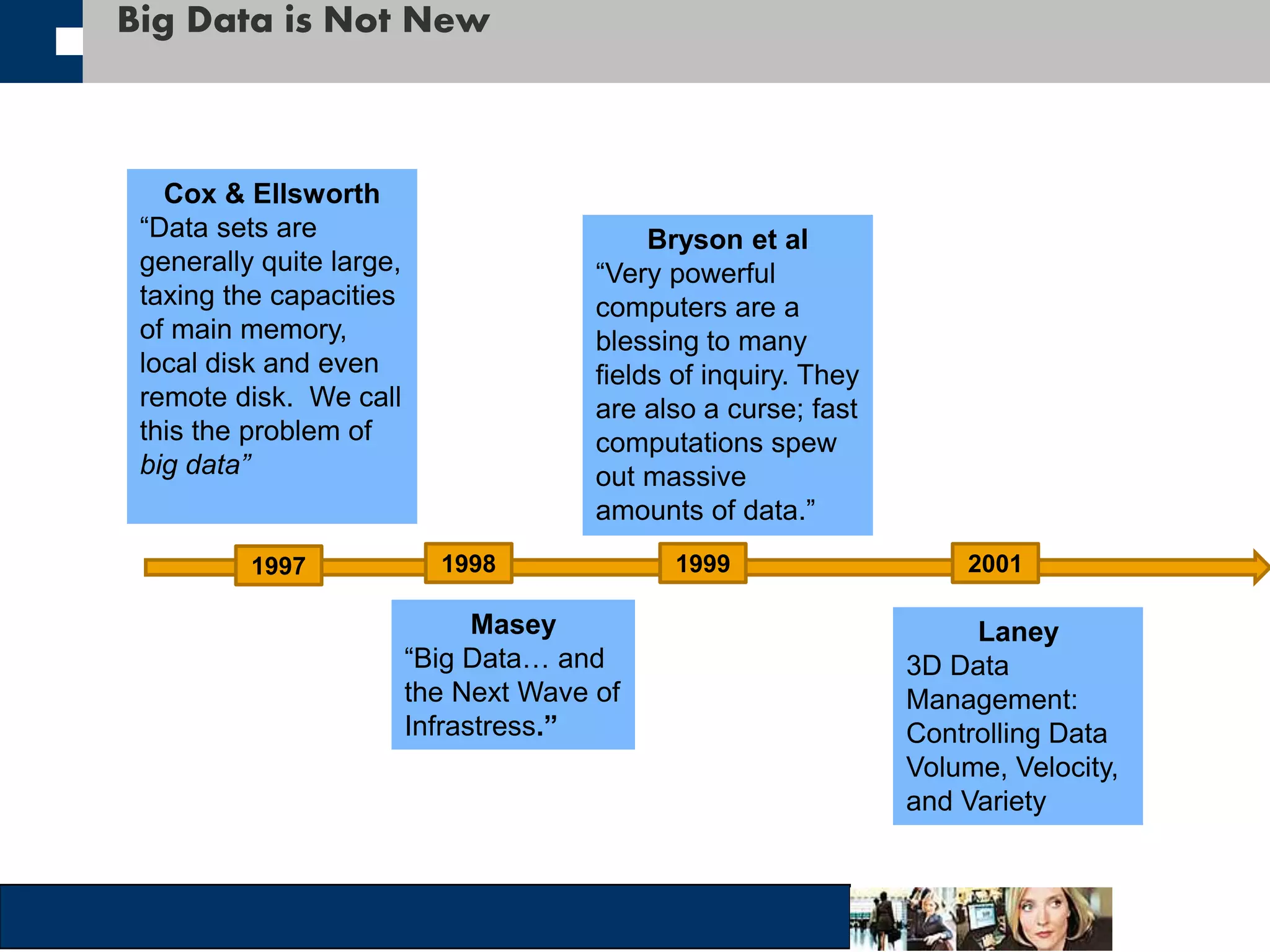
