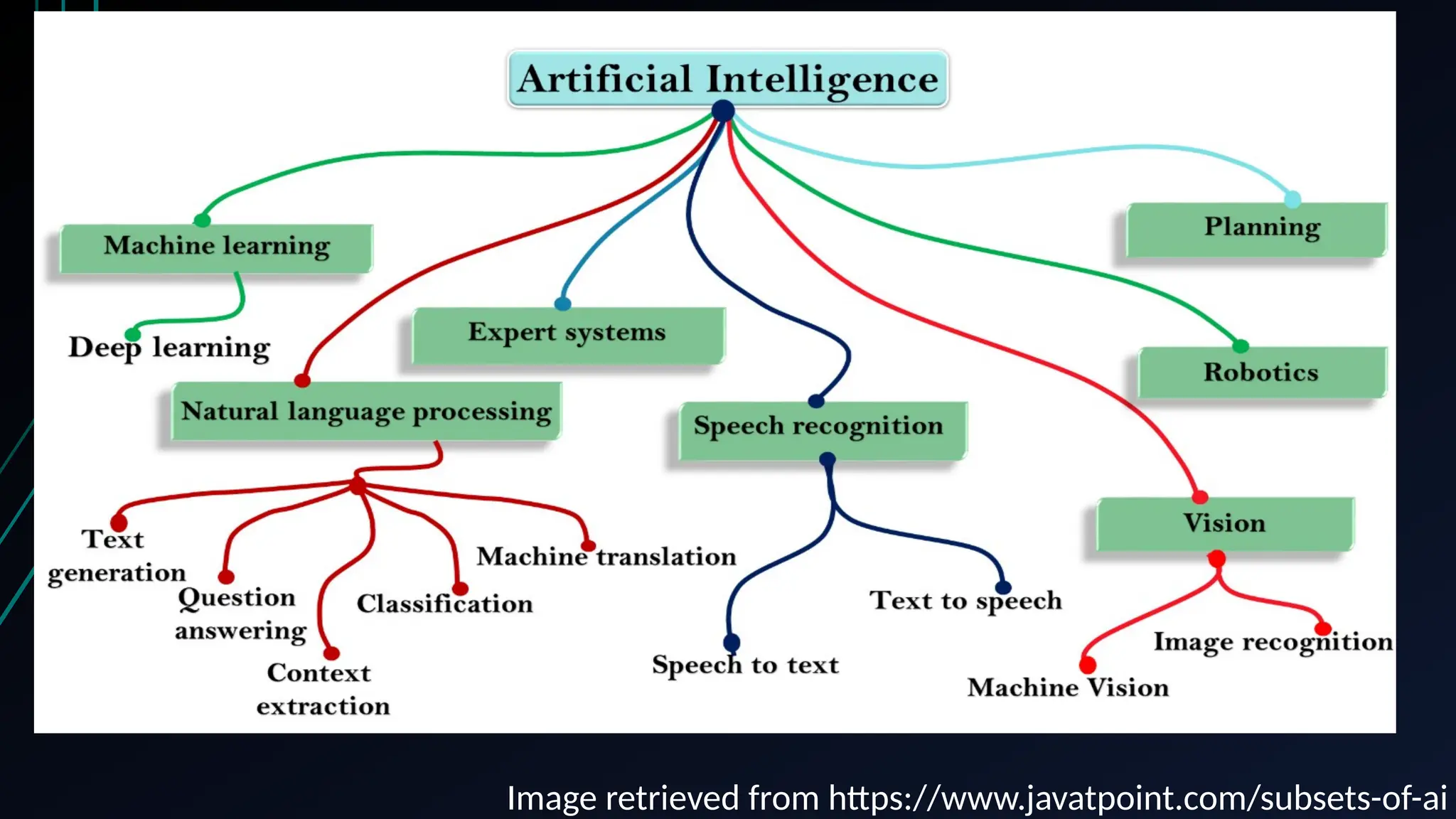
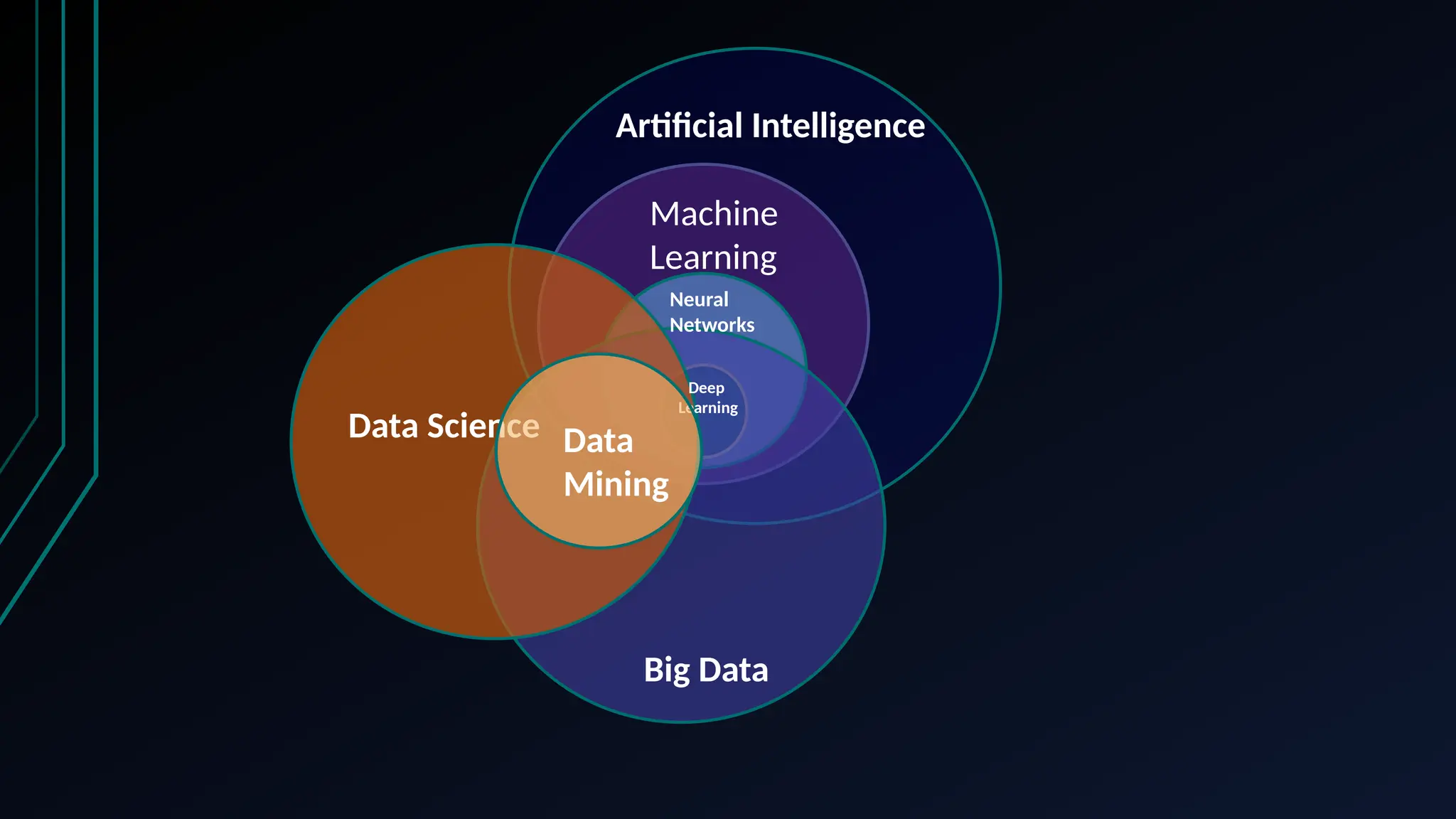
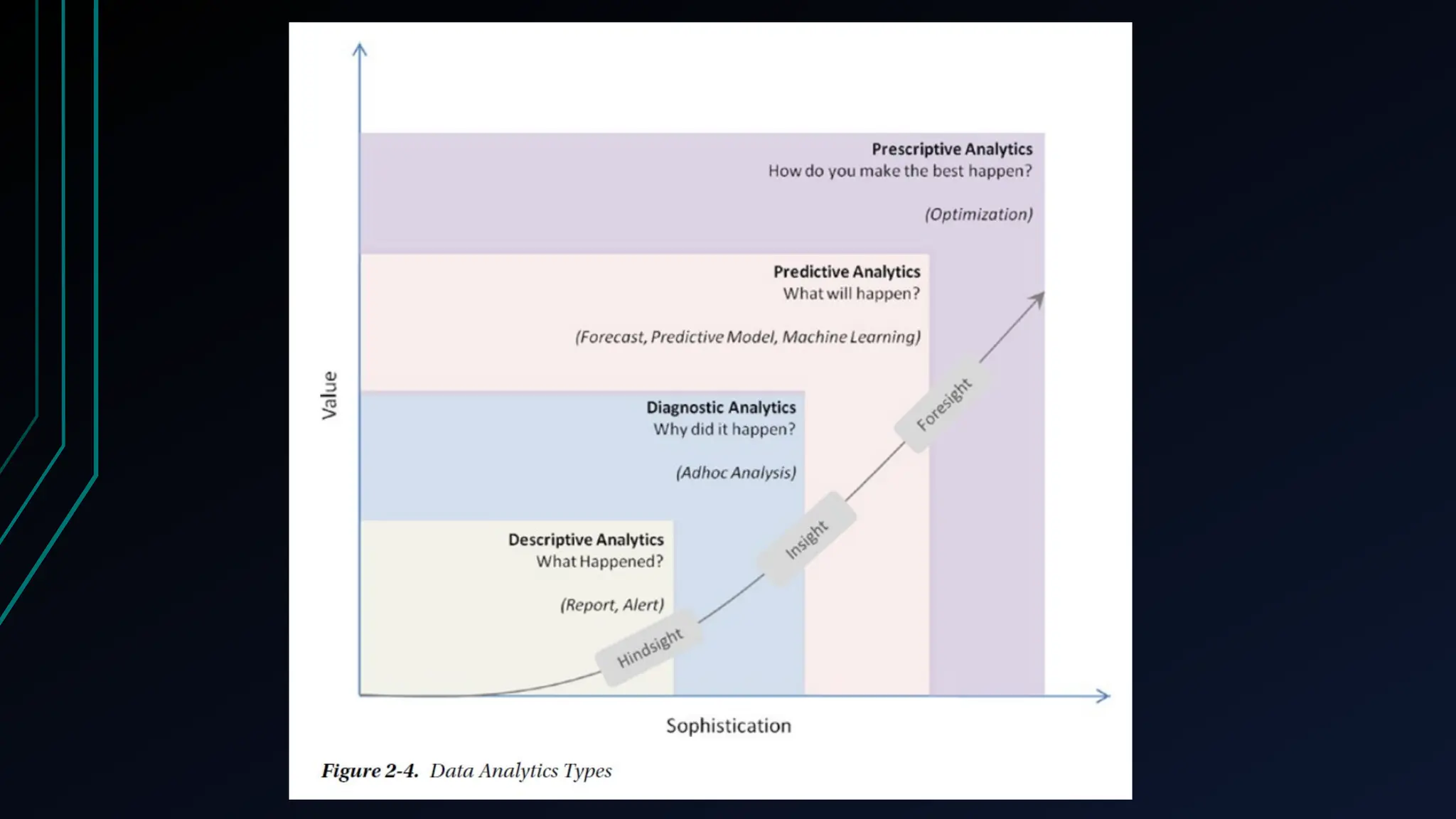
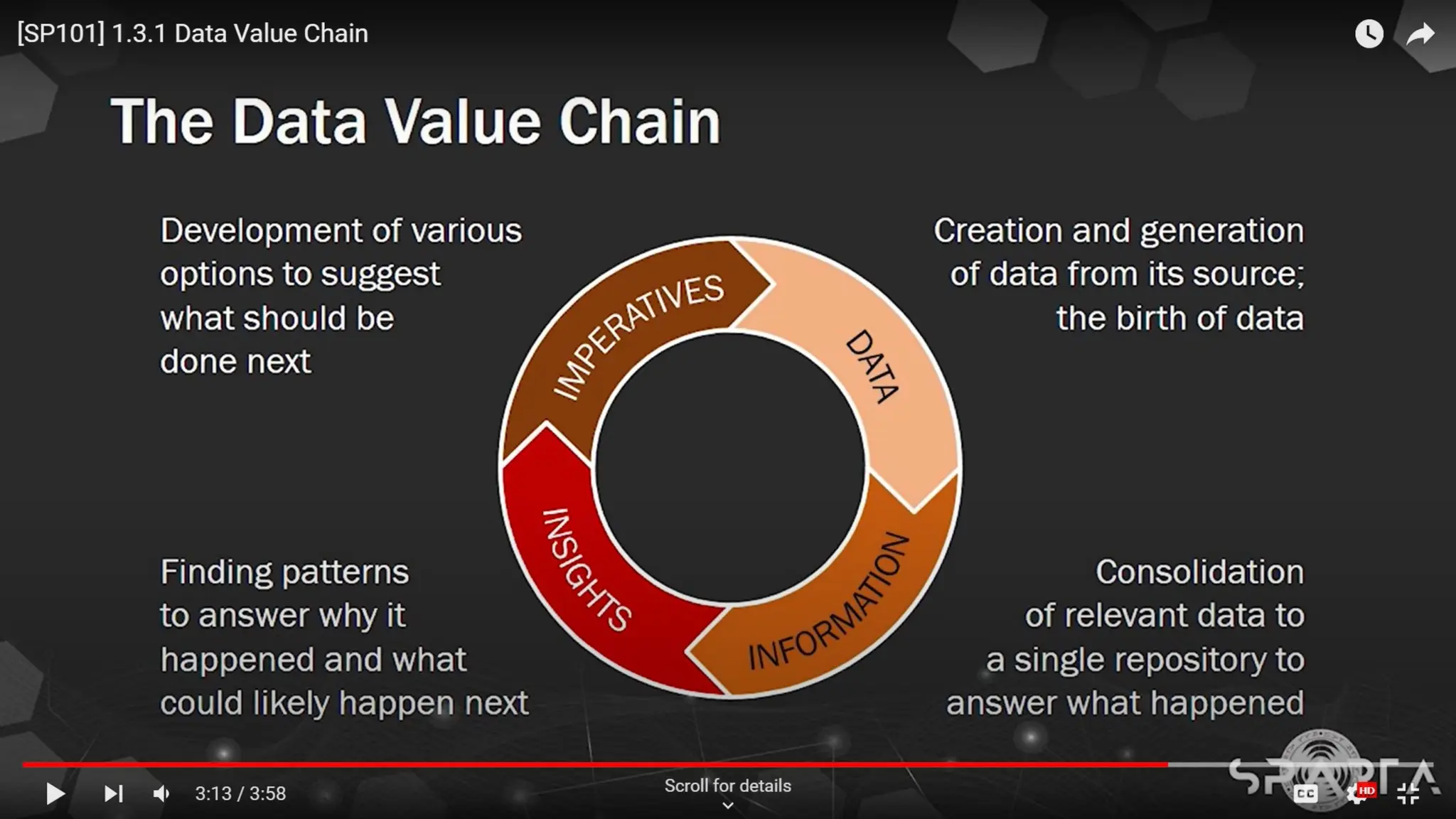
