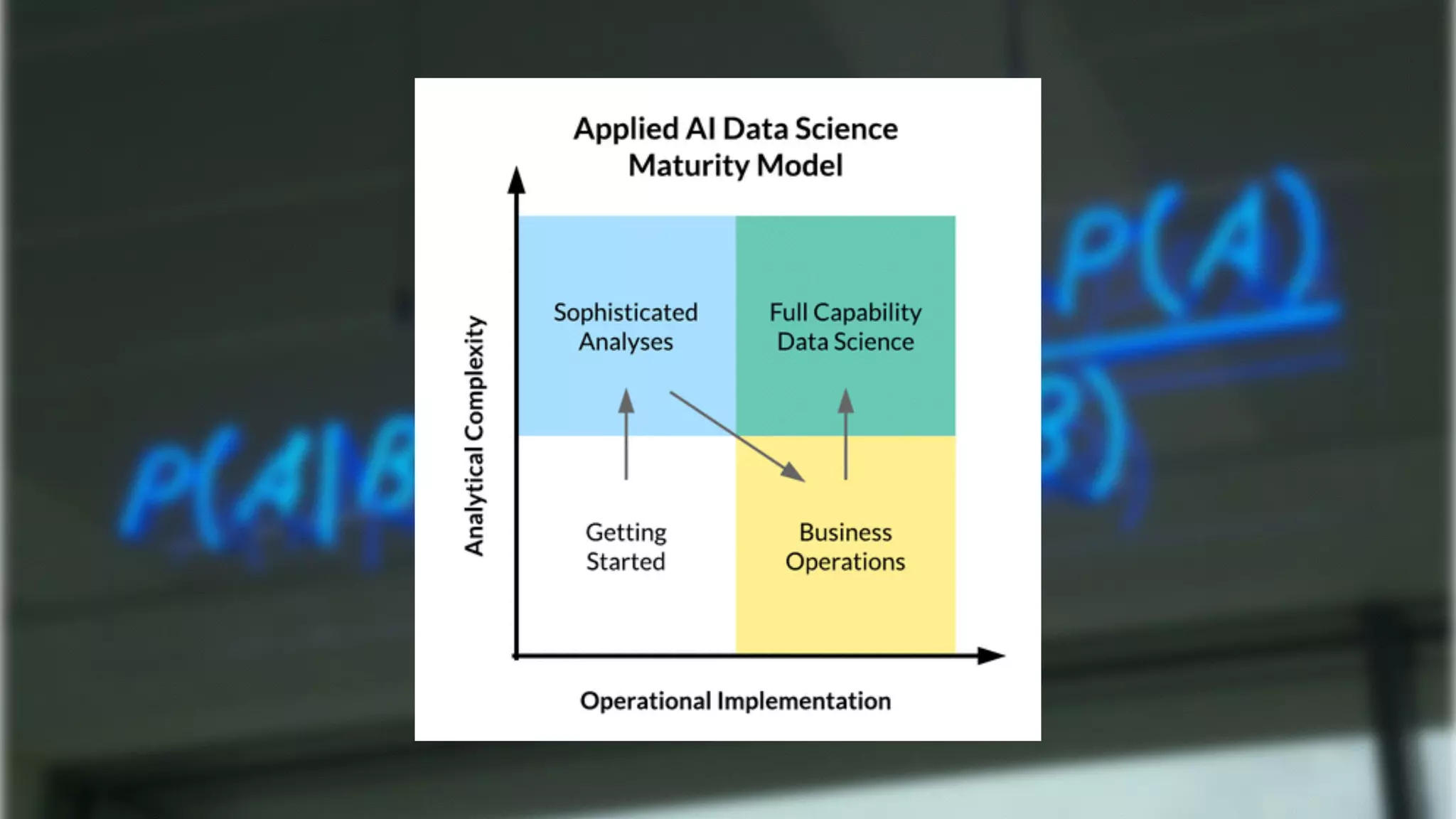
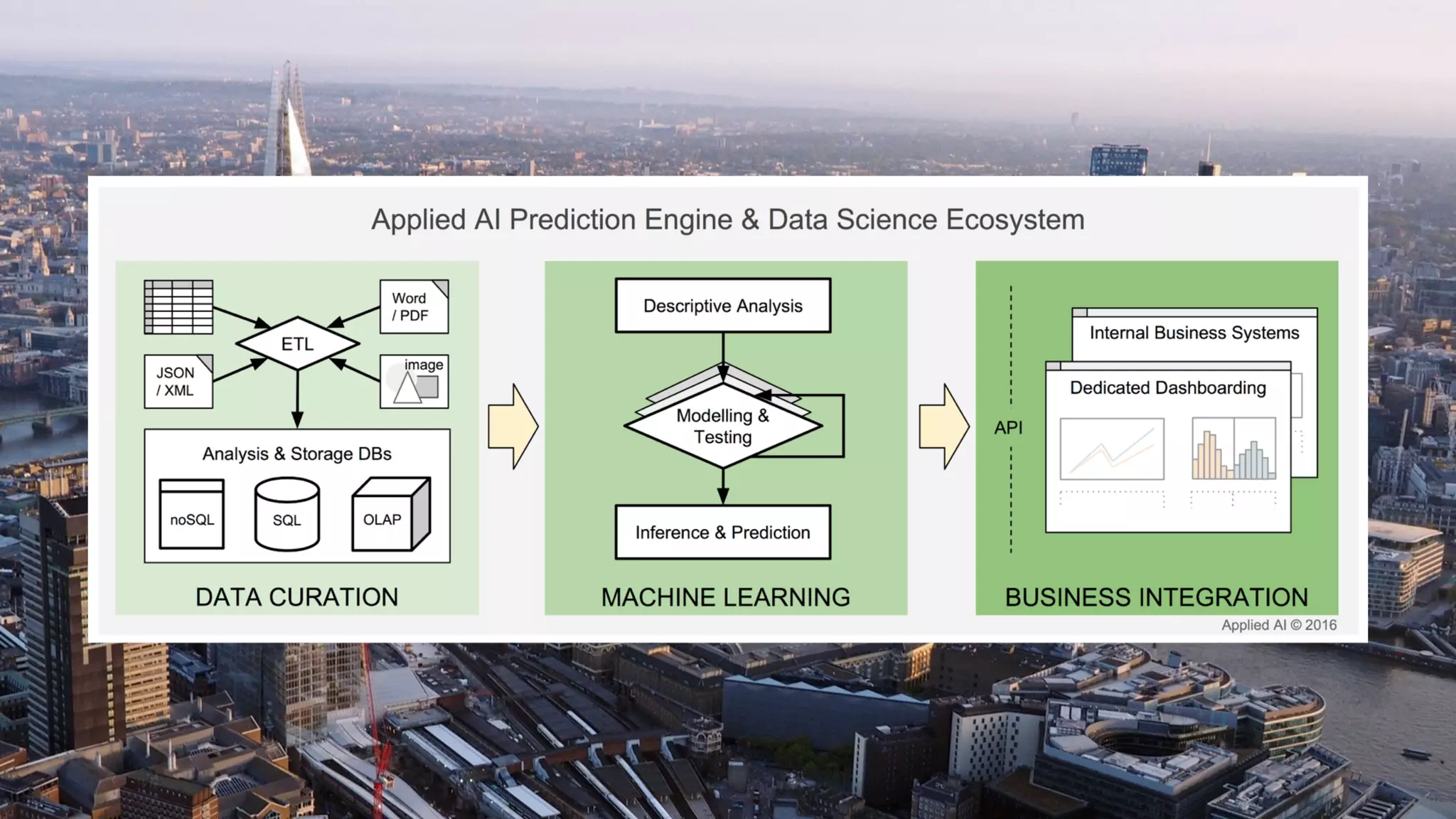
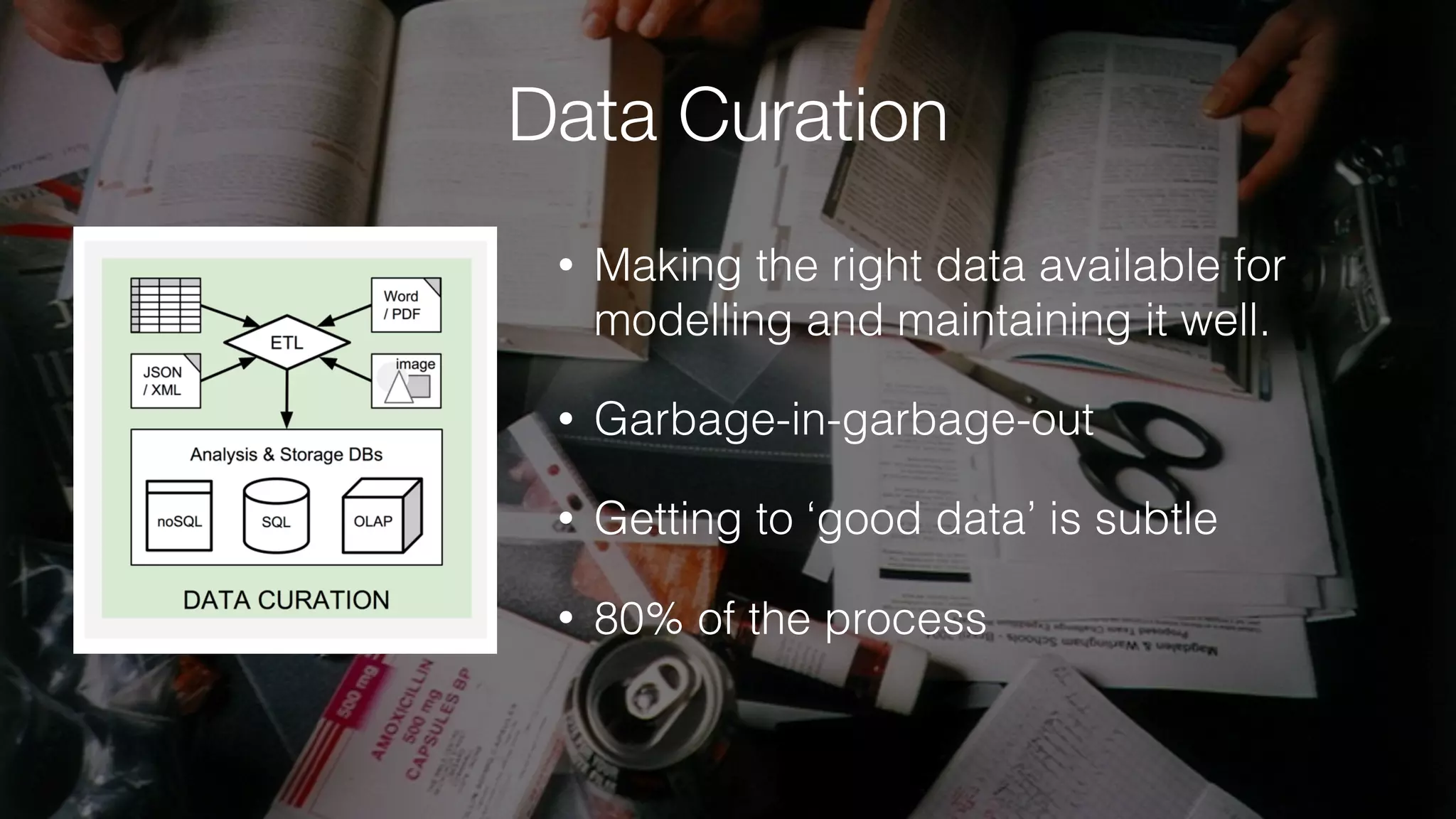
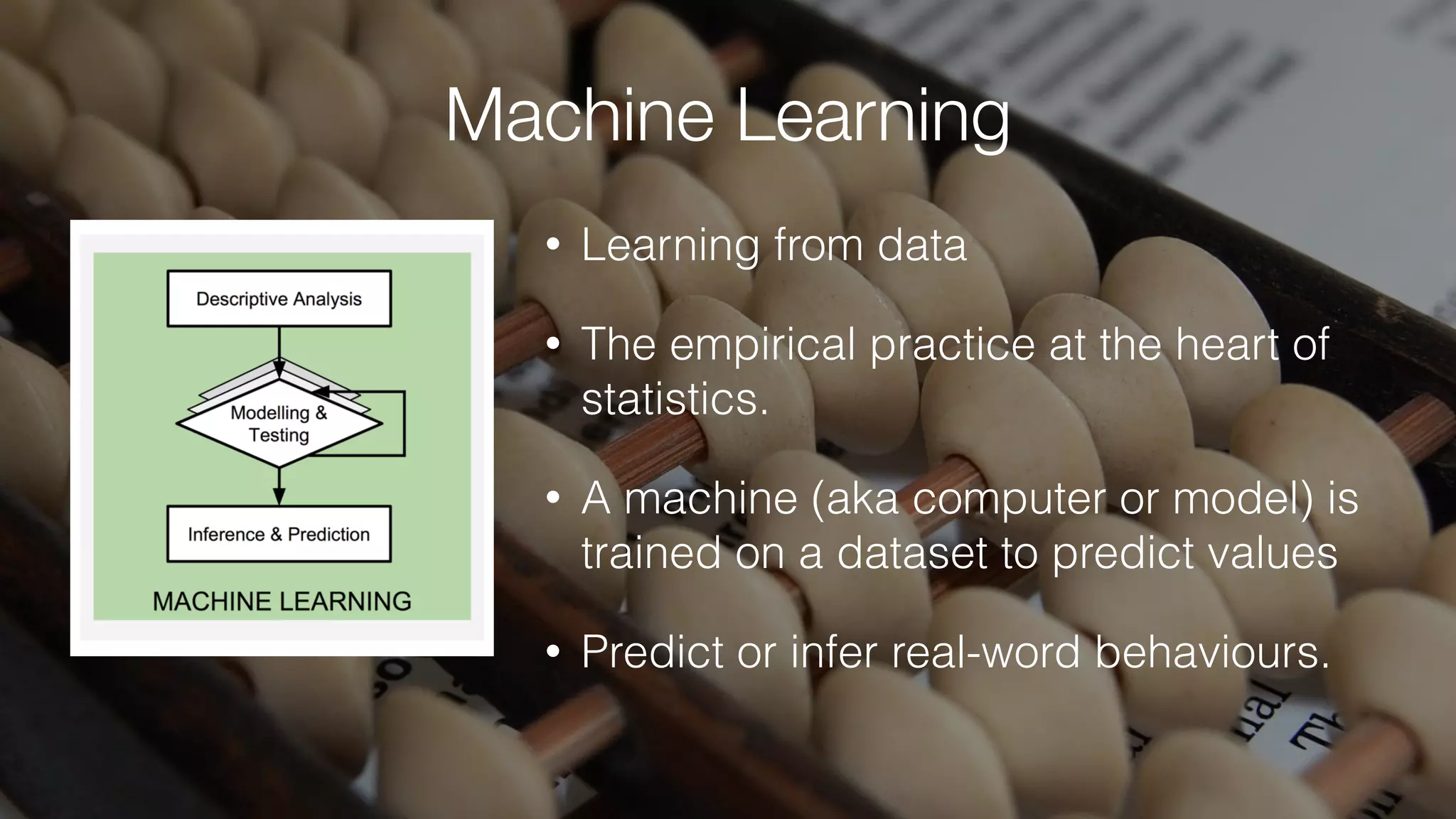
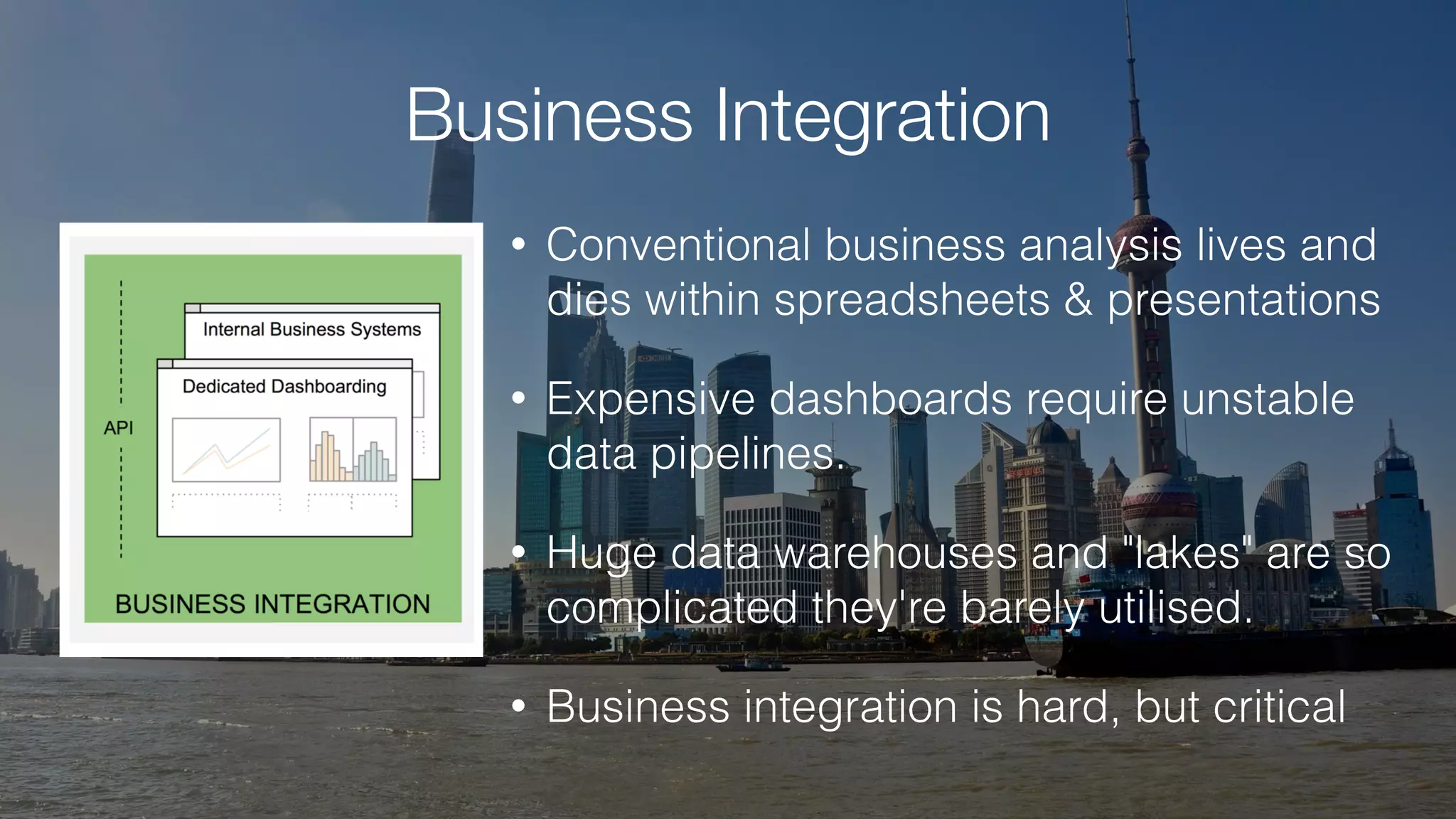