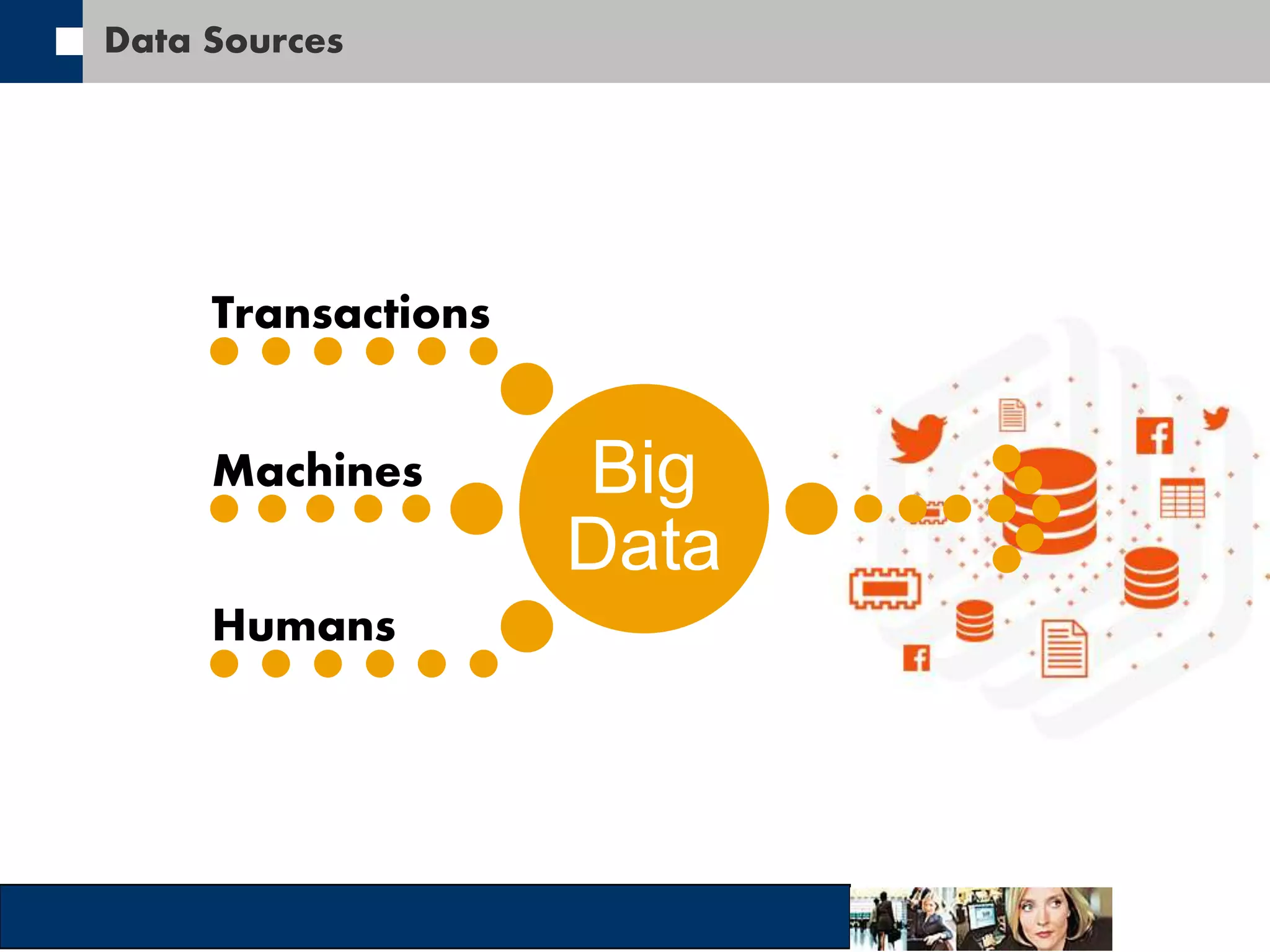
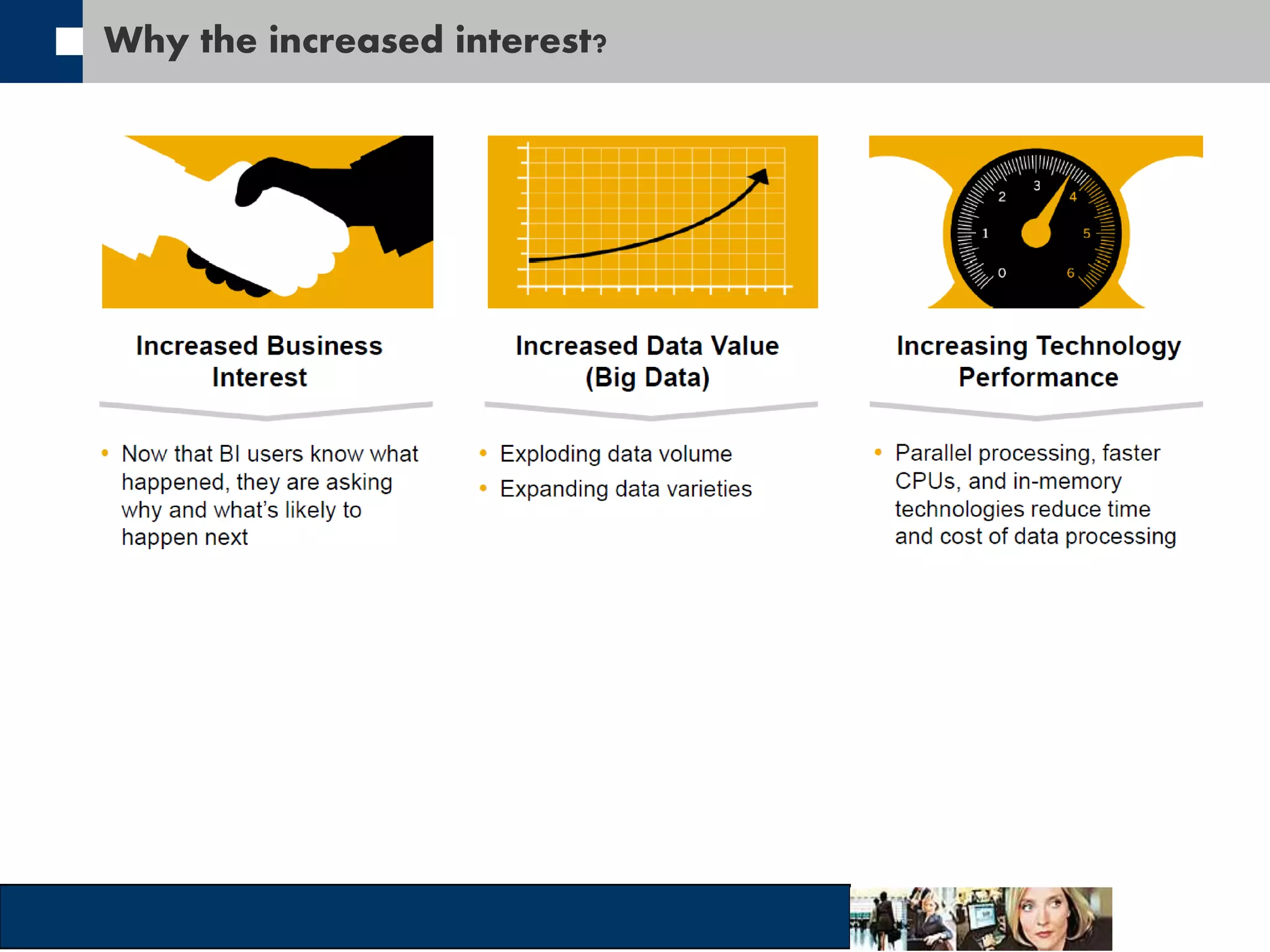