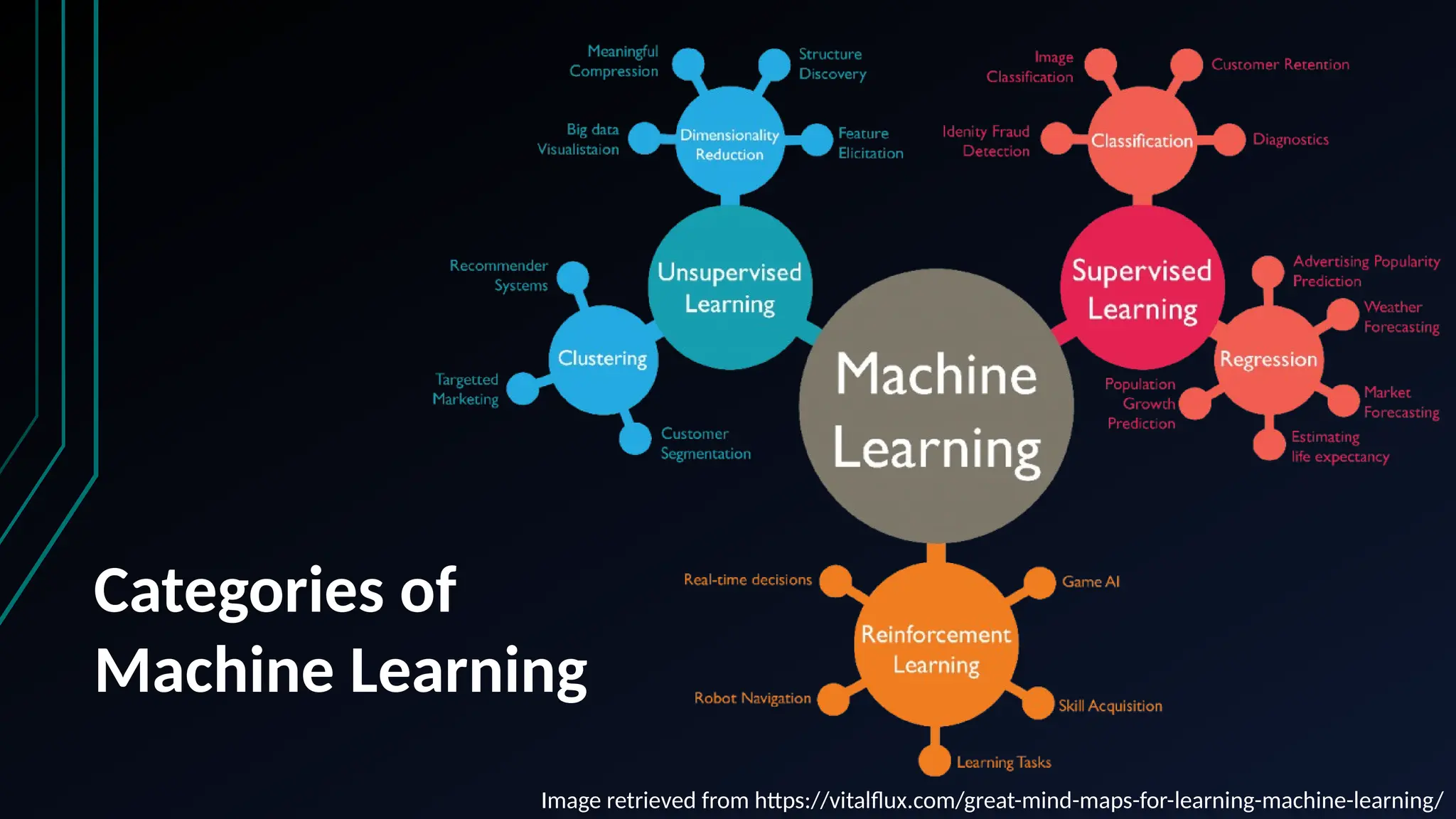
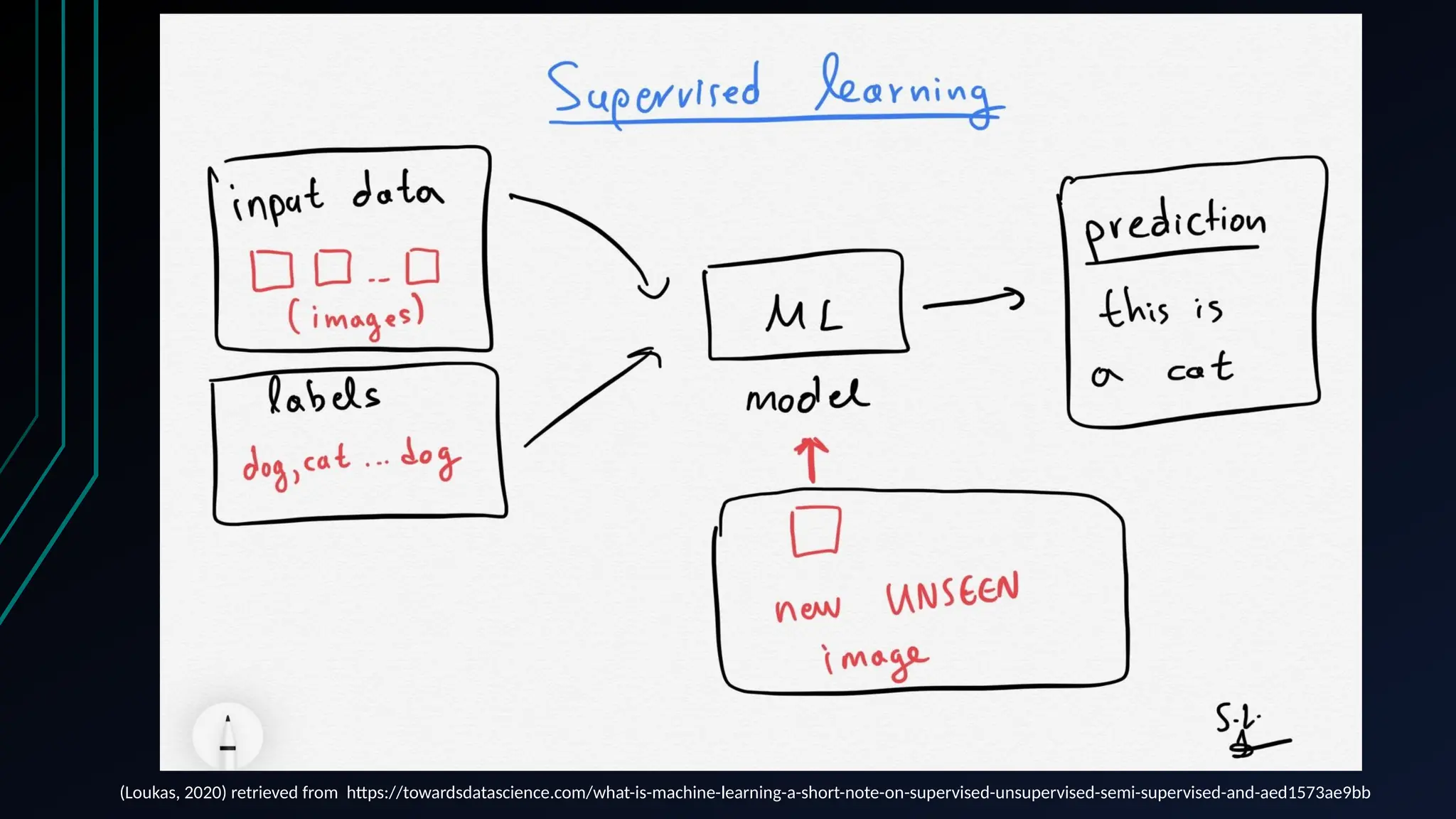
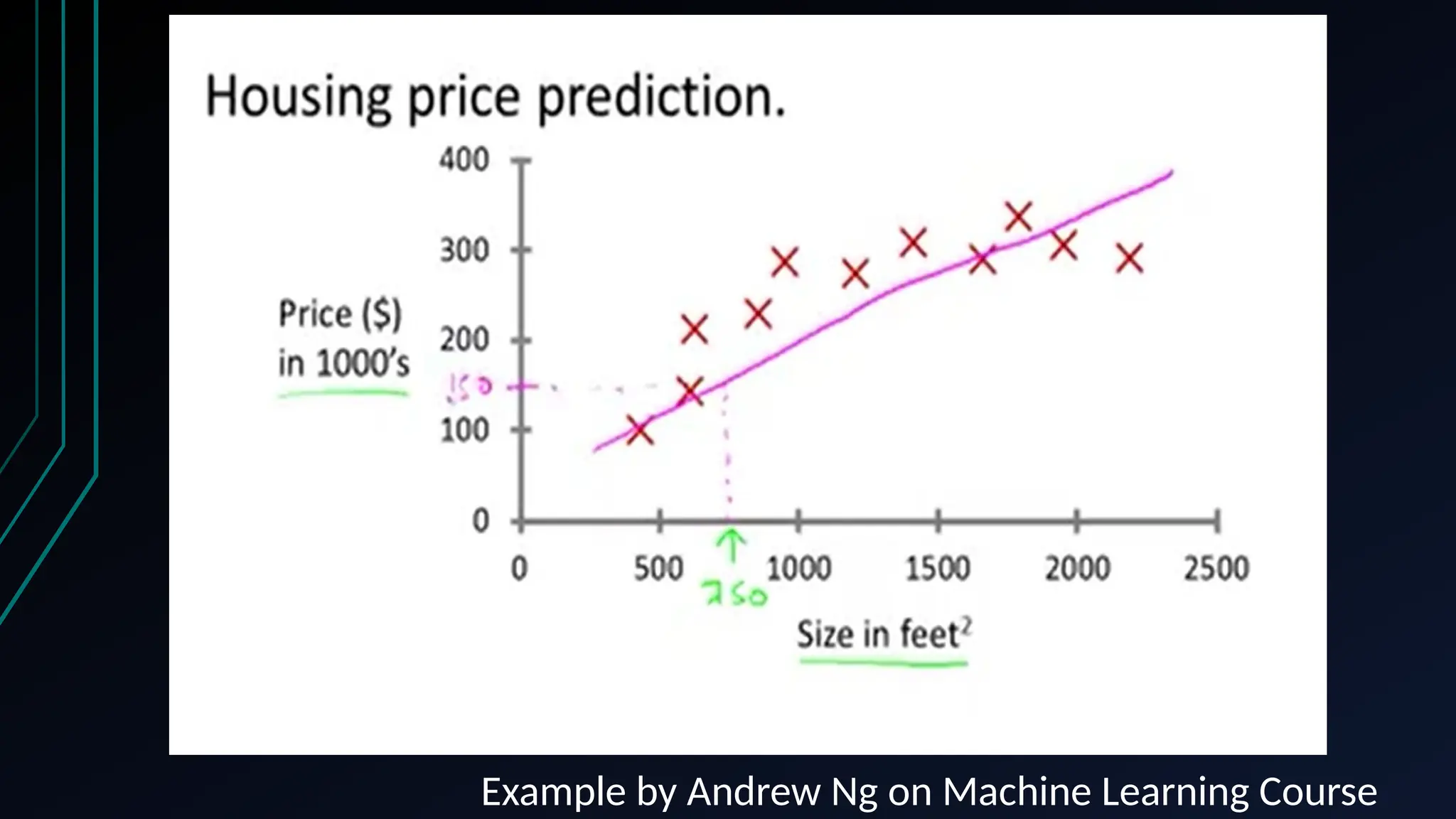
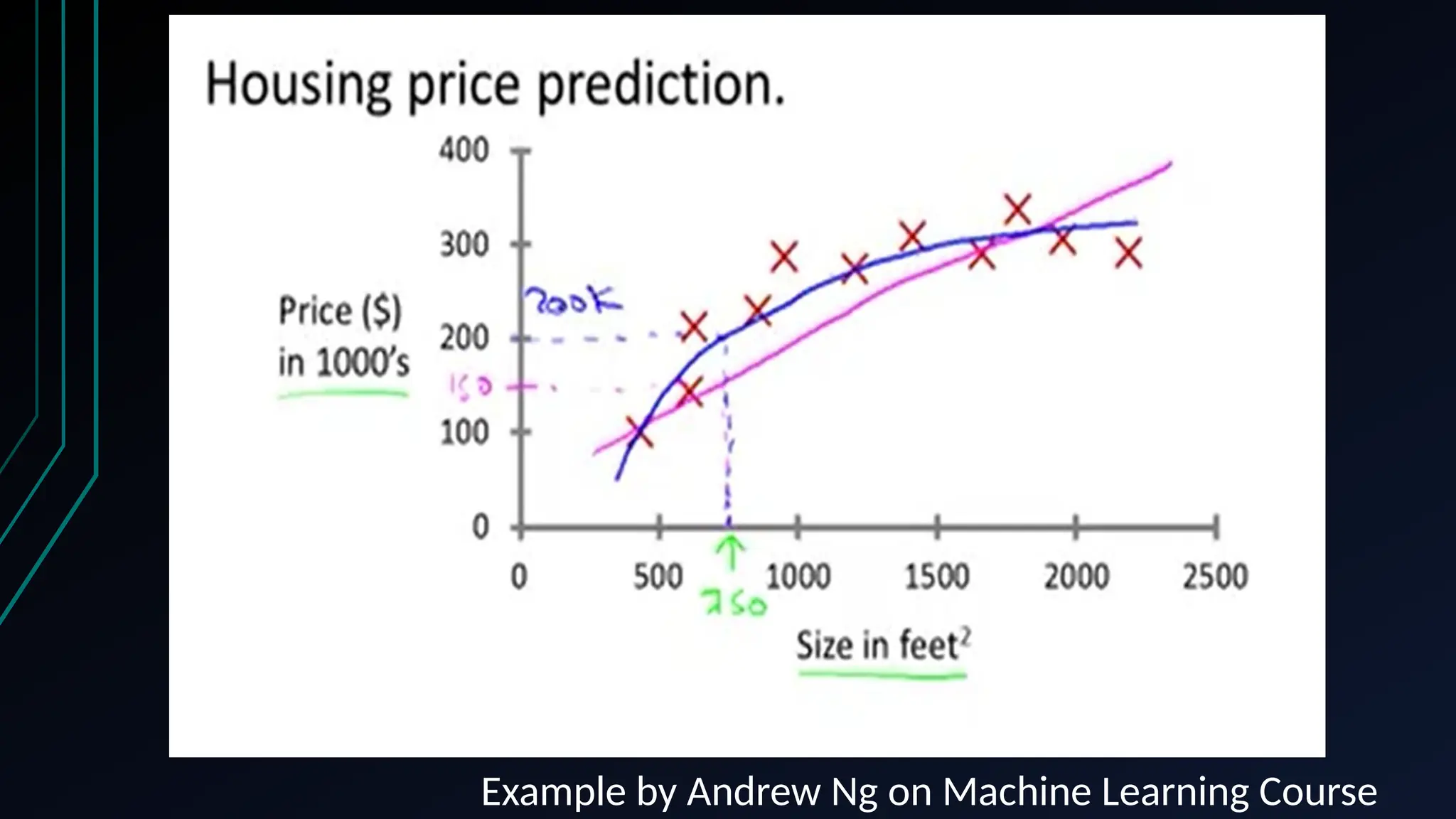