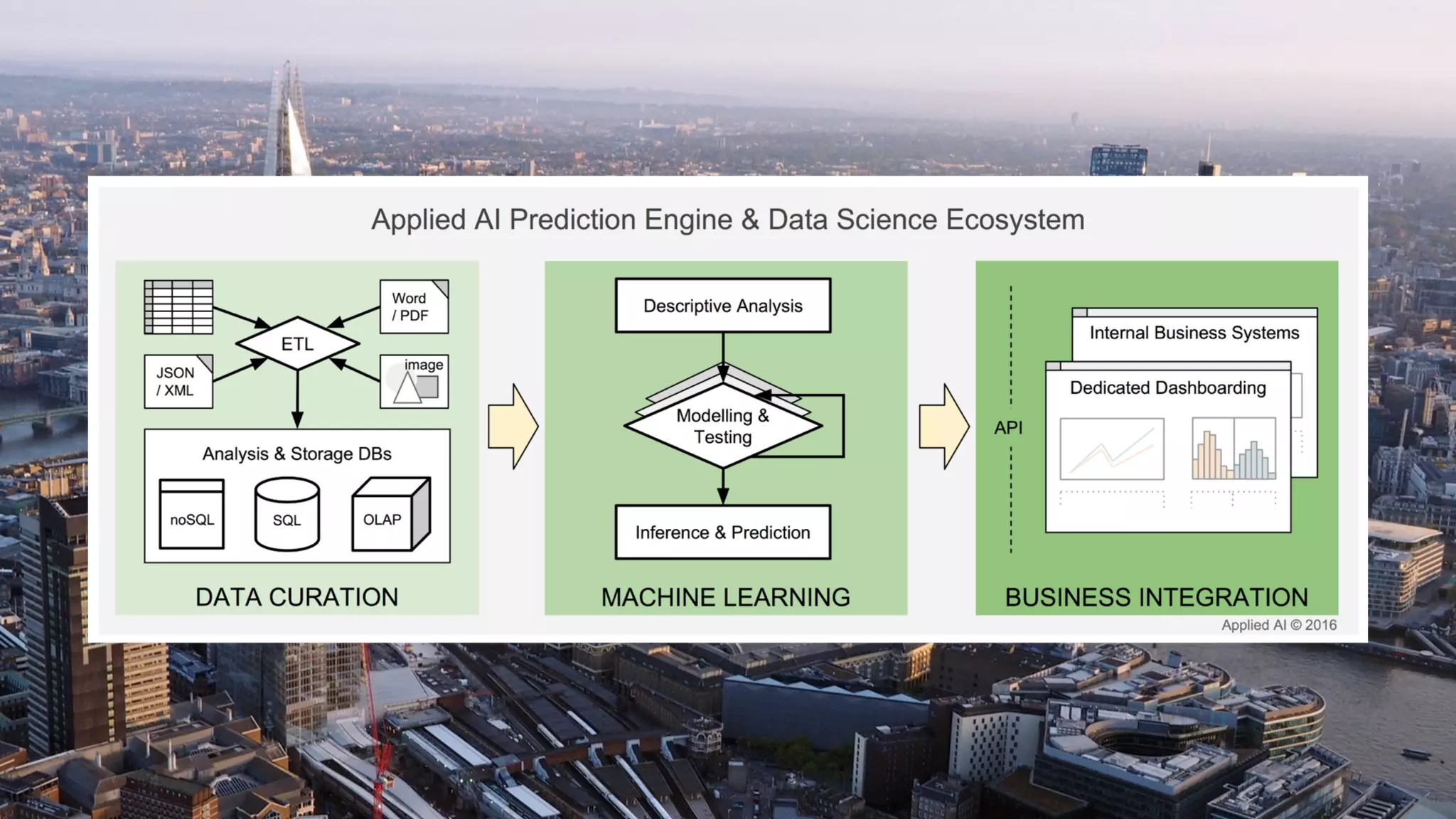
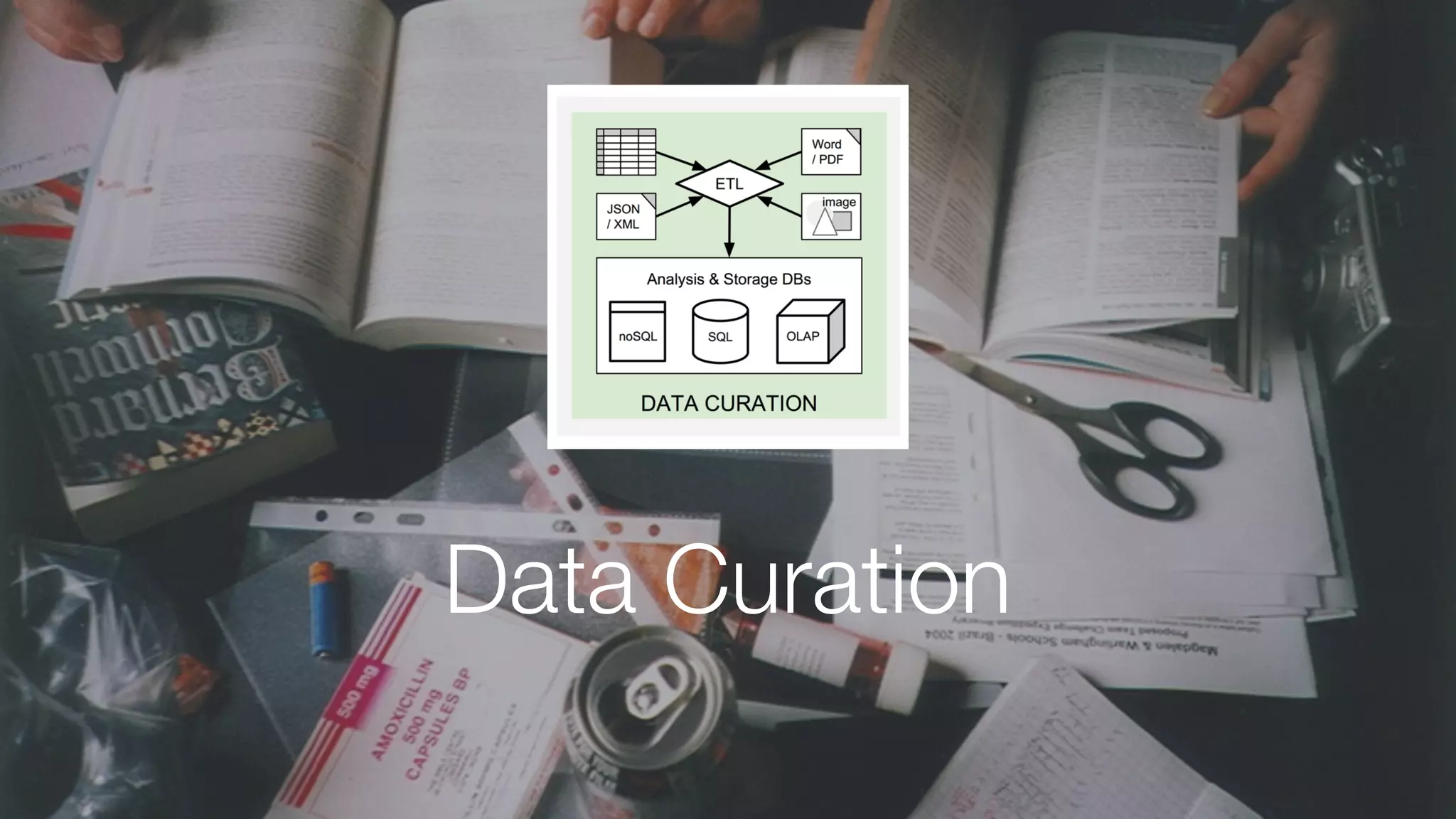
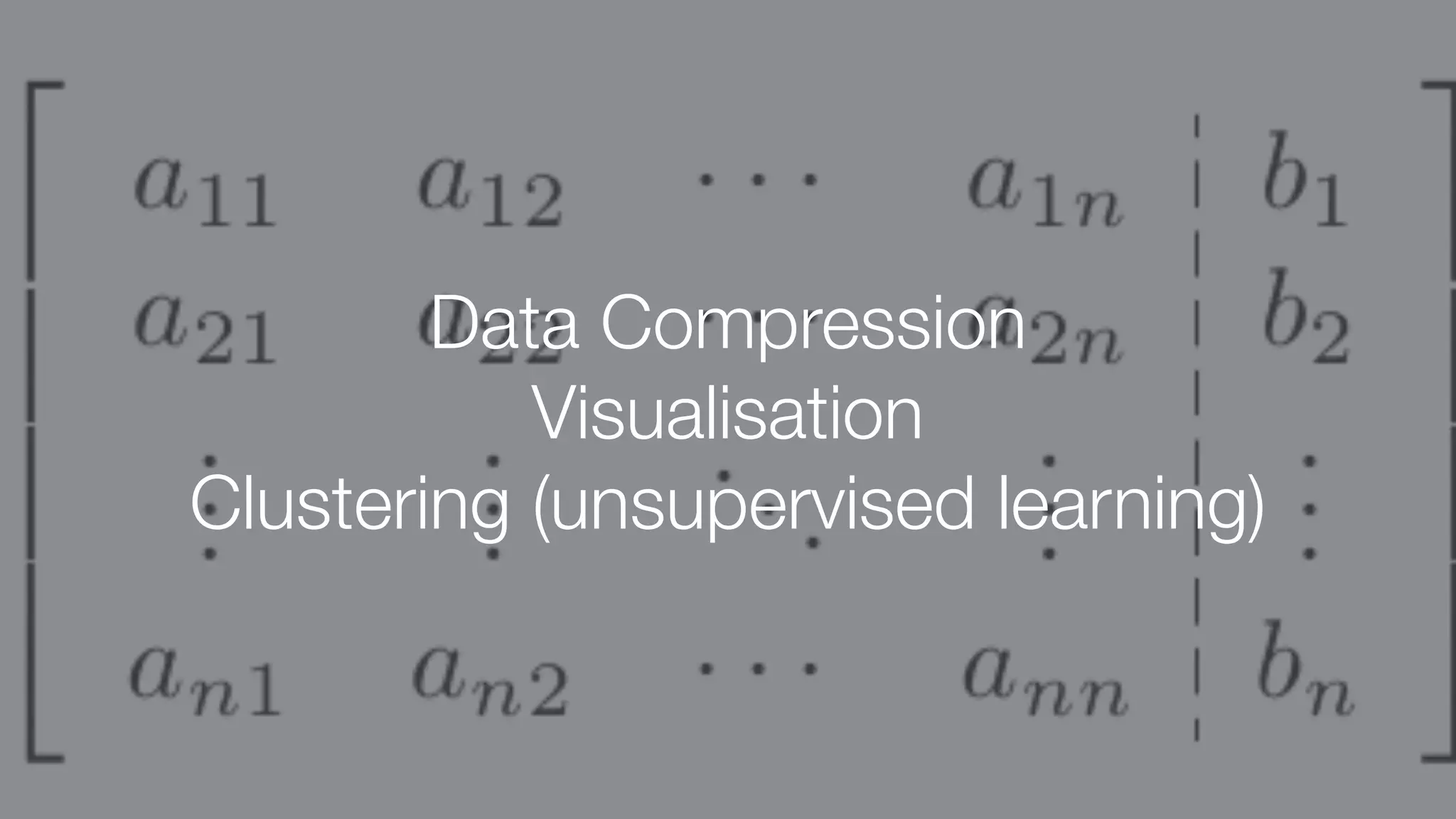
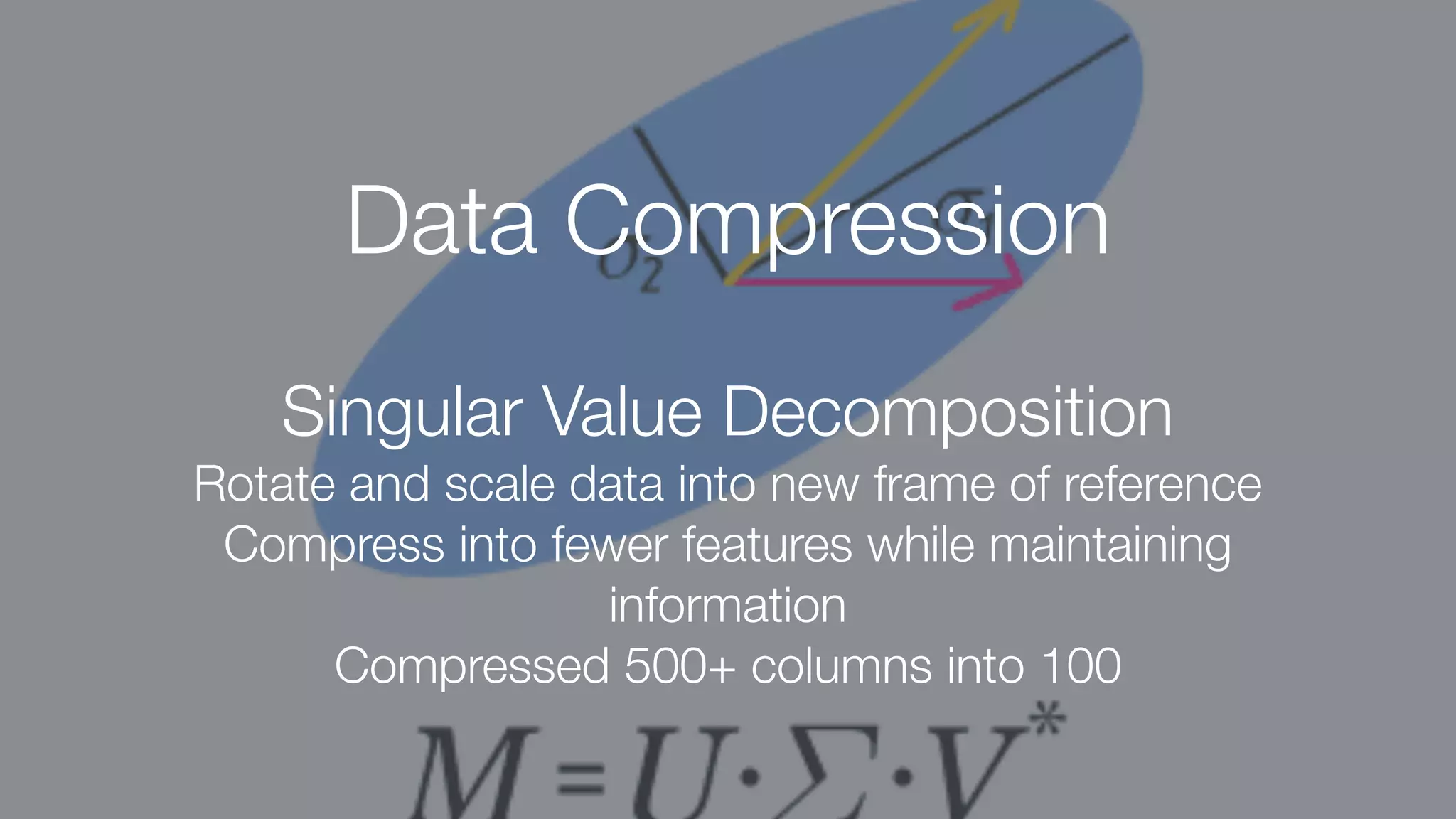
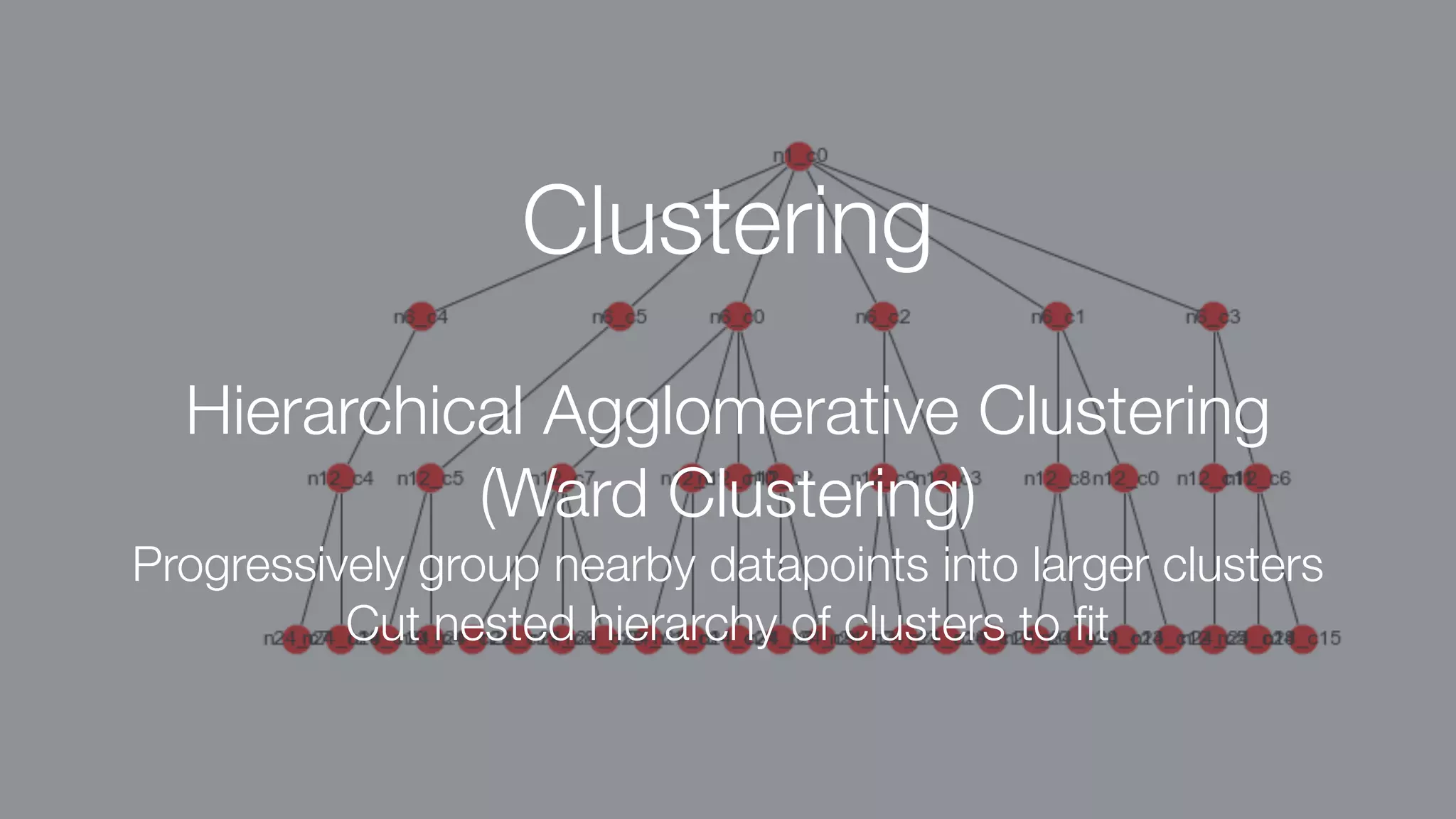