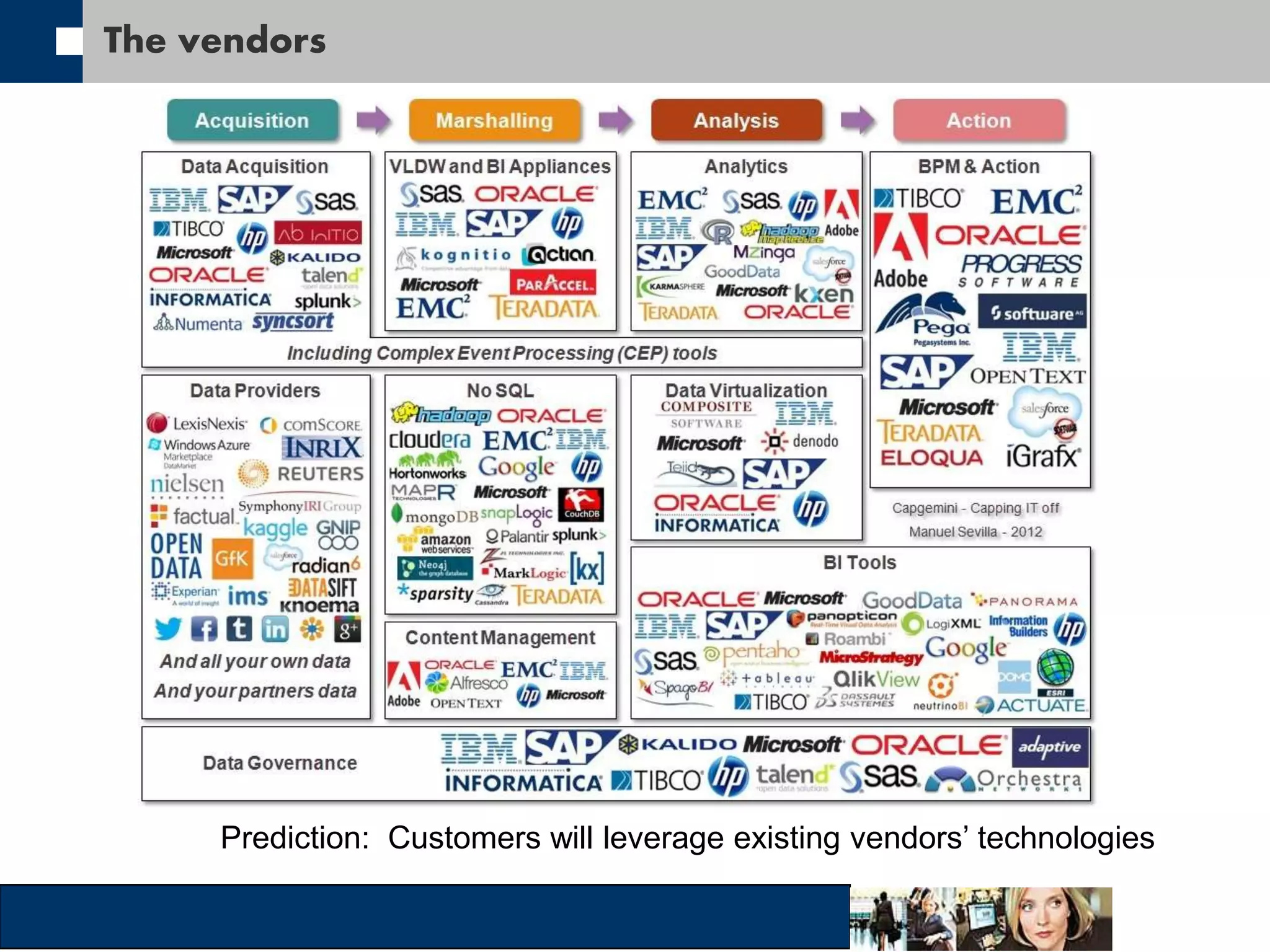