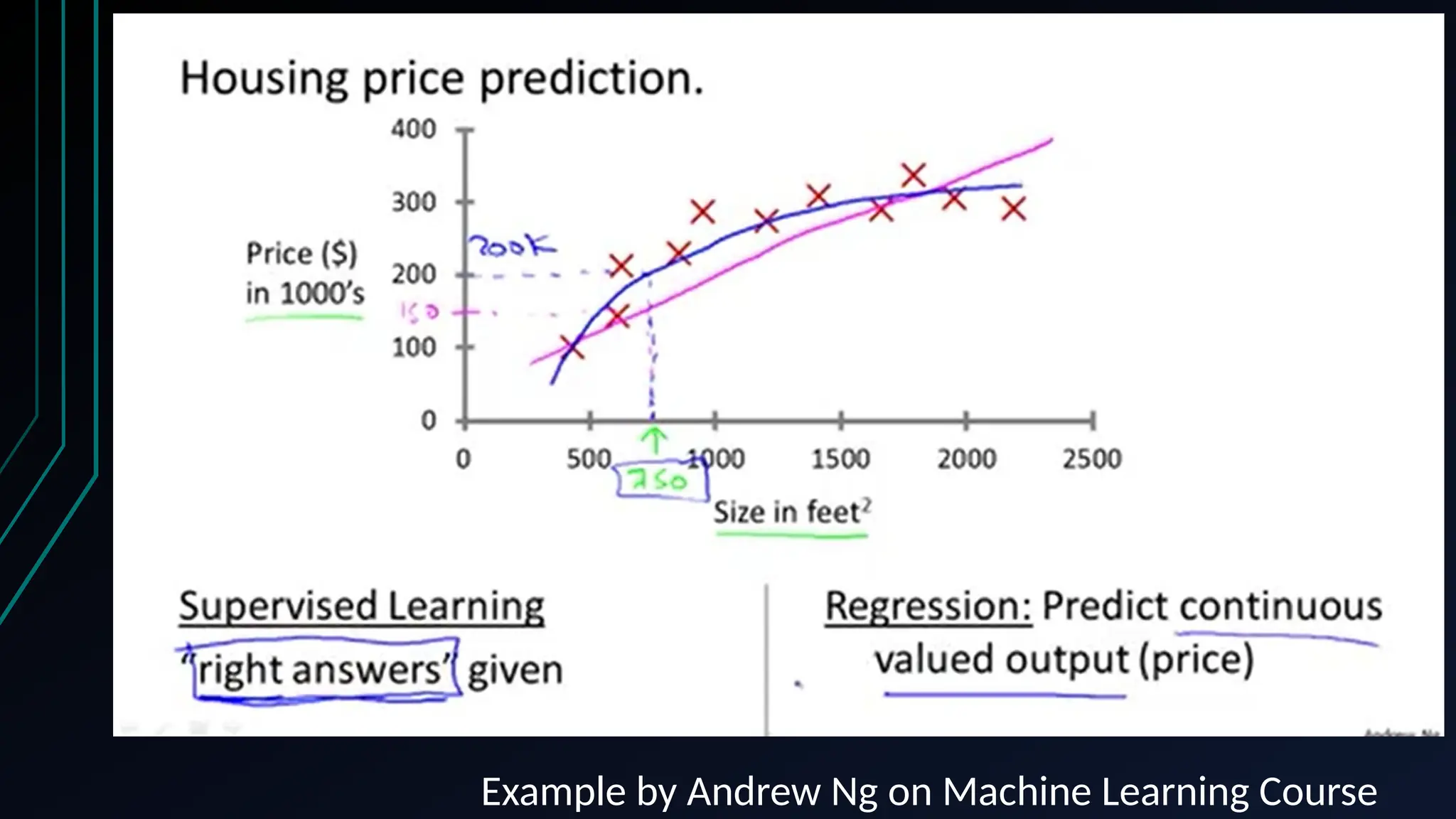
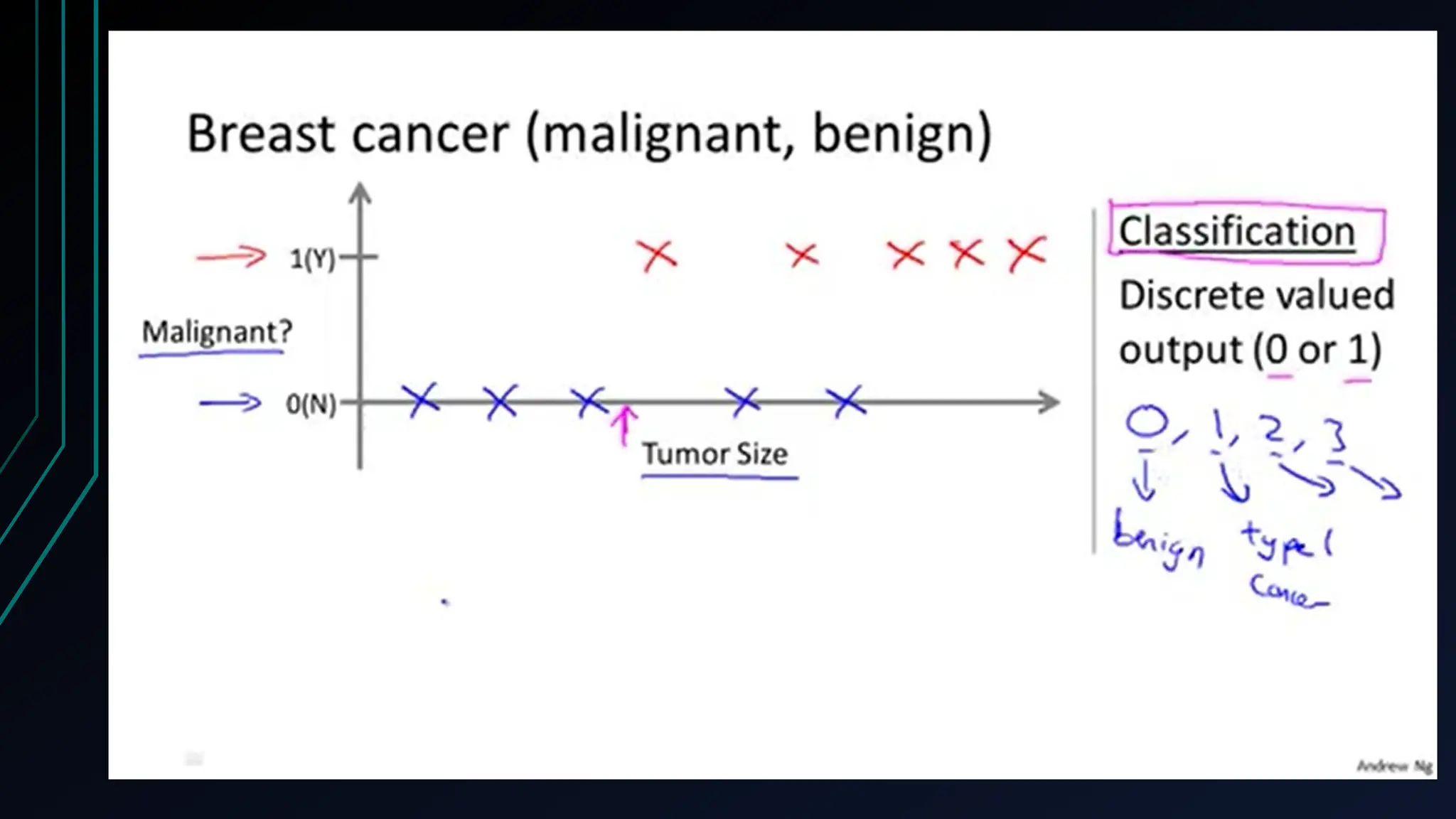
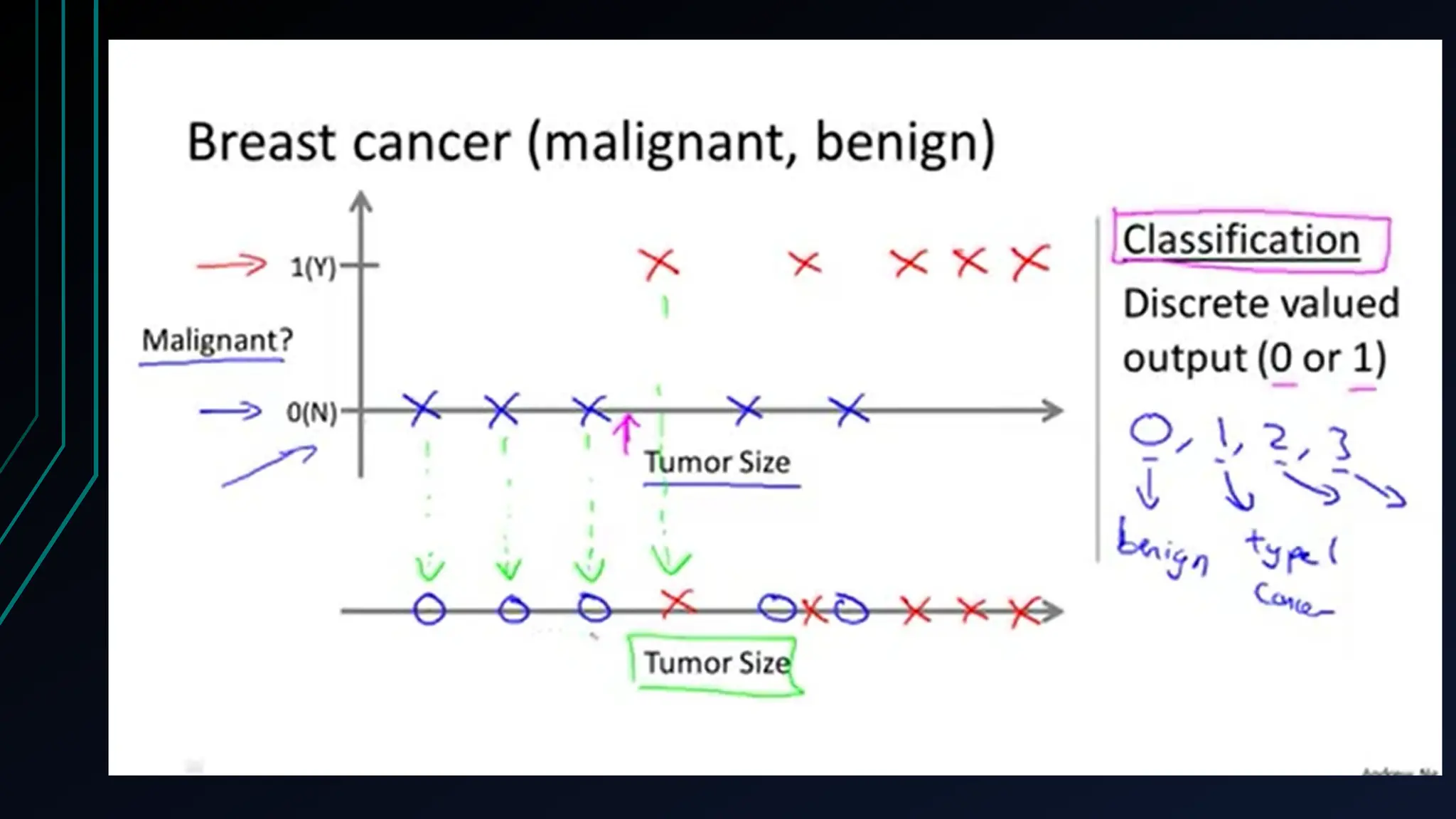
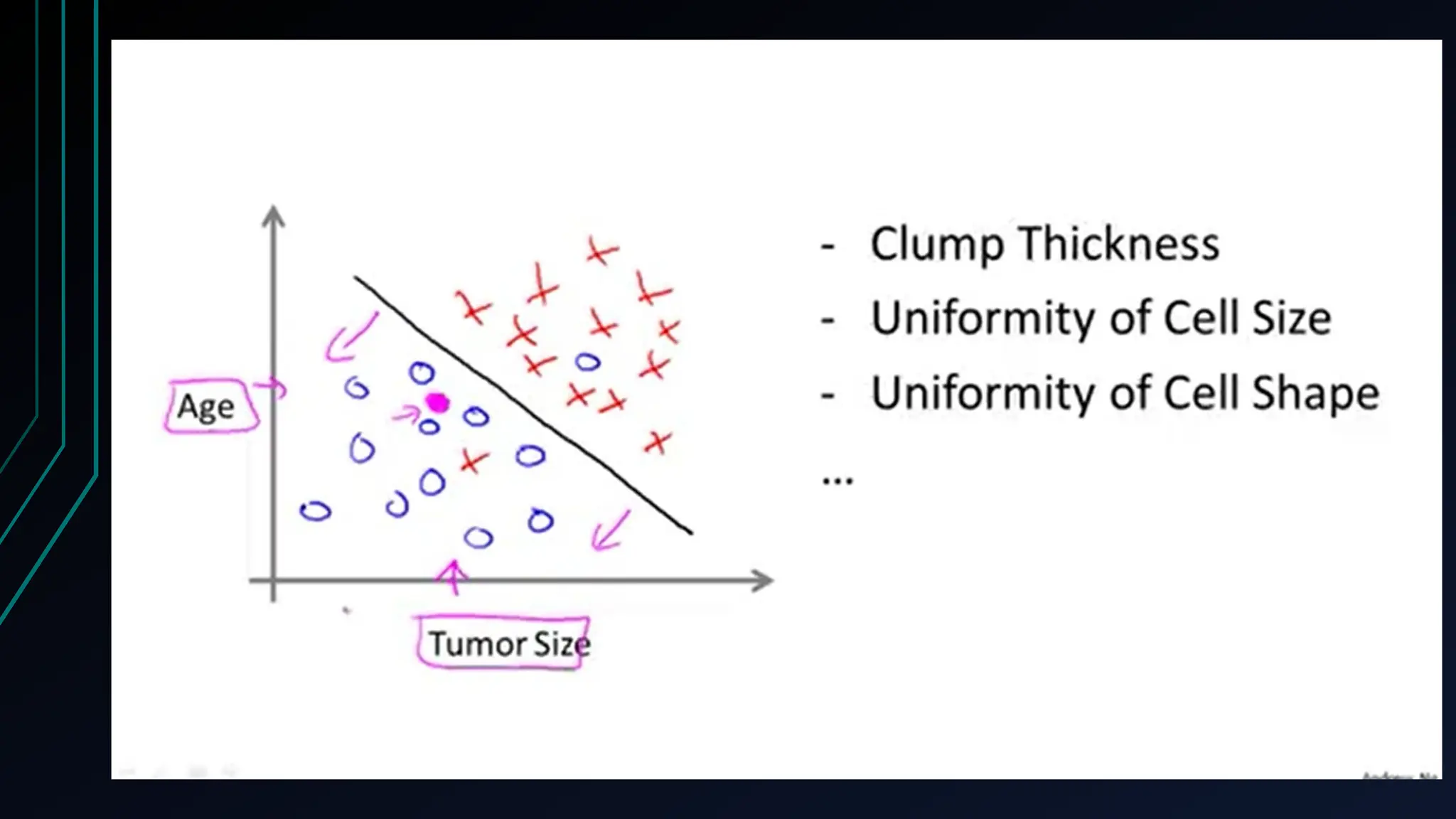