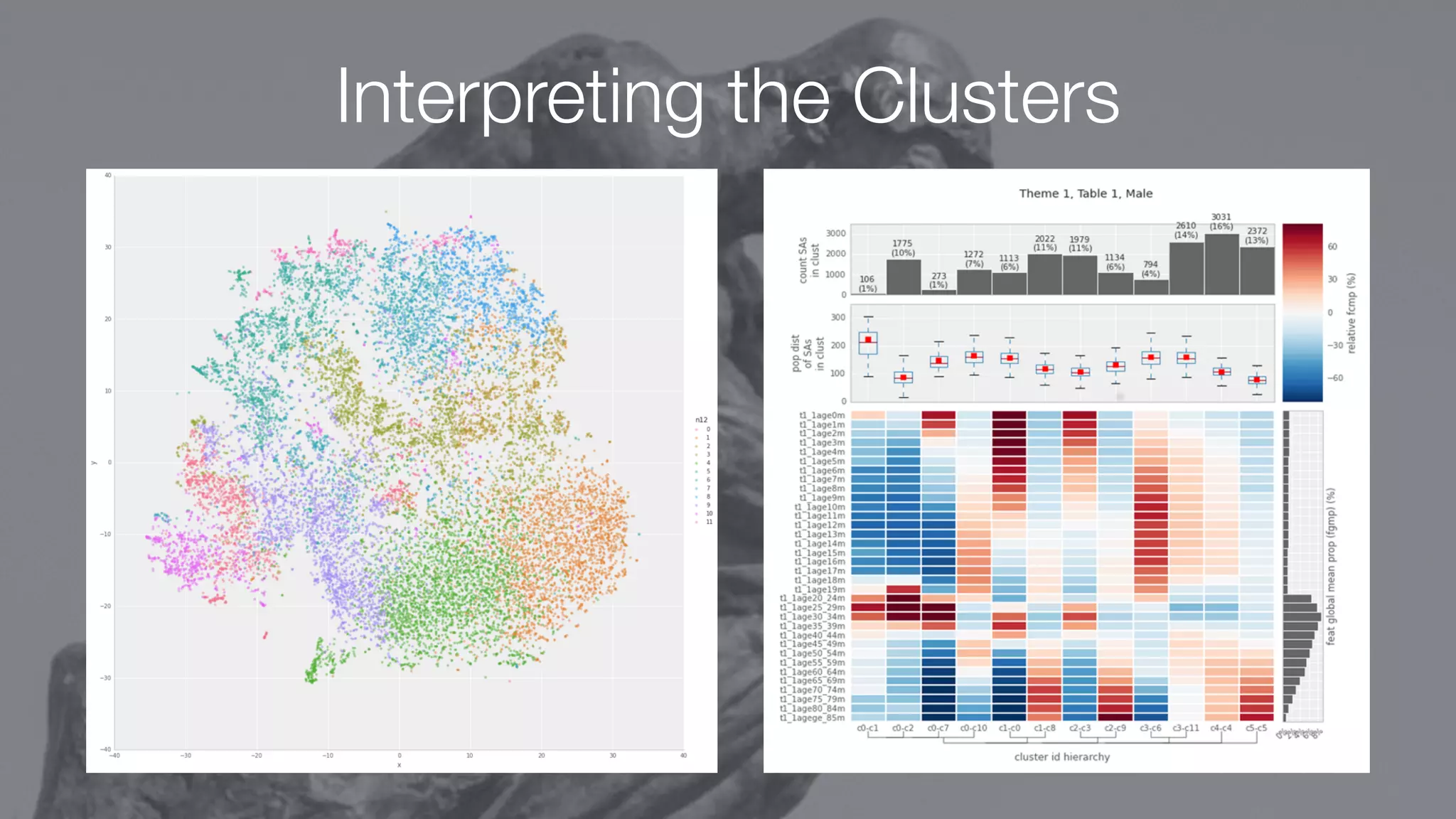
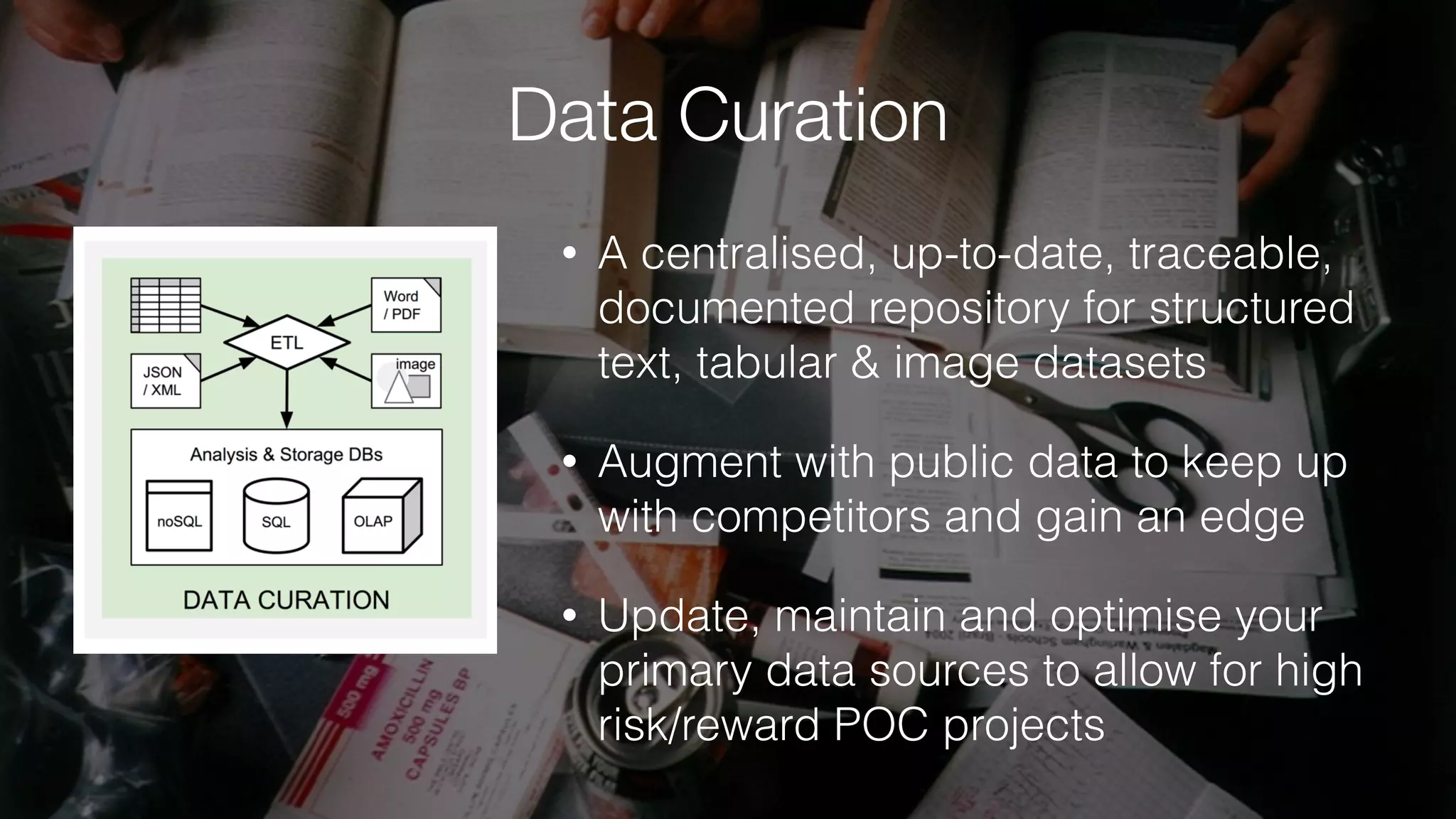
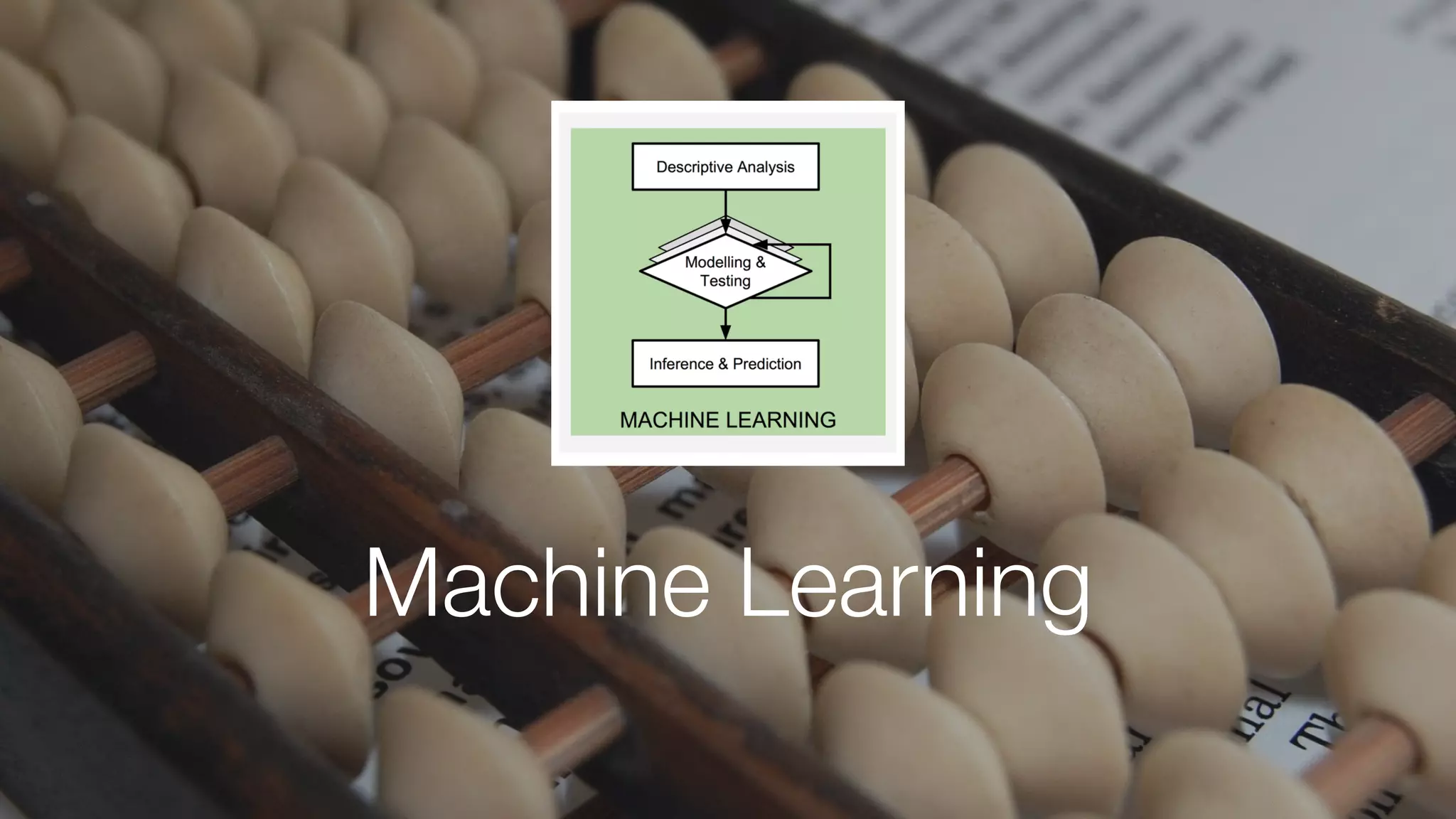
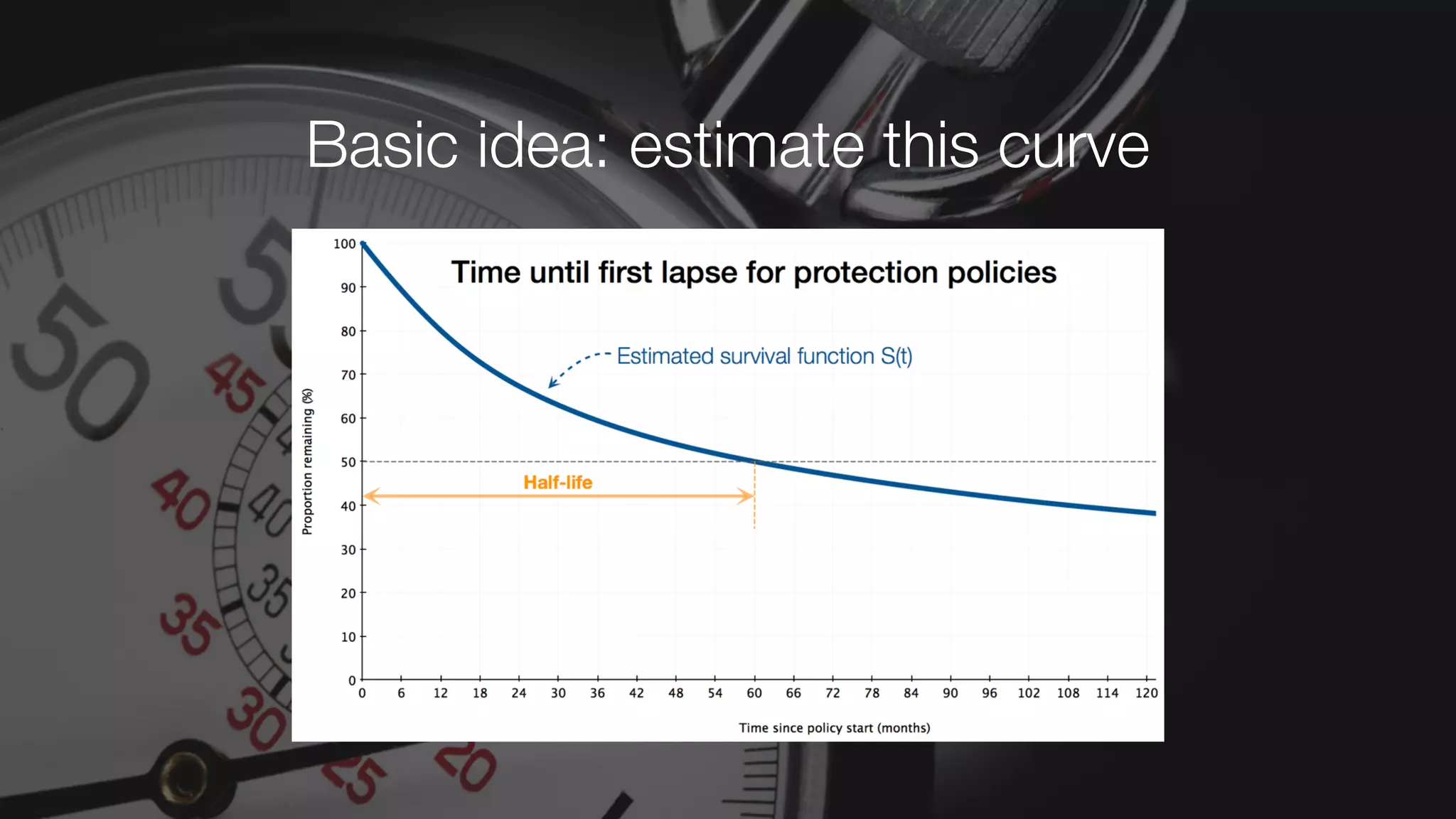
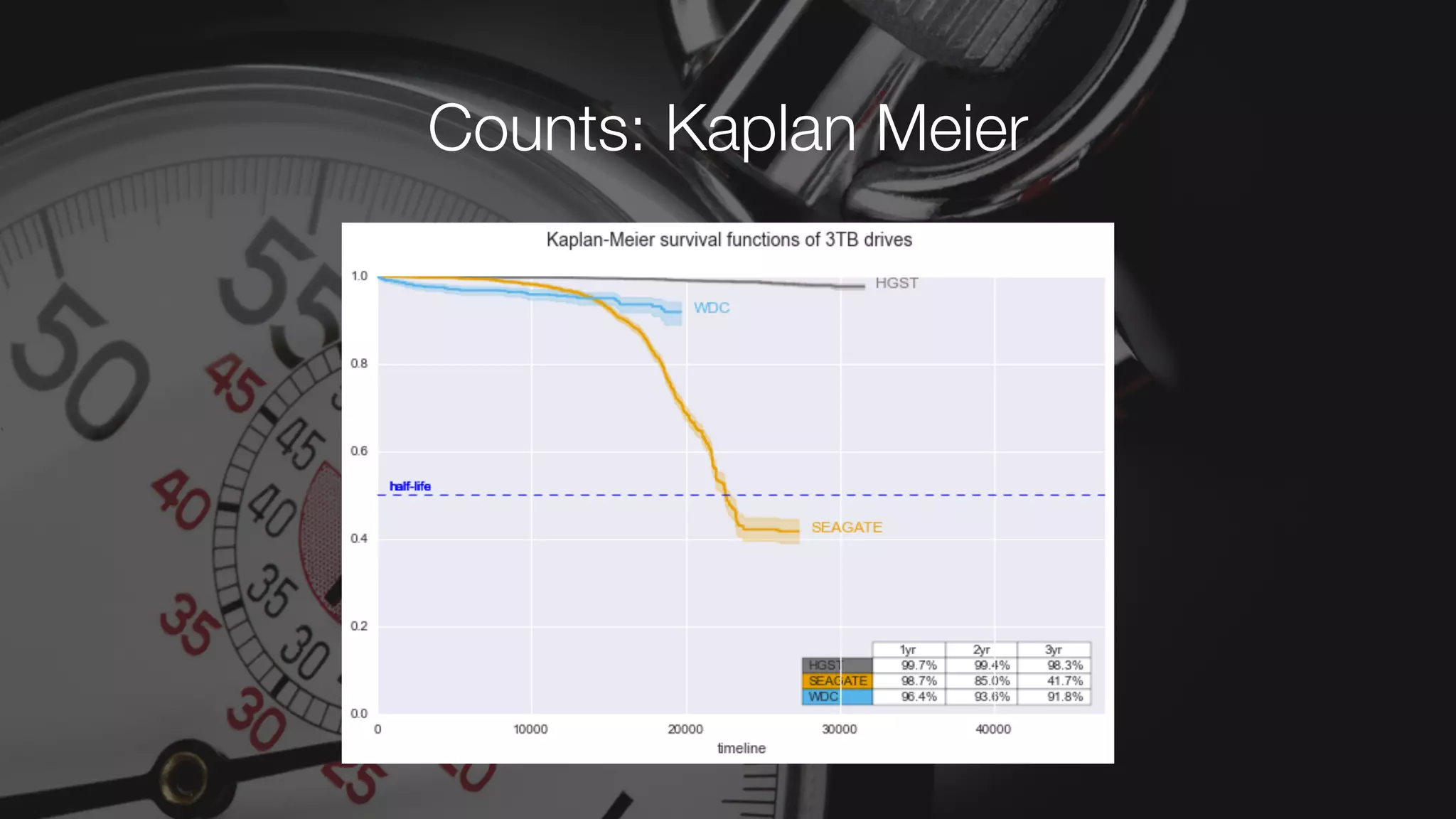