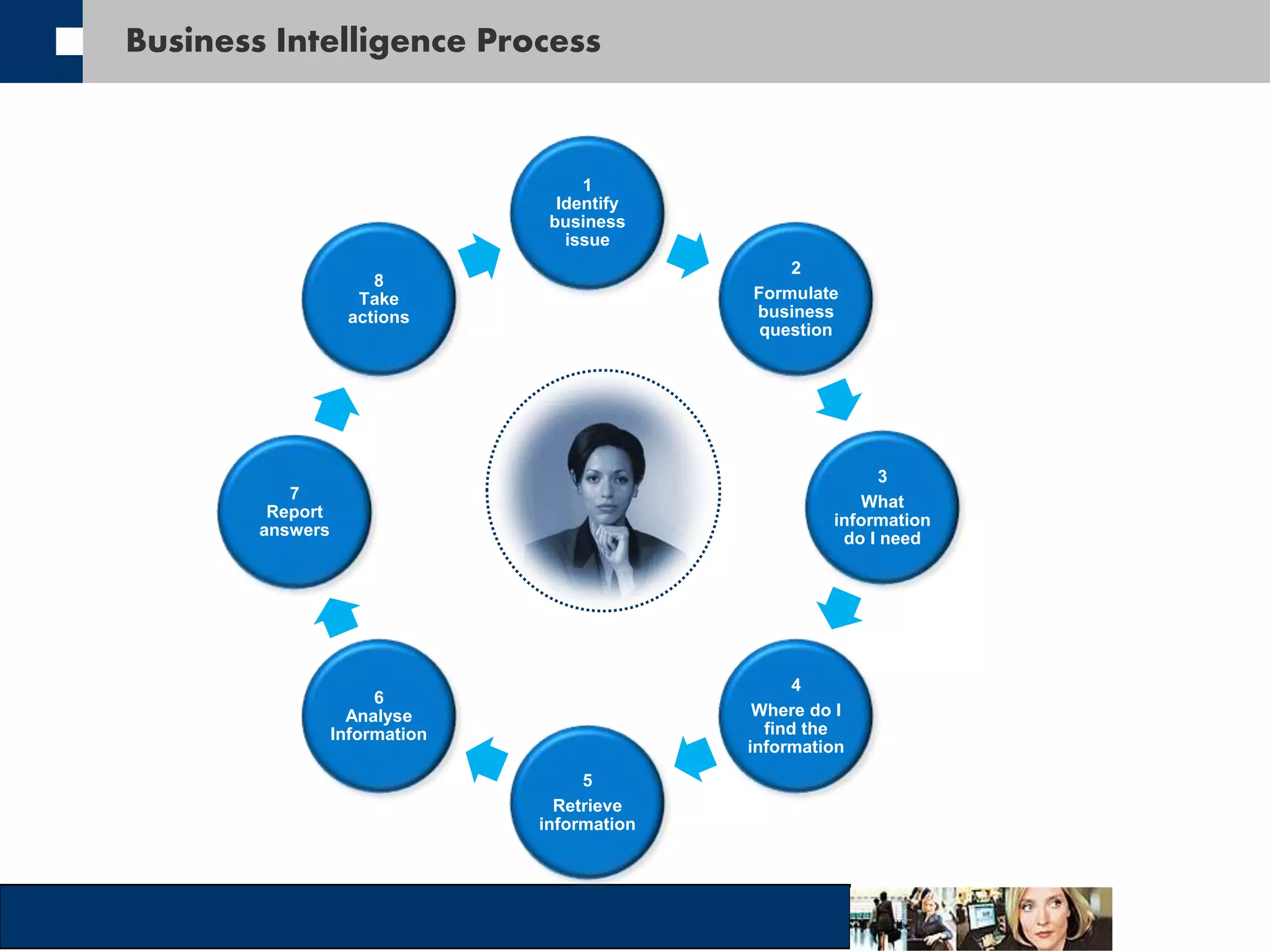
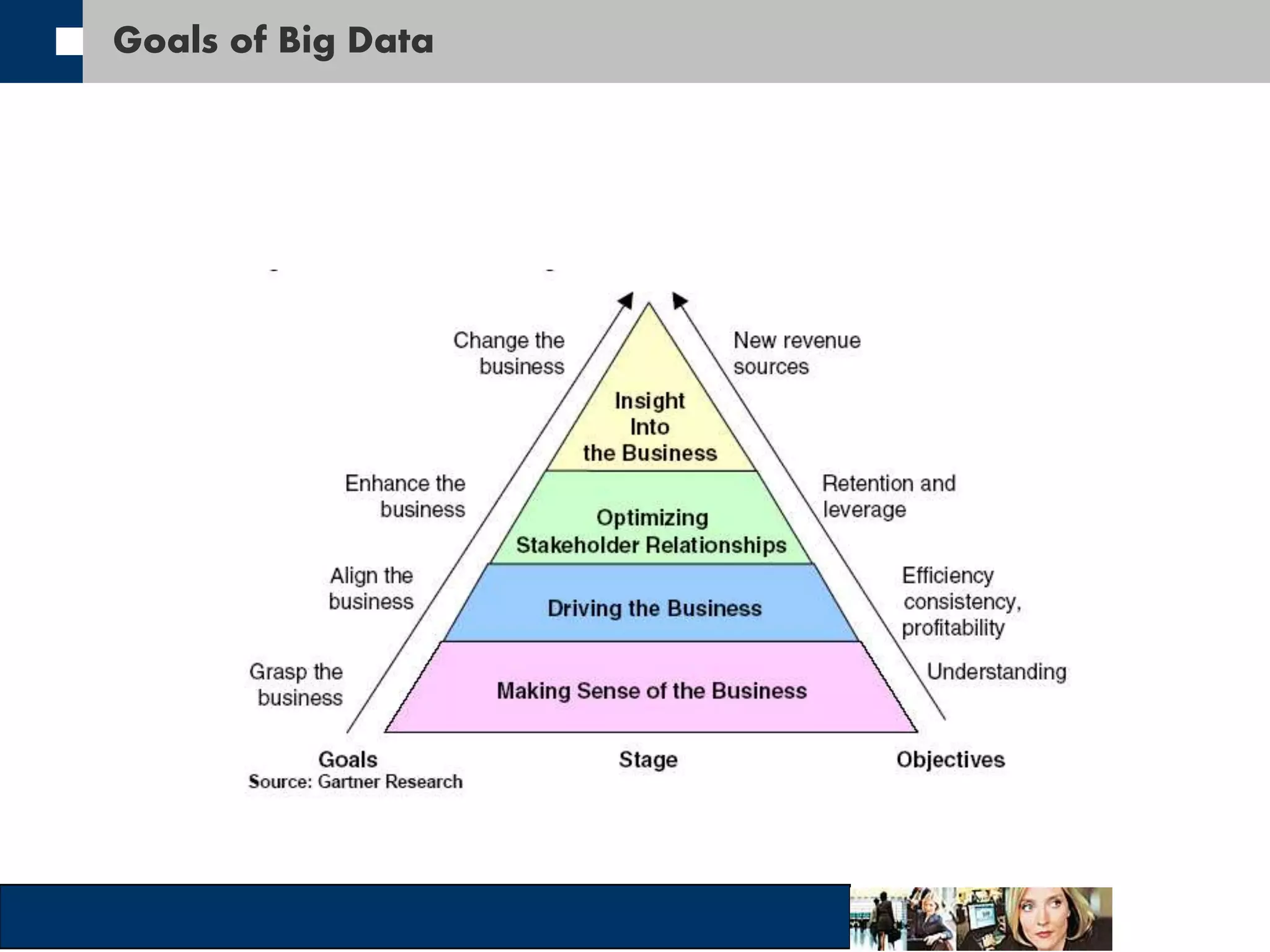