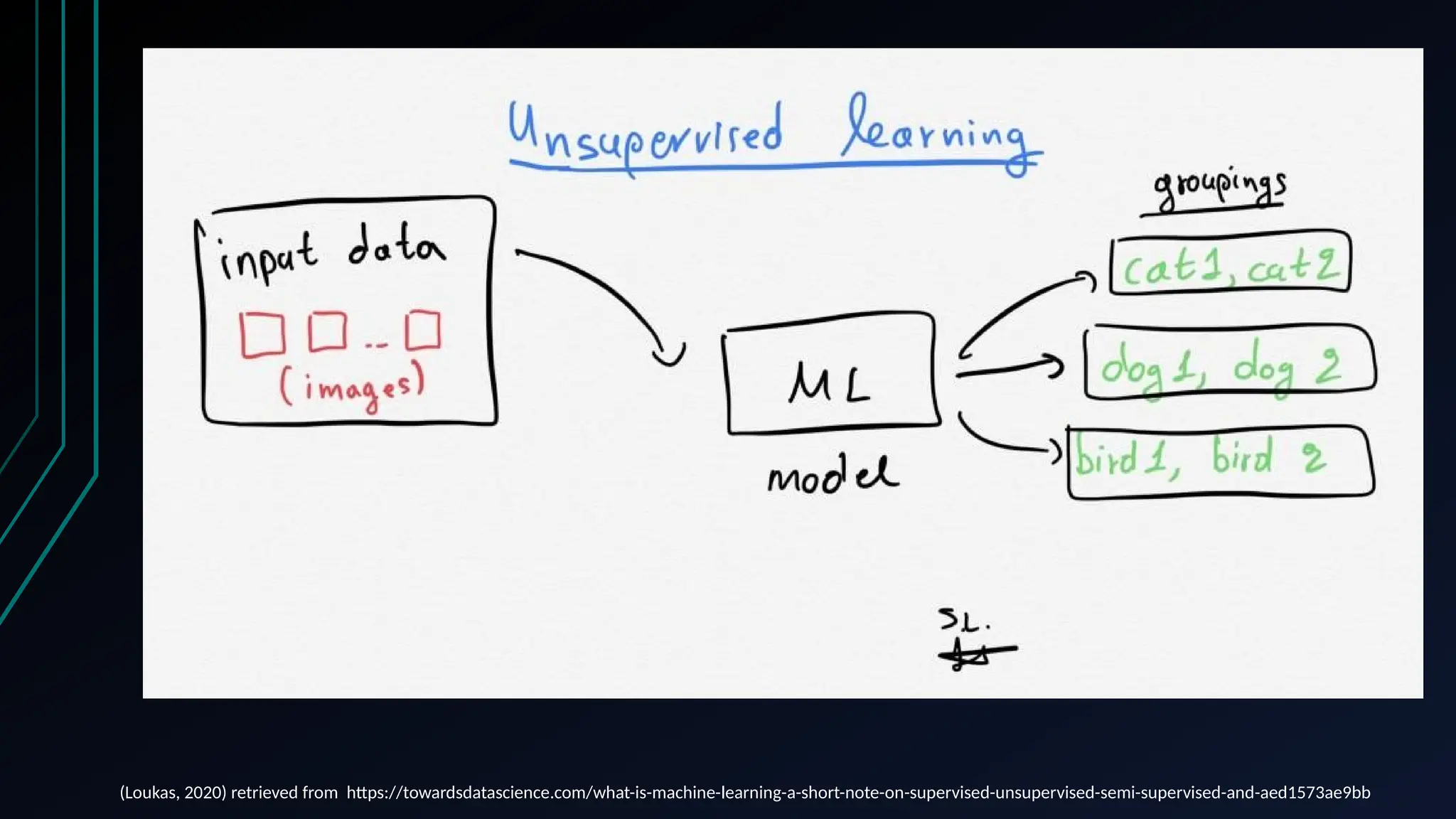
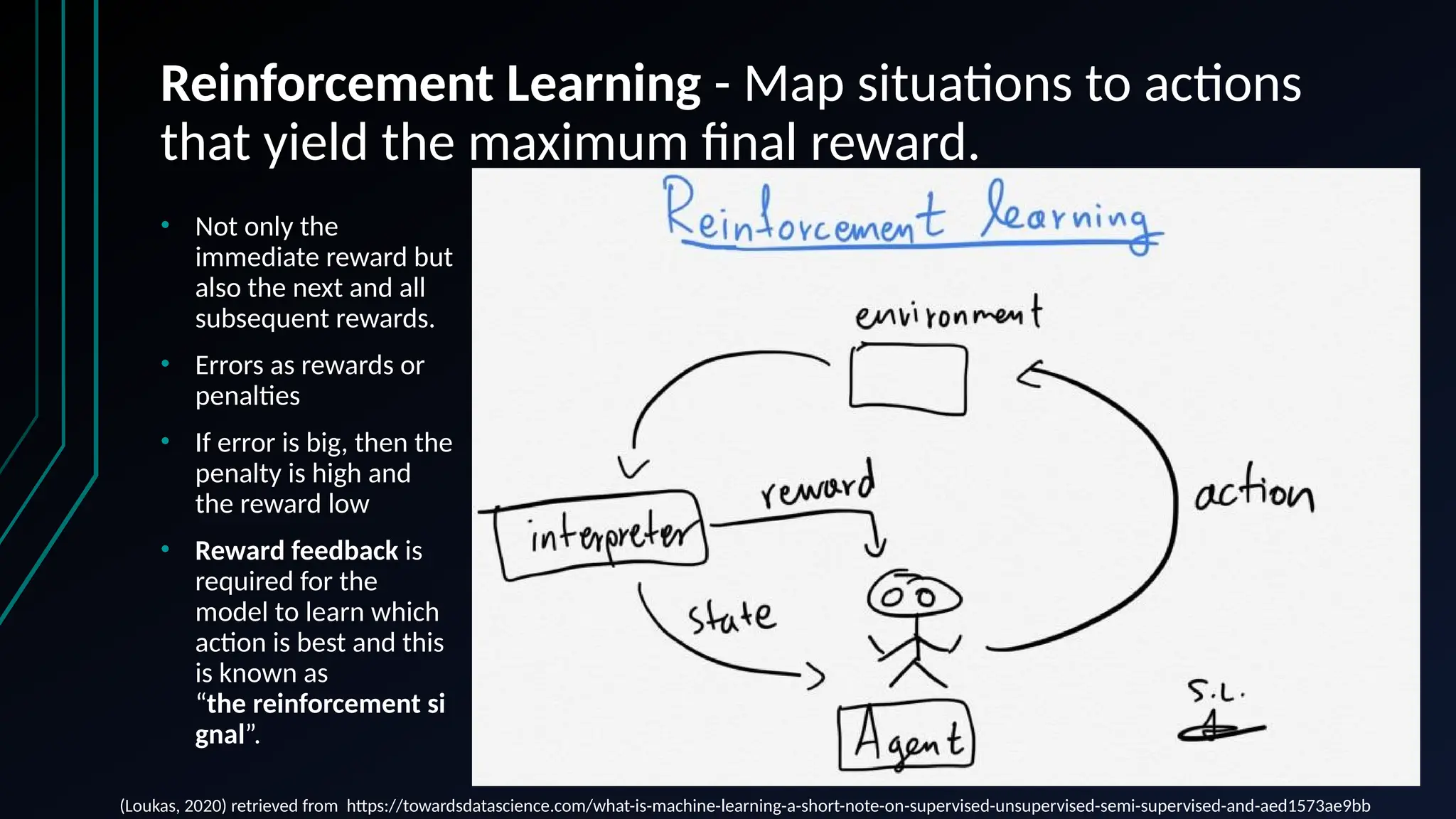
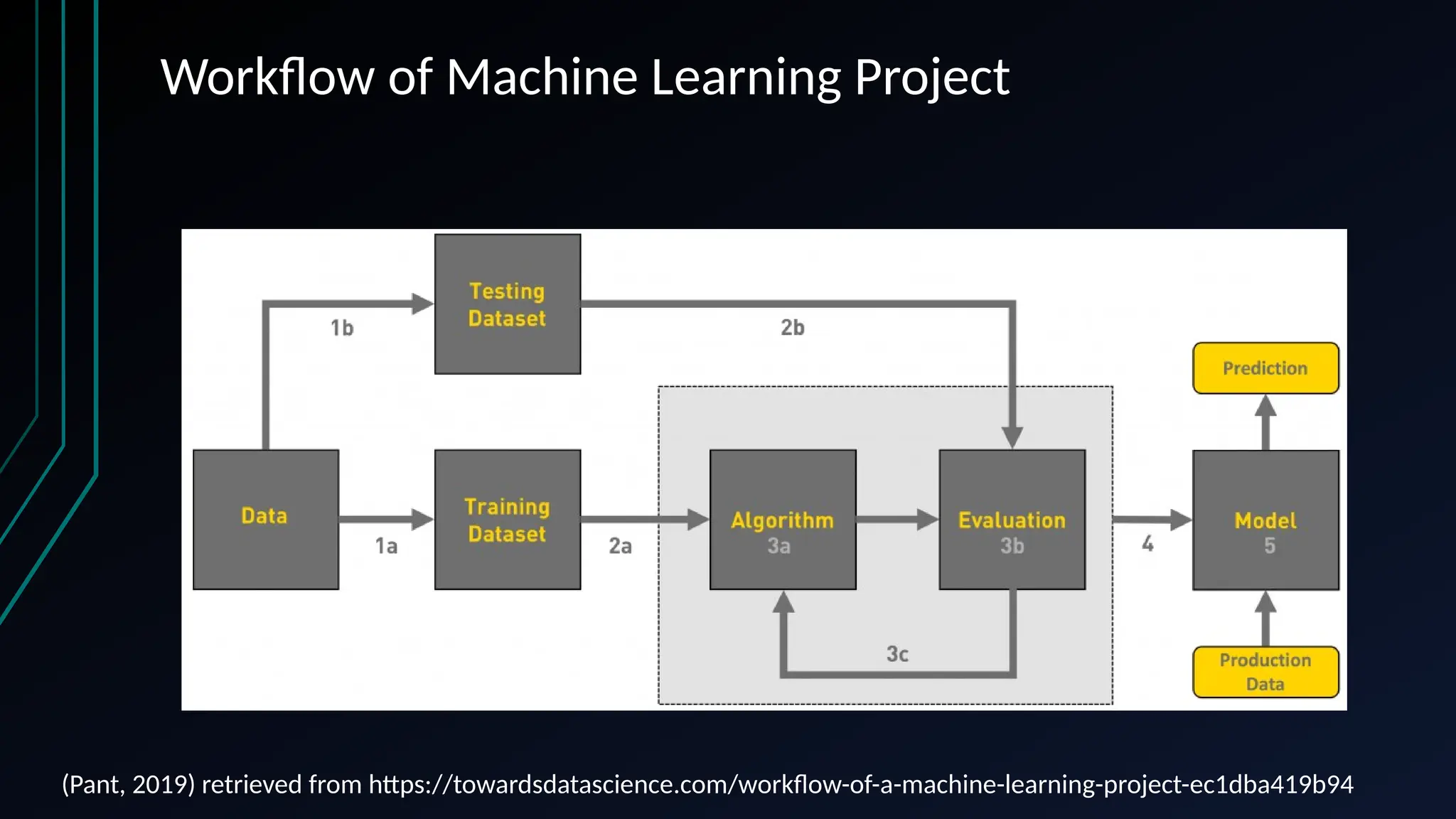
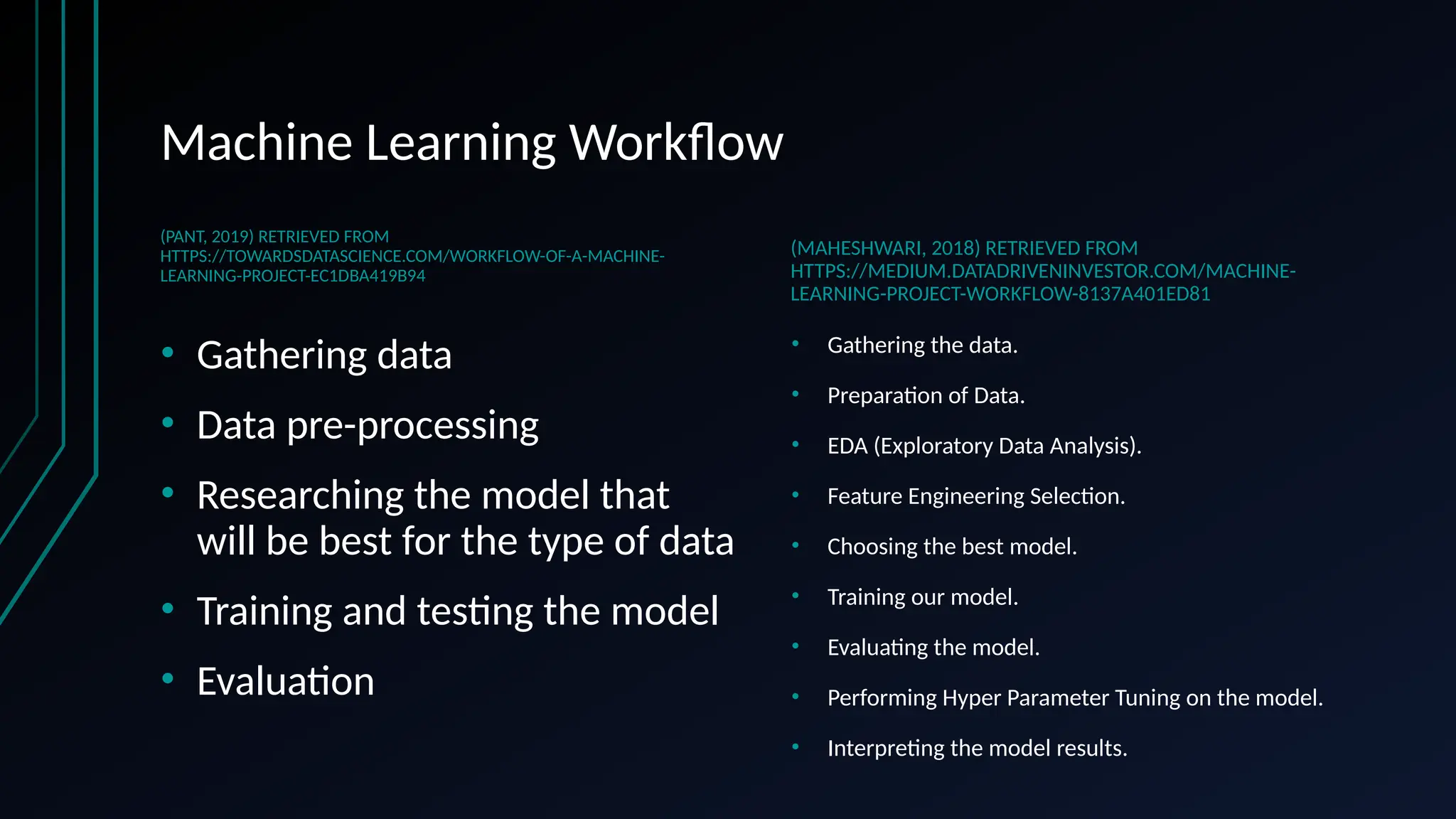