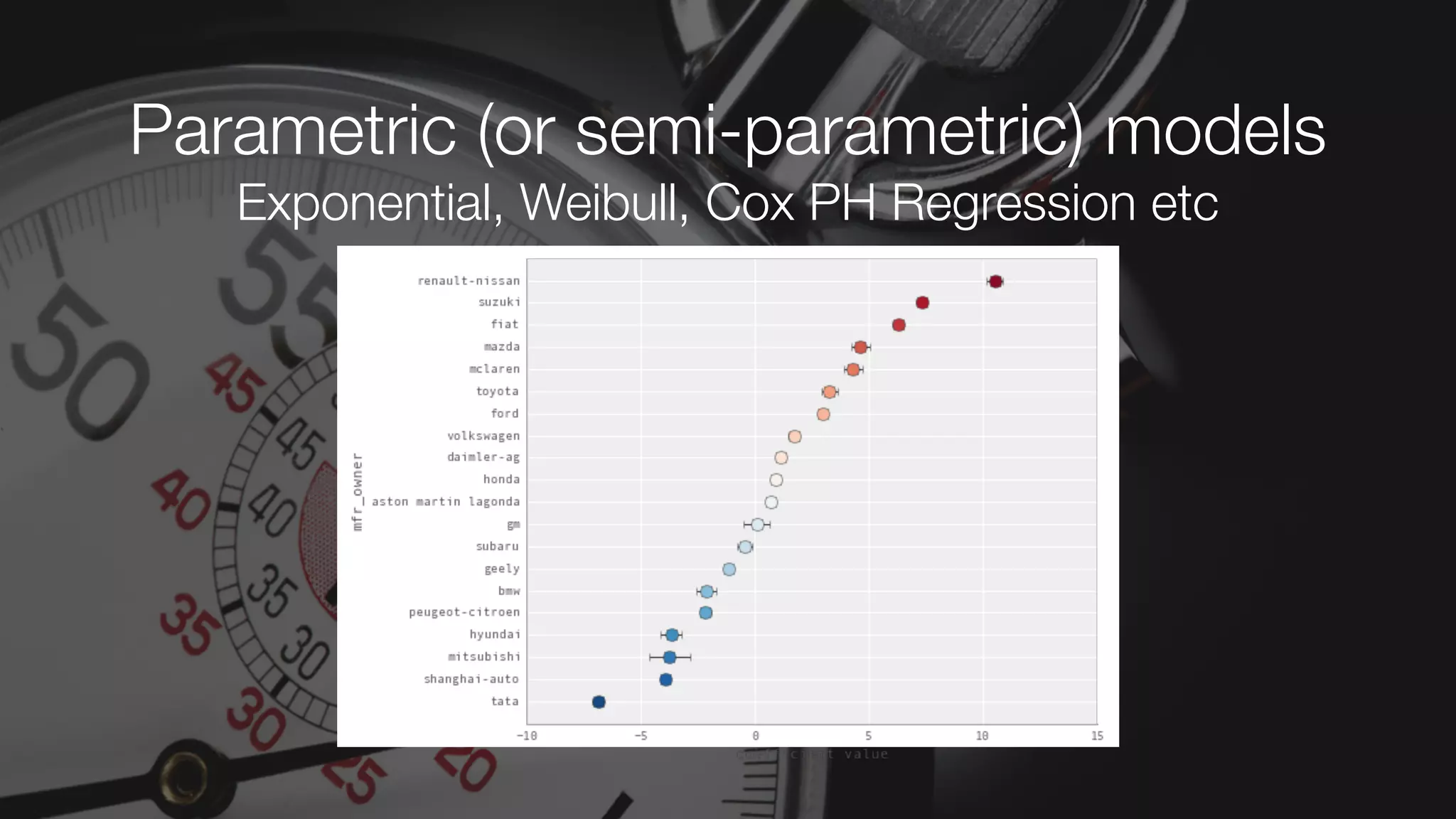
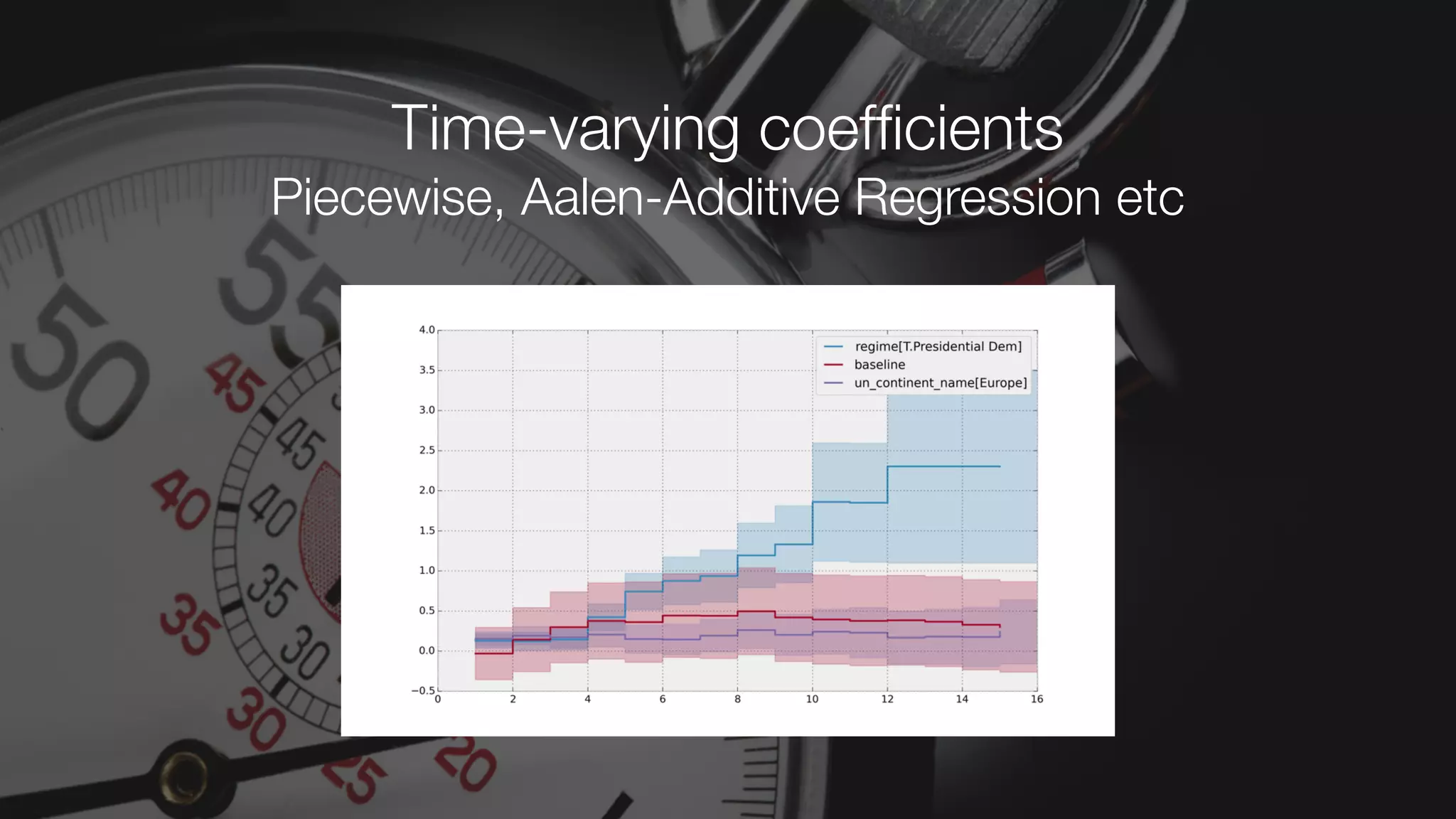
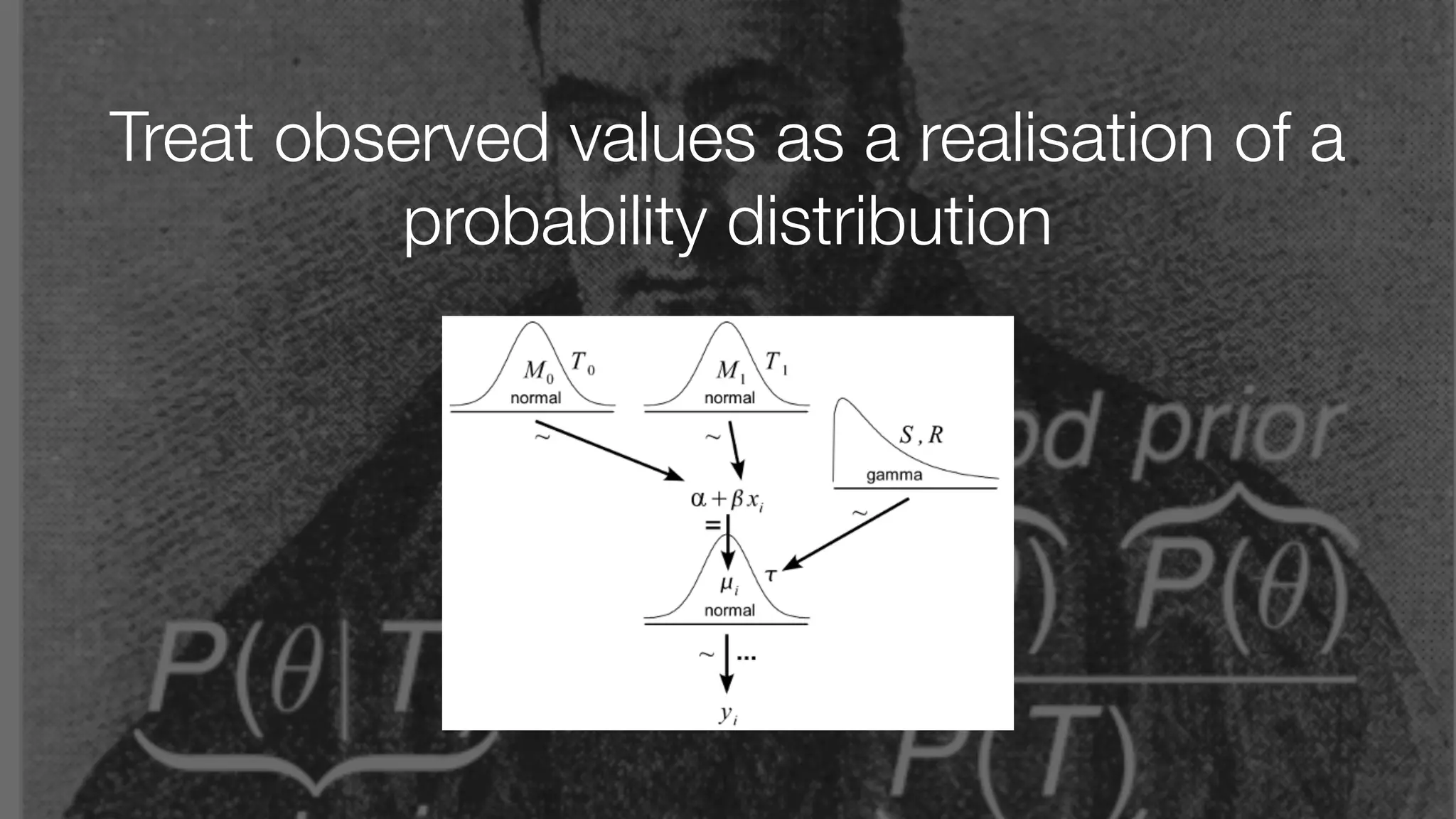
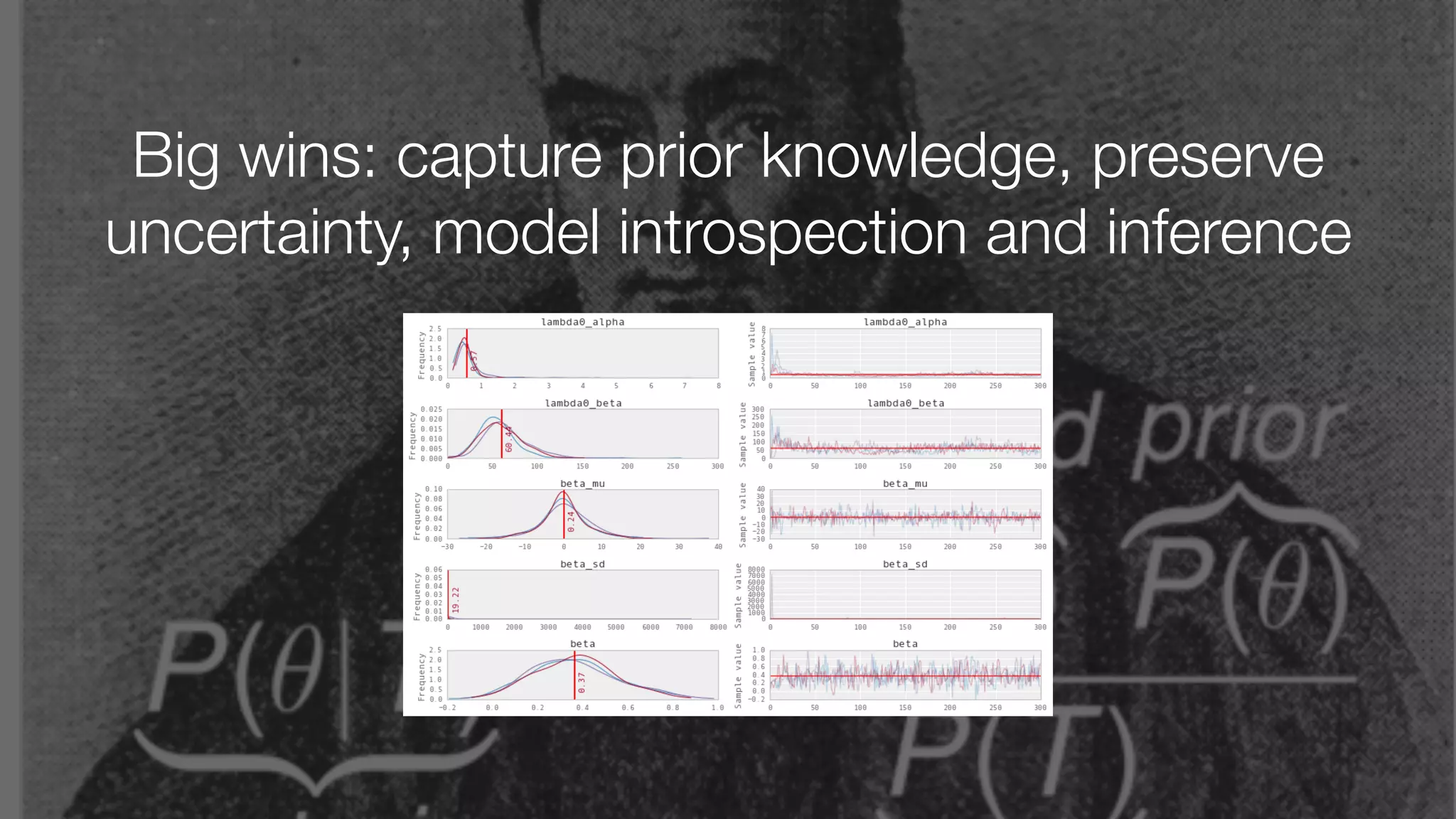
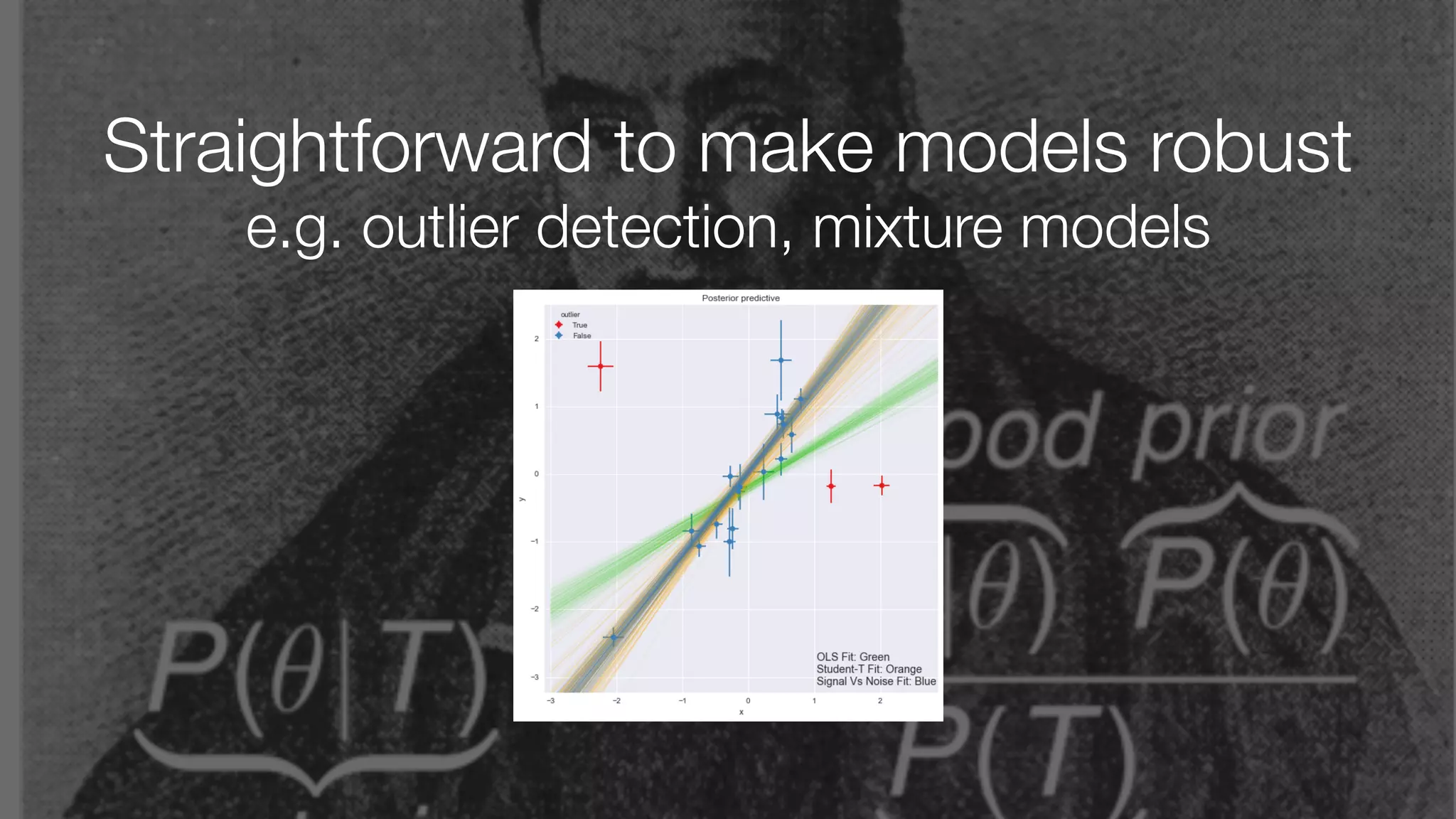