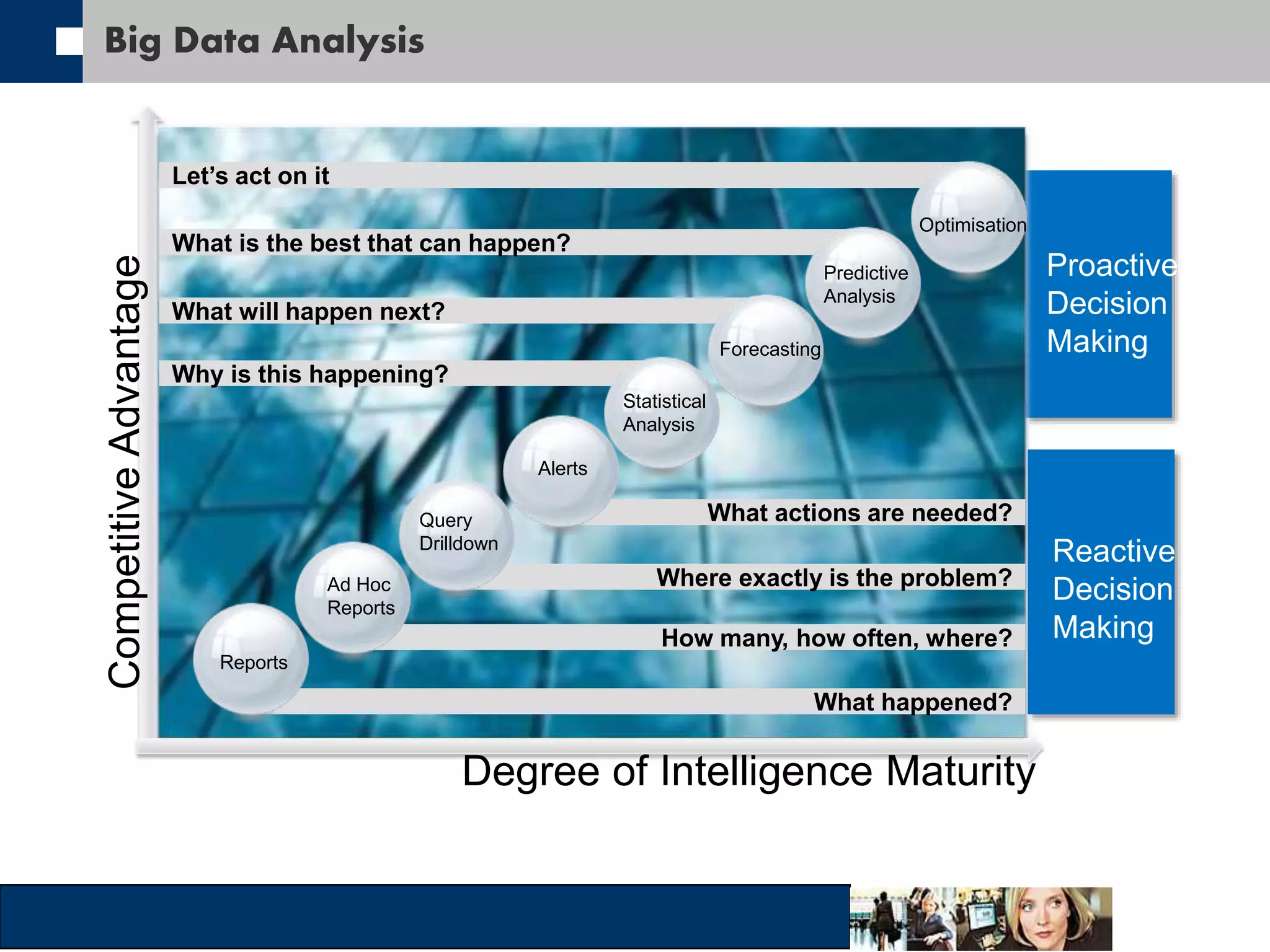