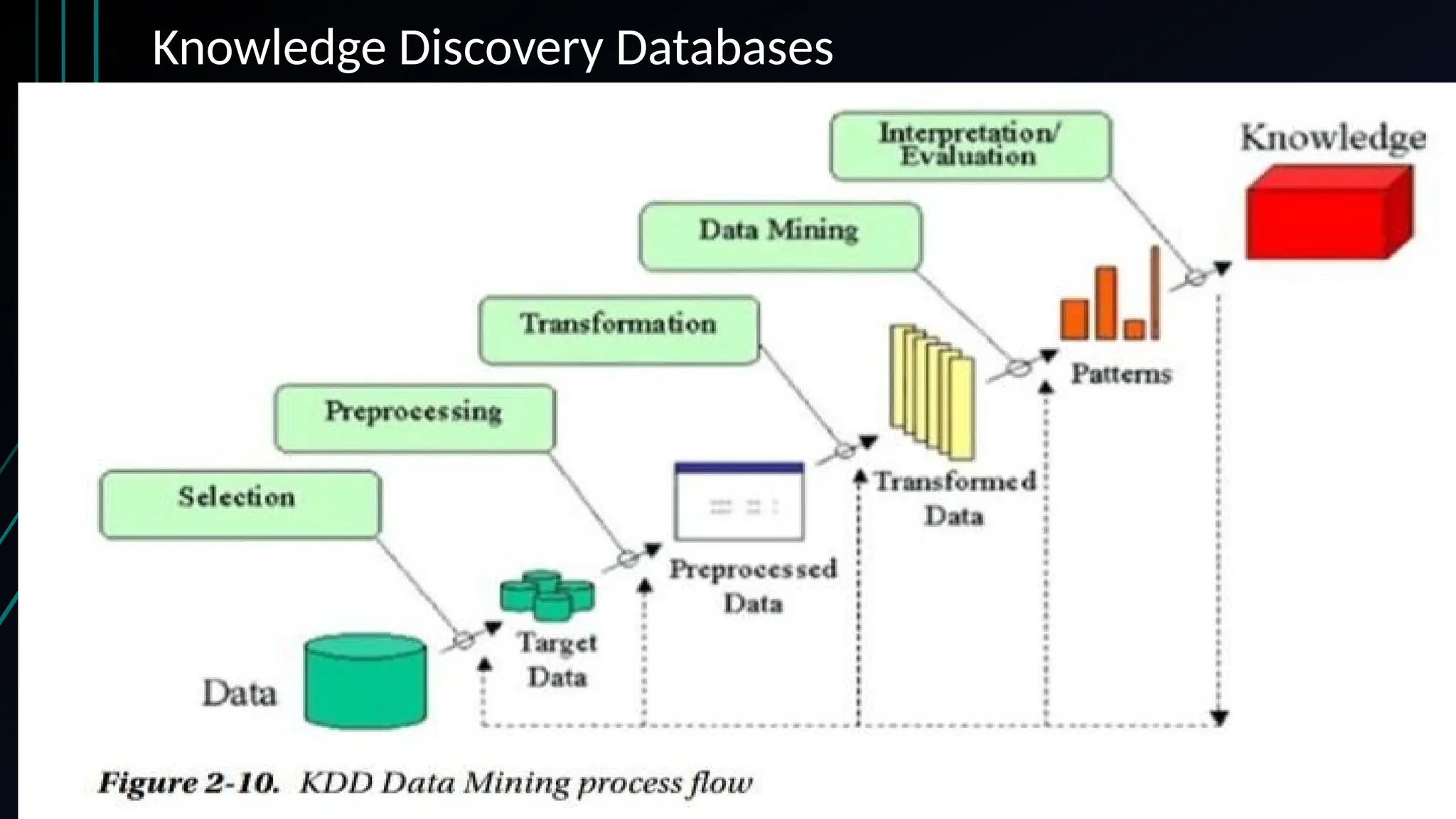
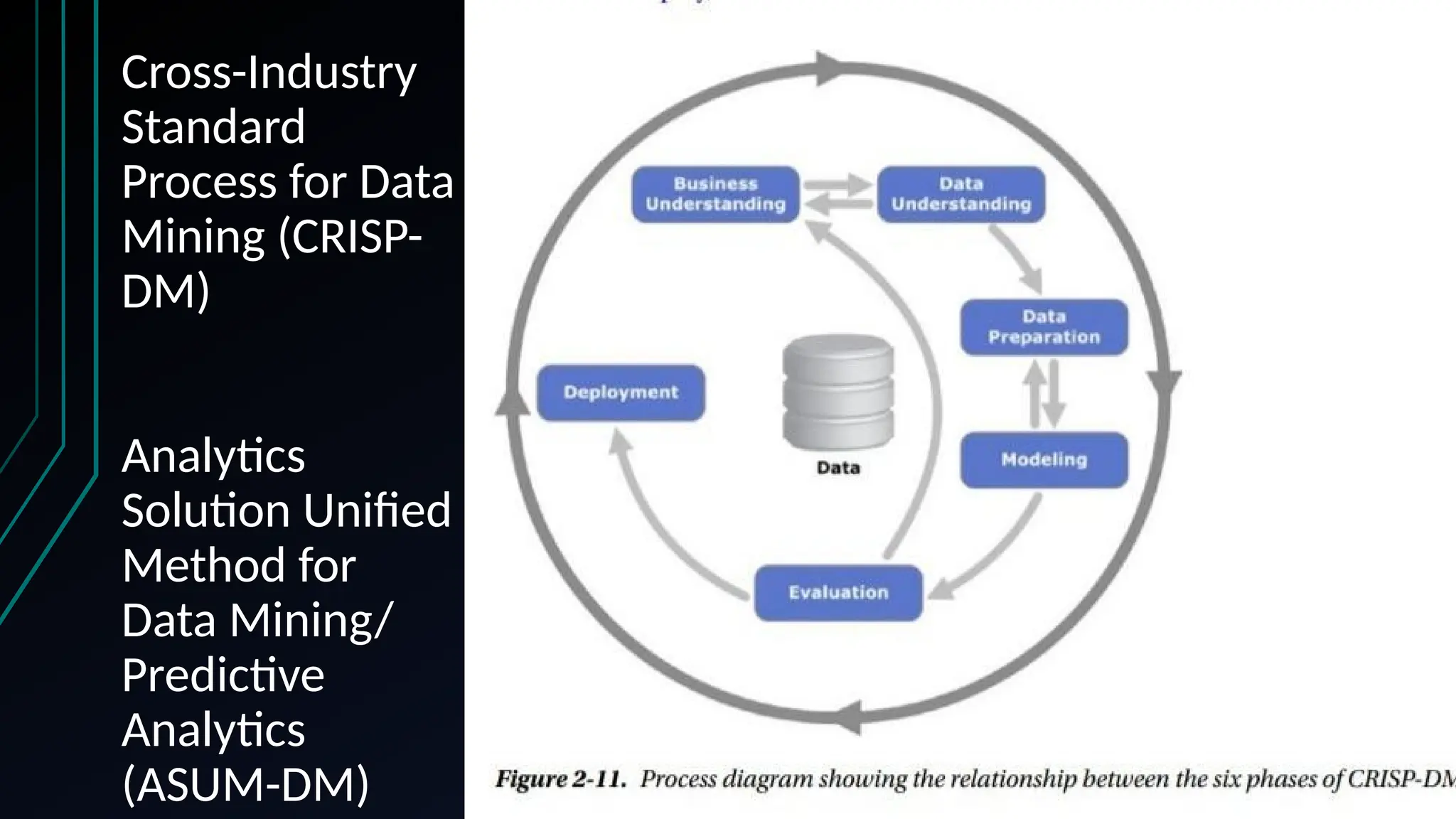
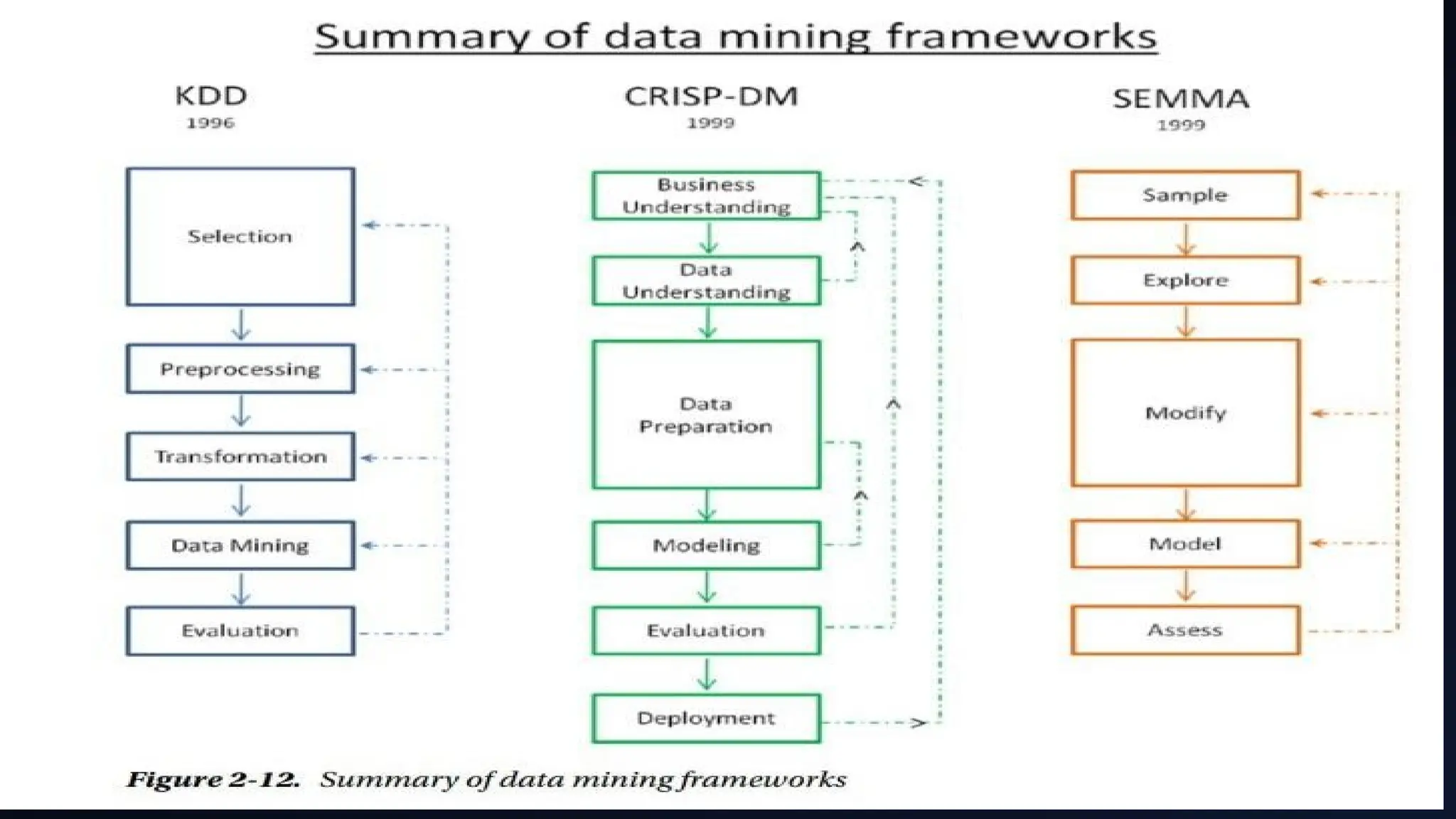
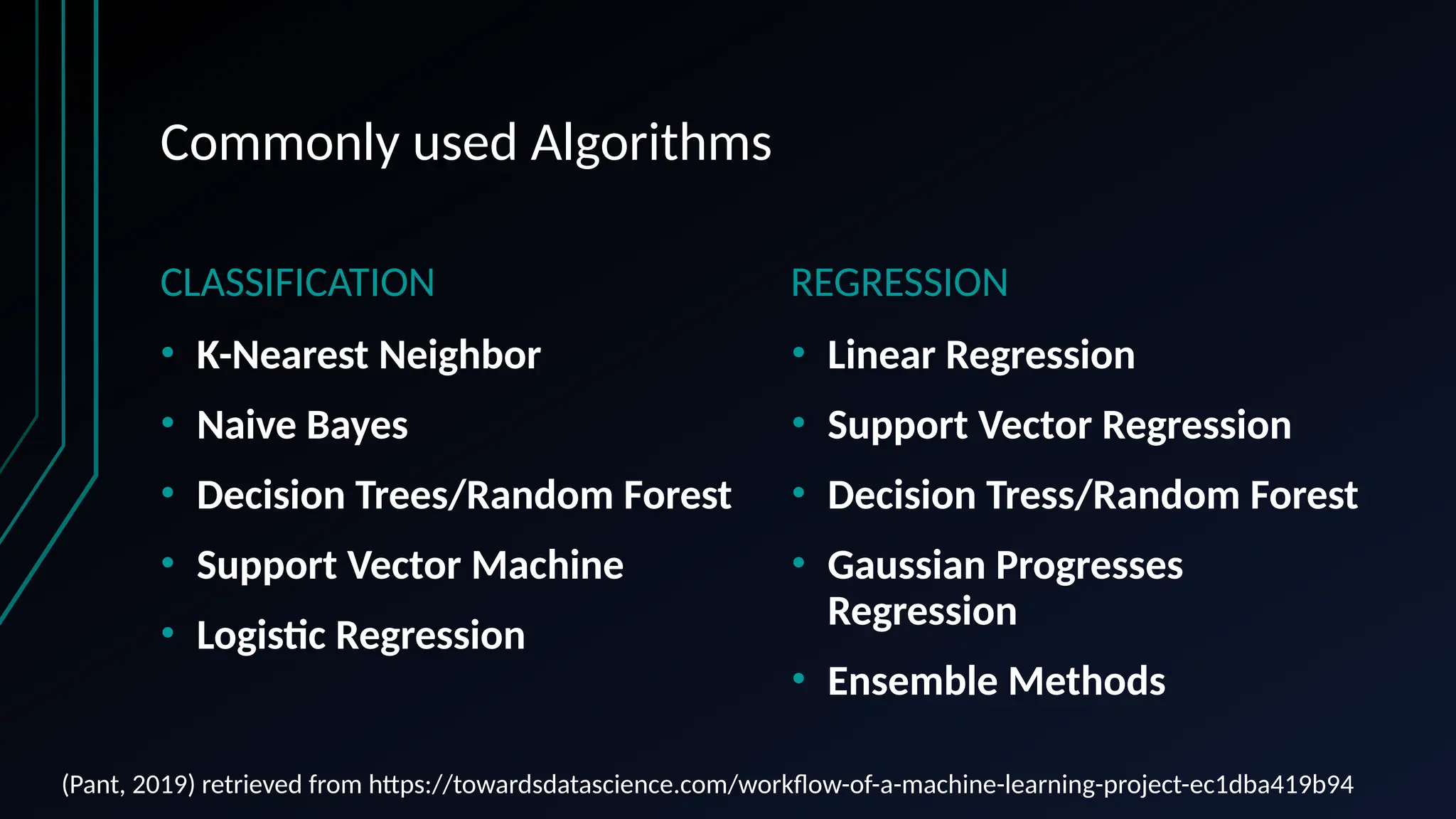
The document provides an overview of data science, machine learning, and analytics, explaining how these fields interrelate. It covers different types of analytics such as descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive, along with categories of machine learning including supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning. Additionally, it highlights the workflow of a machine learning project and tools commonly used in data analysis.