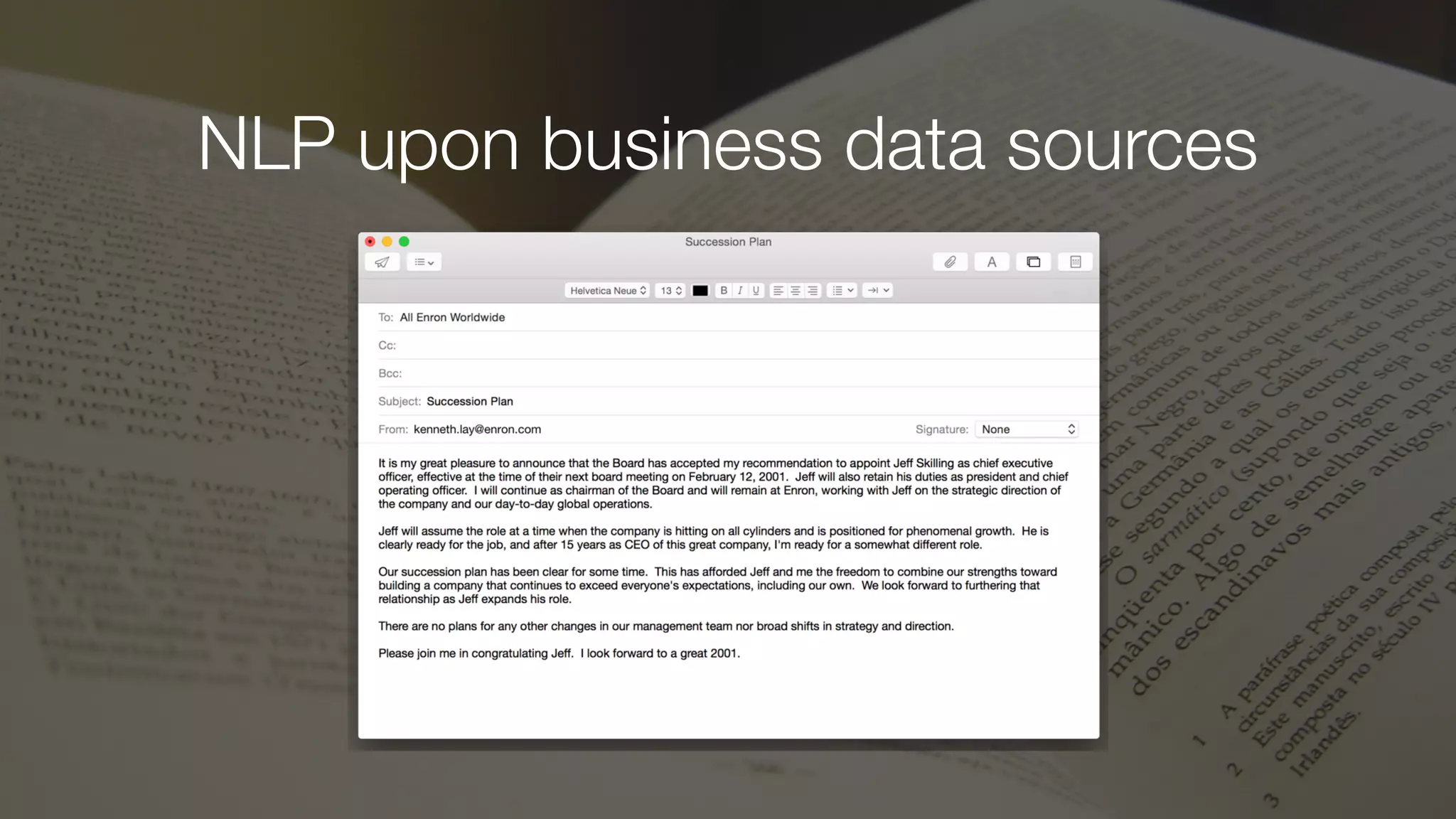
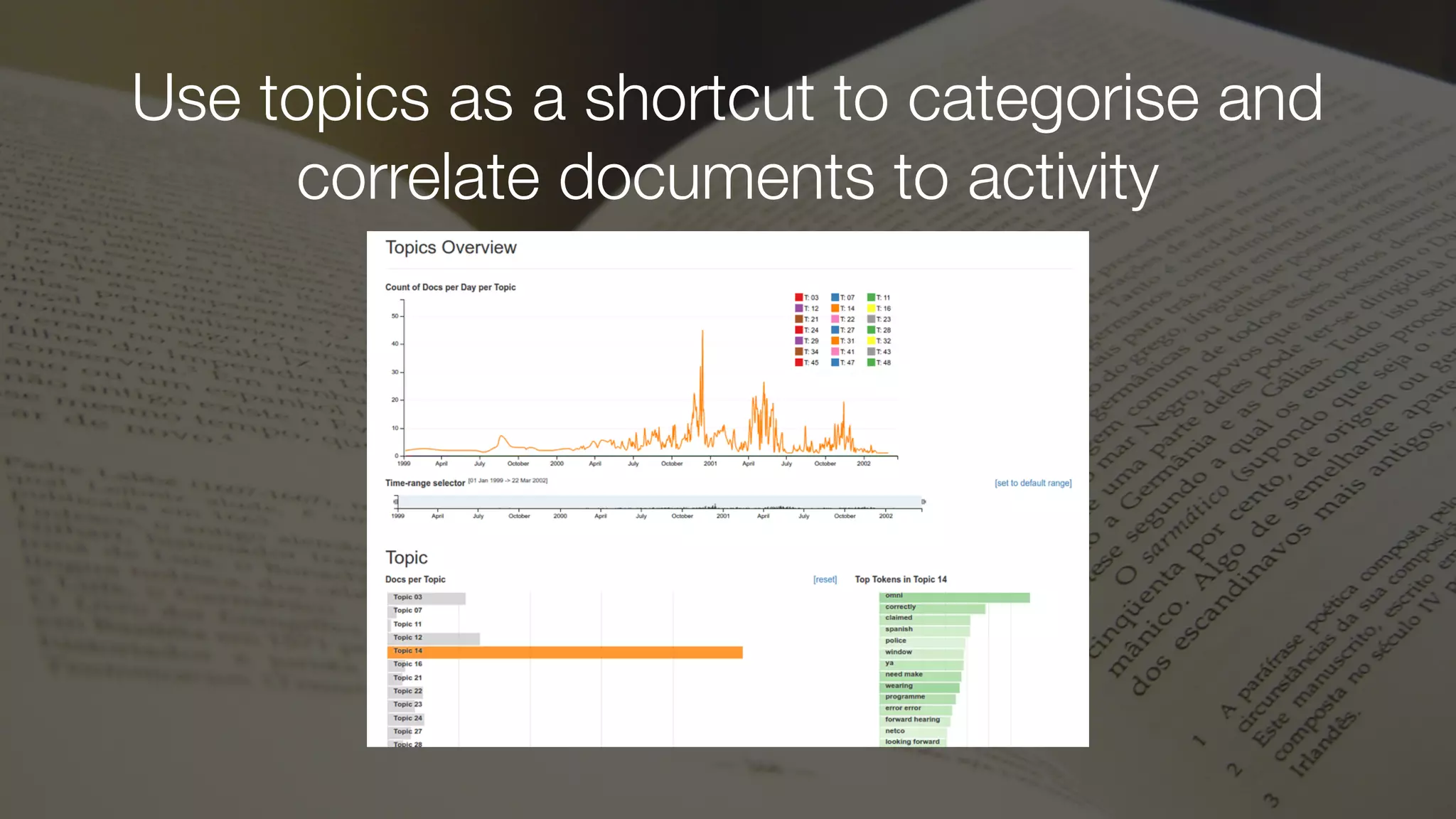
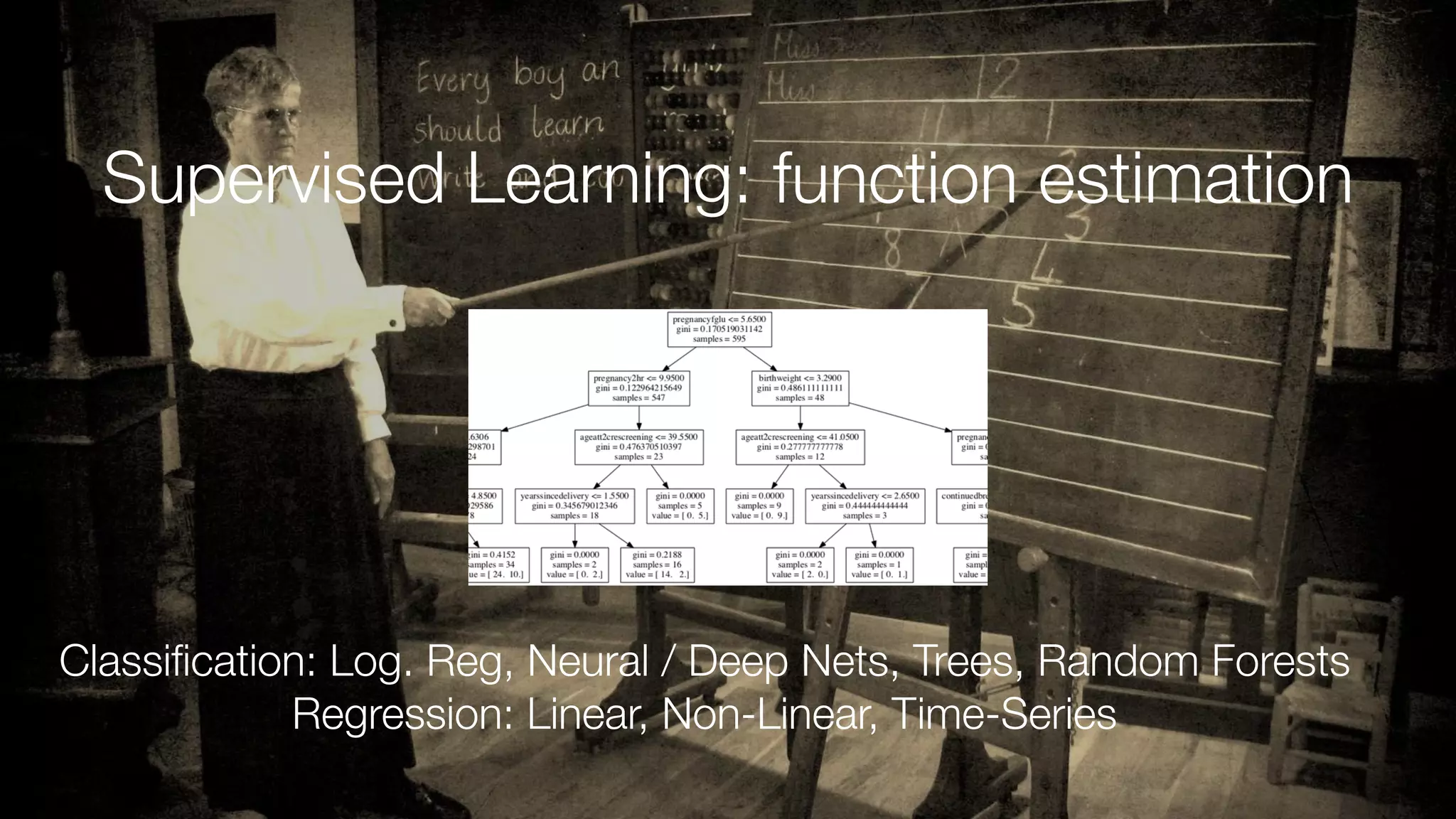
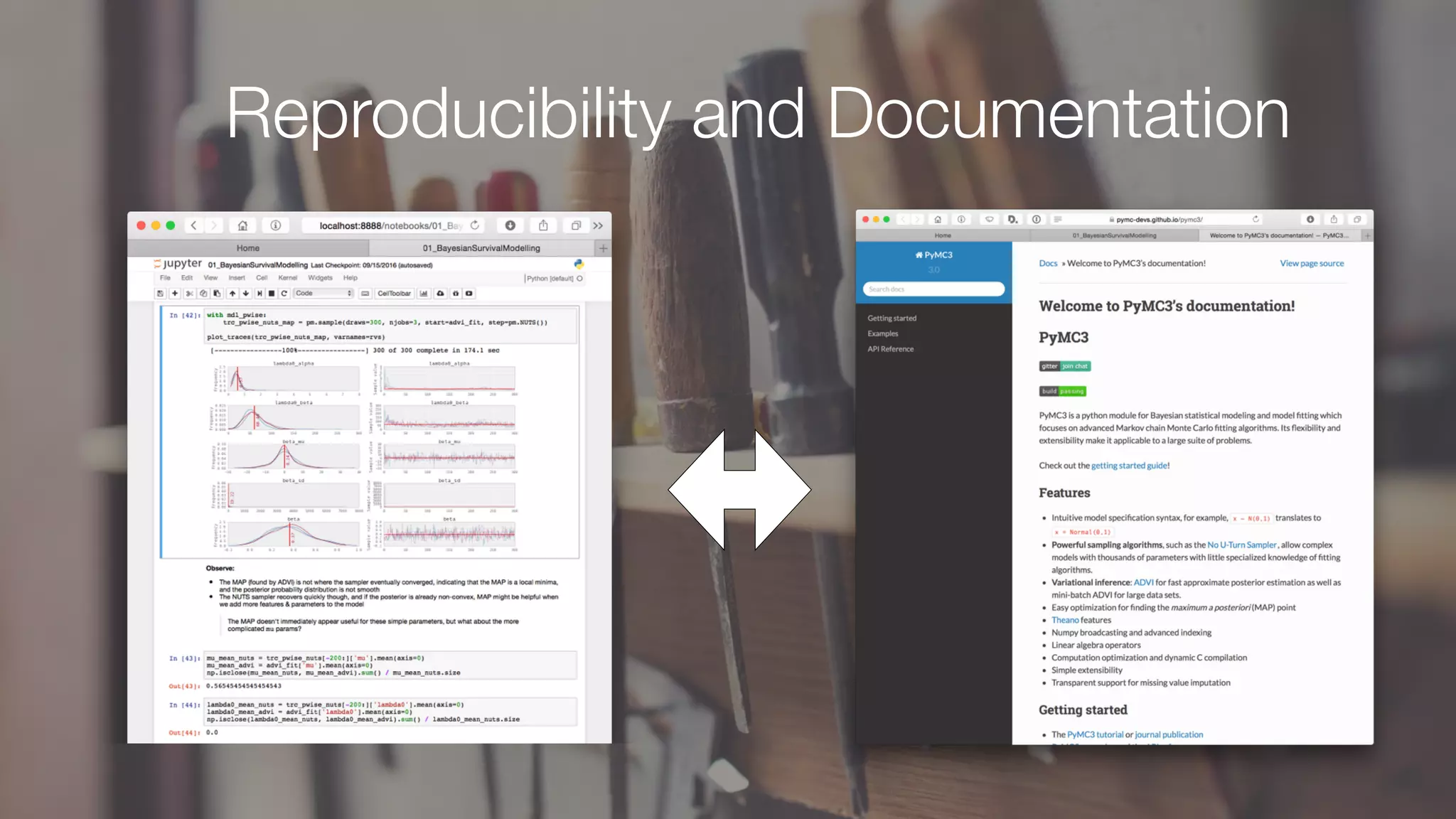
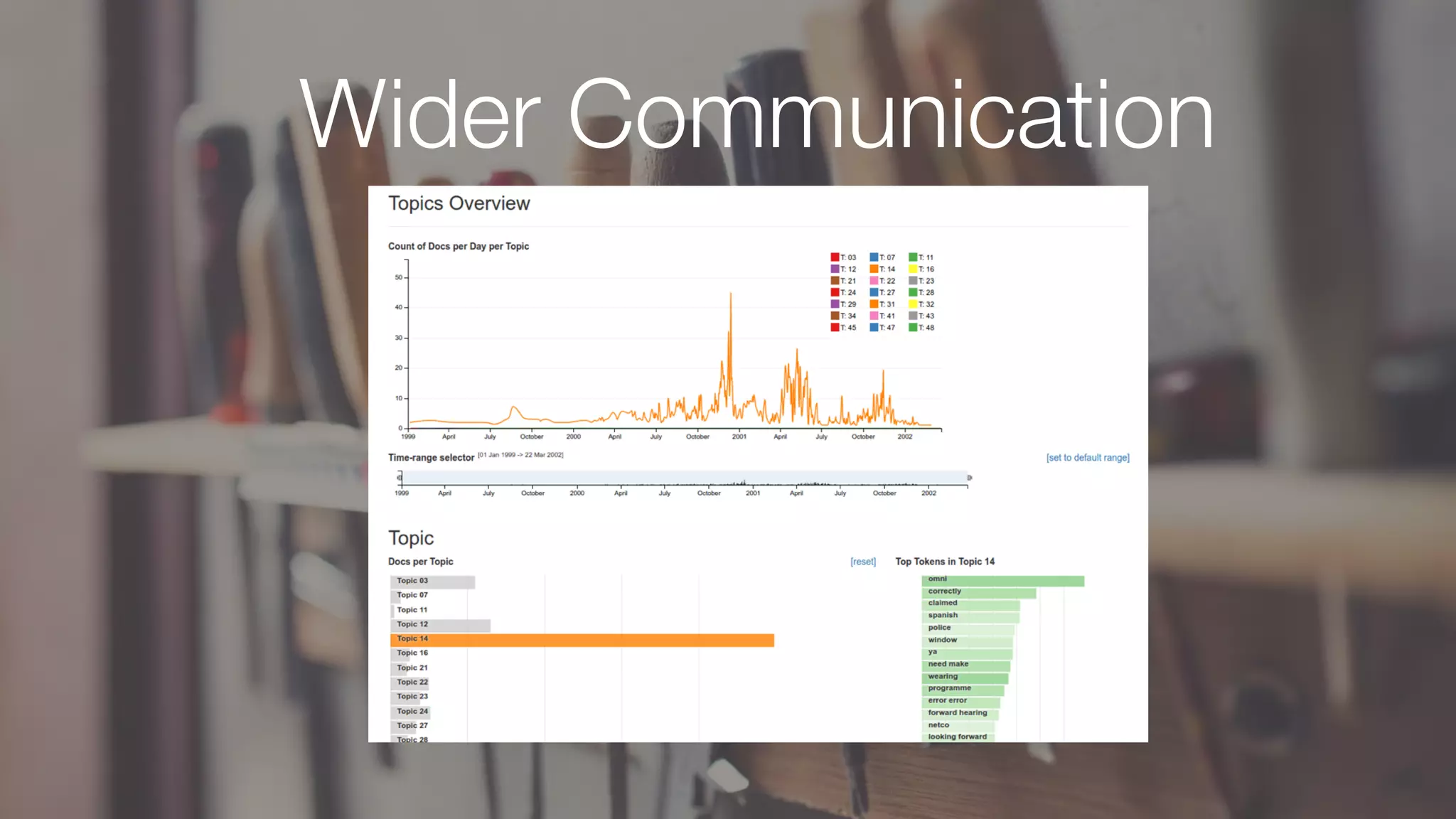