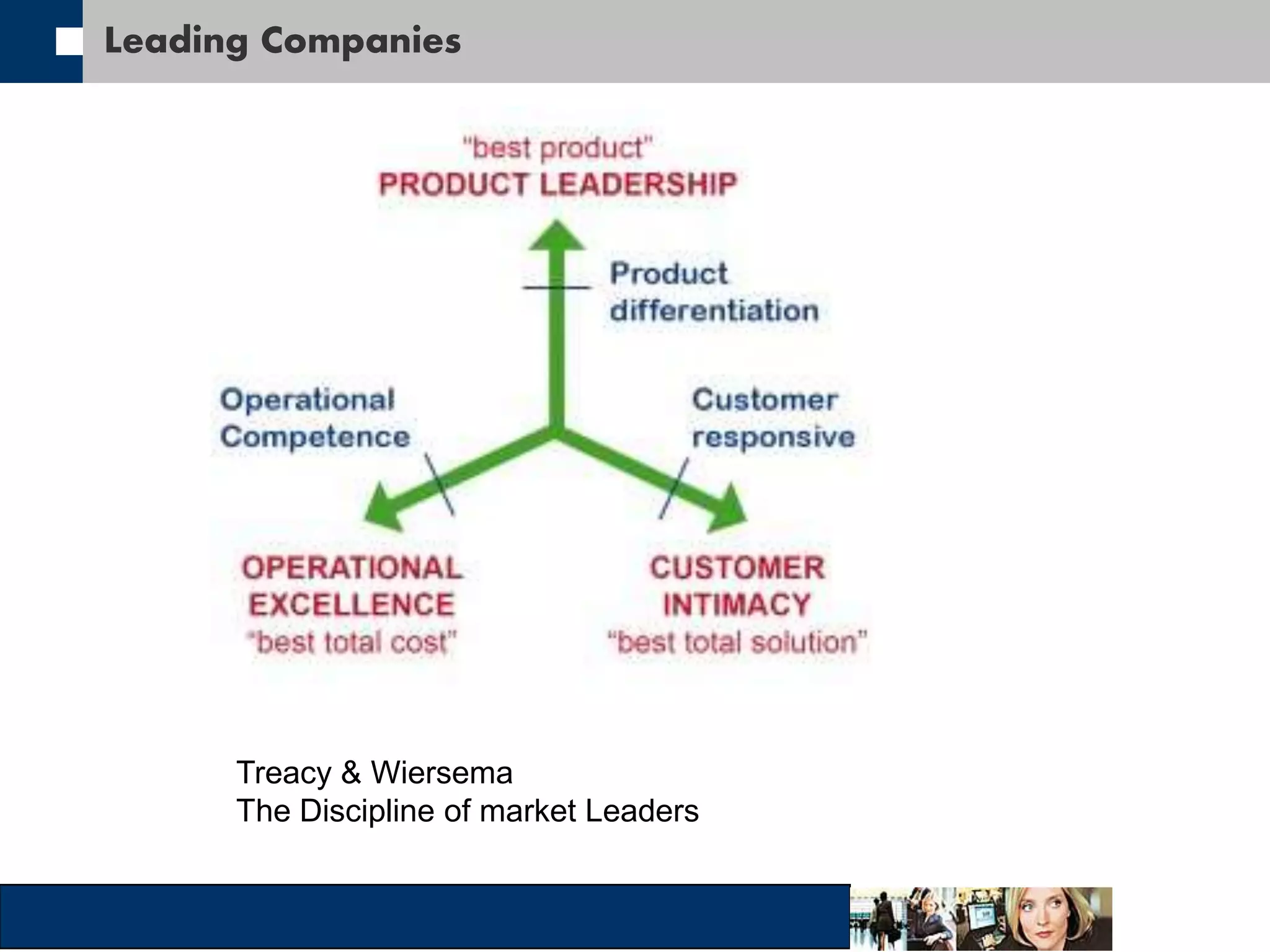
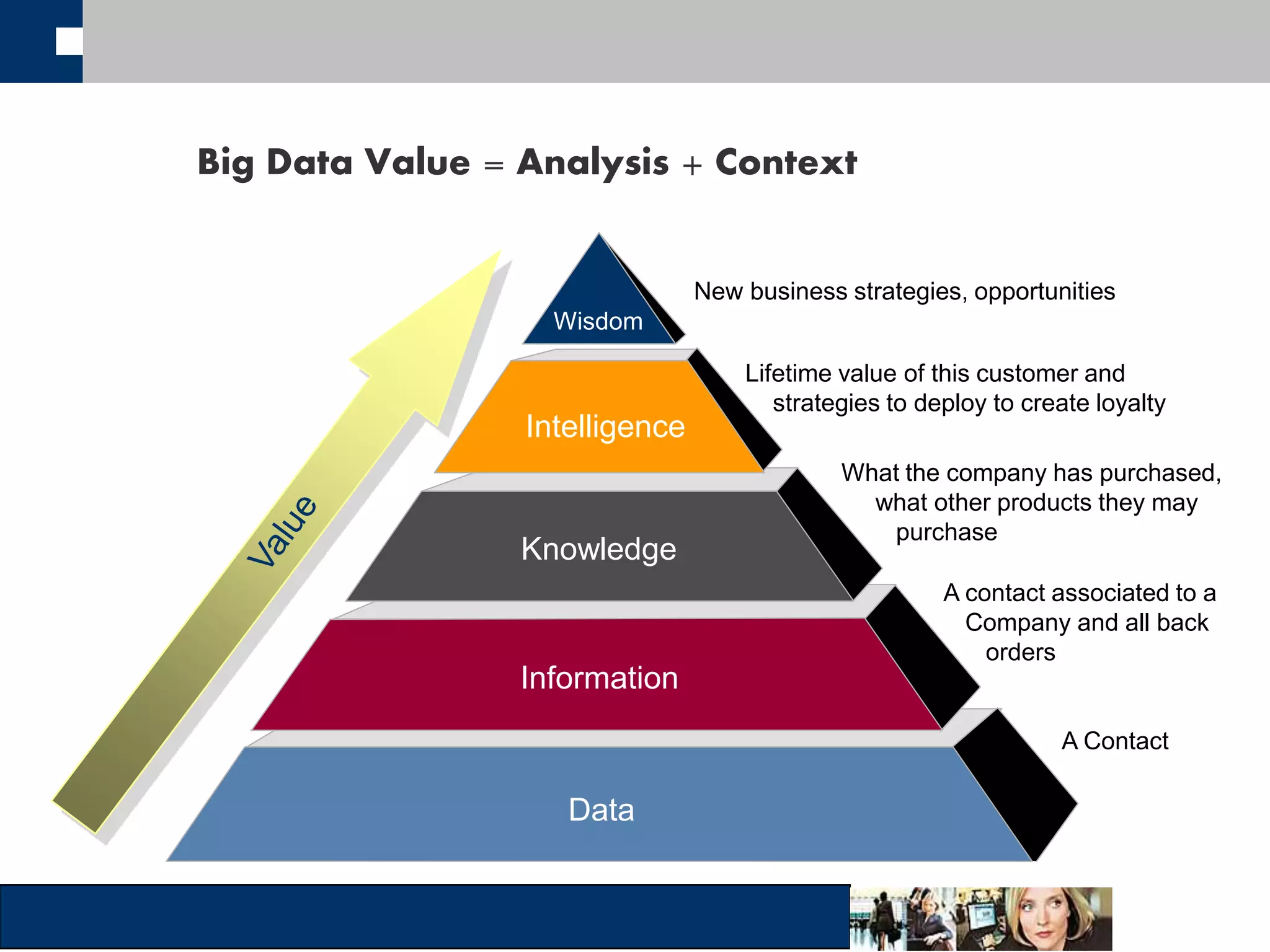
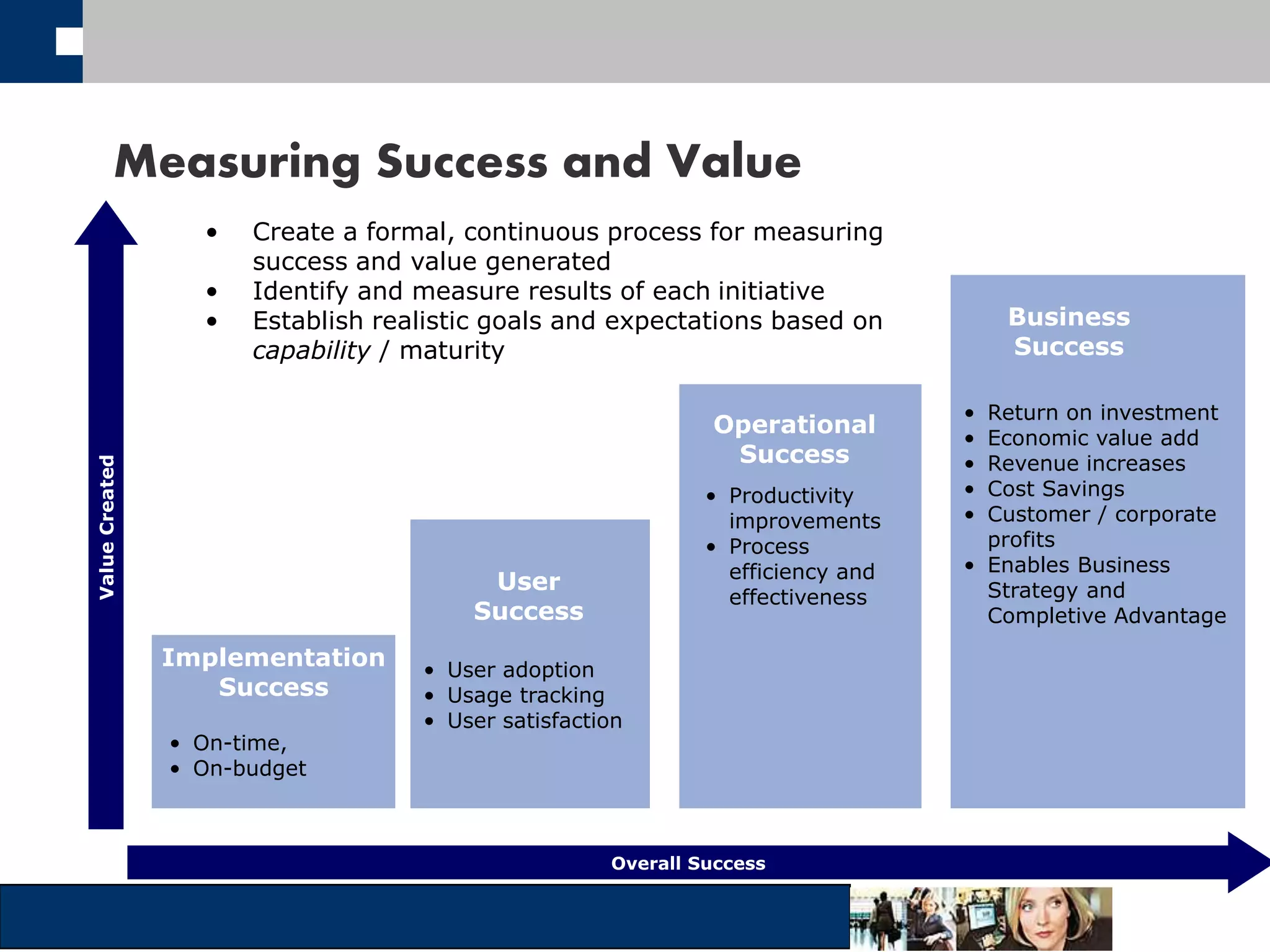