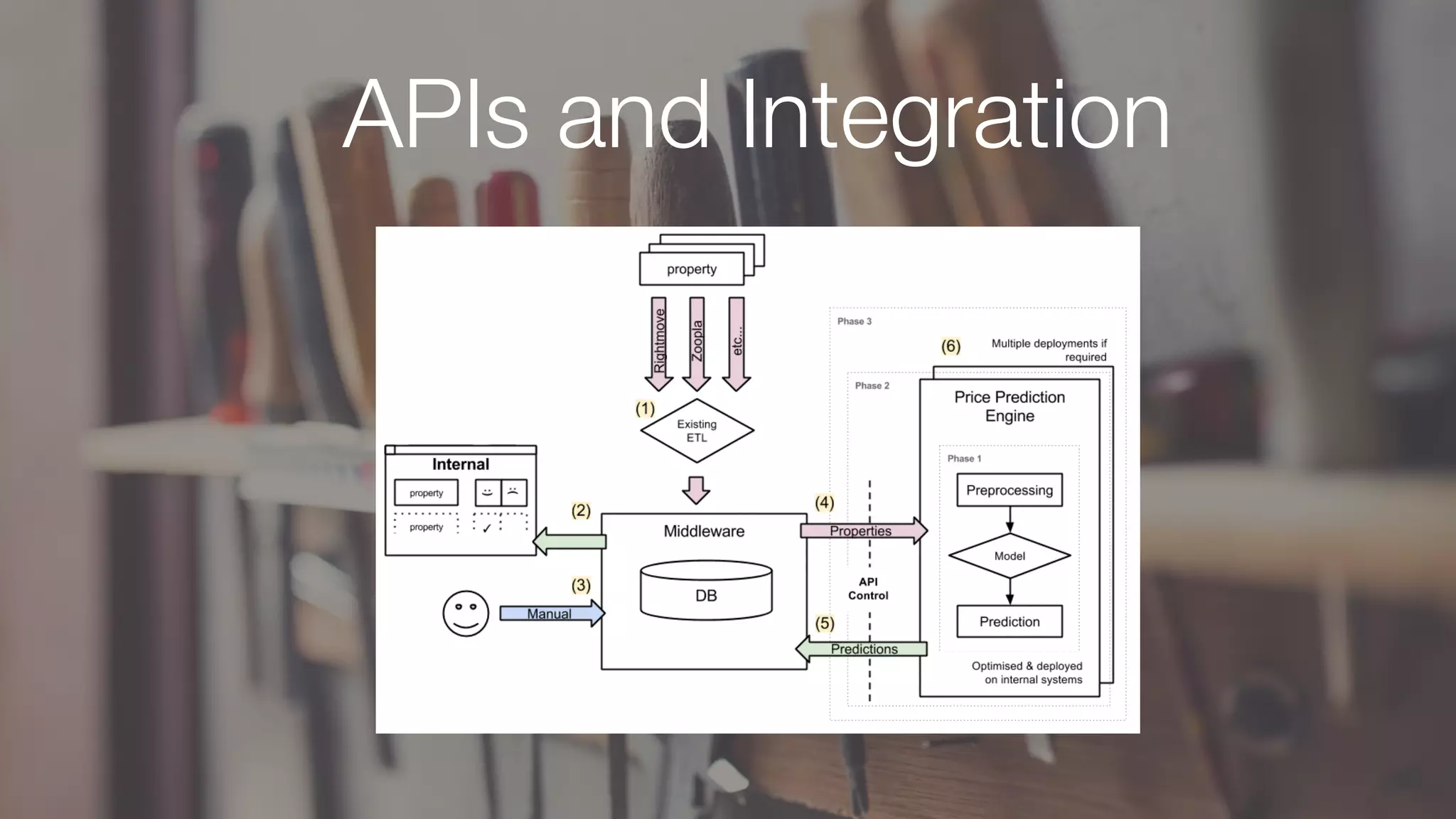
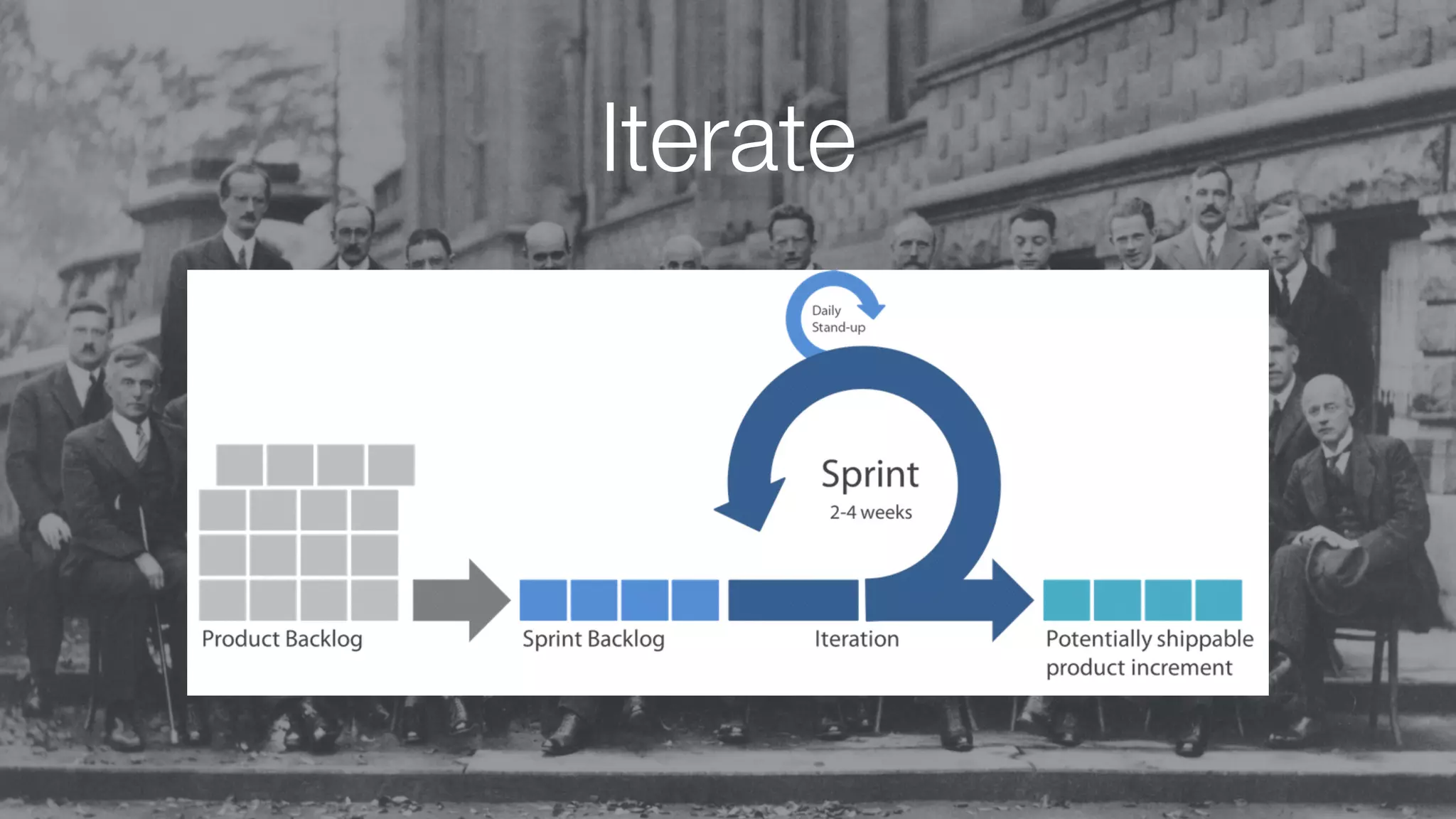
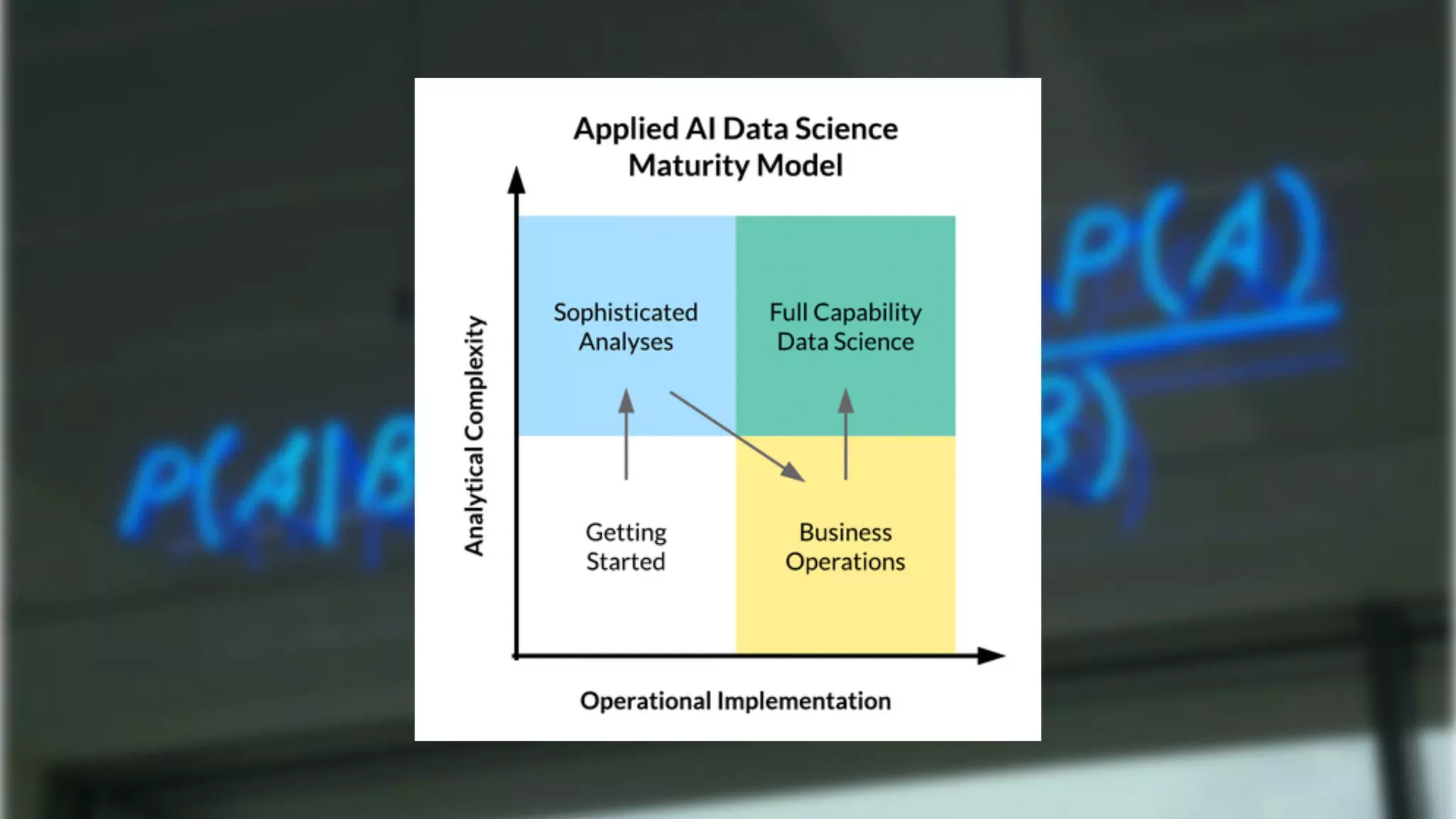
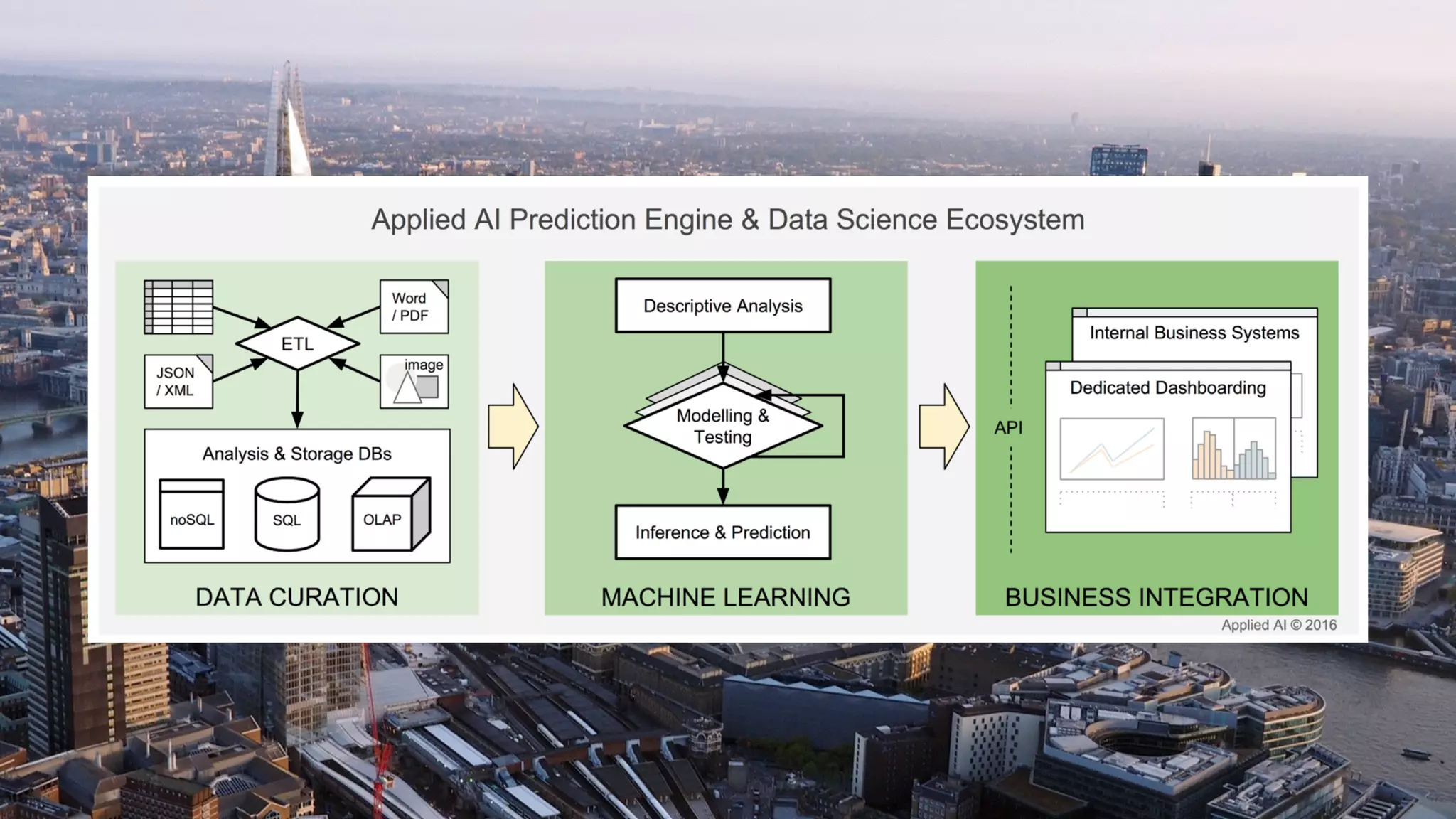
The document discusses demystifying data science by providing motivations, a maturity model, and an ecosystem model with practical examples and advice. It explains data science concepts like data curation, machine learning, and business integration. Examples are given of using data science for time-to-event modeling, topic modeling, and anomaly detection. The importance of communication, iteration, and understanding models as approximations is emphasized.