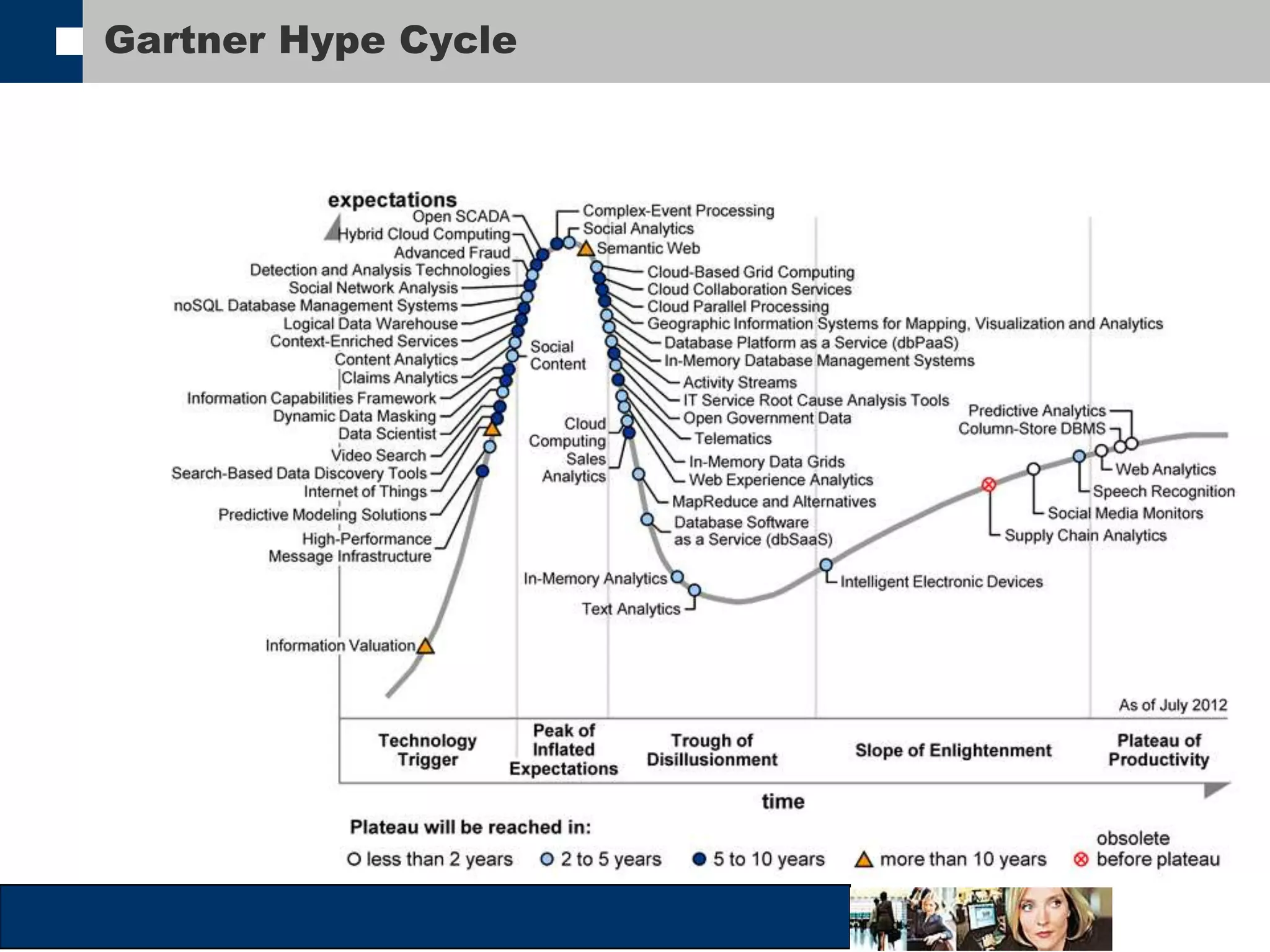
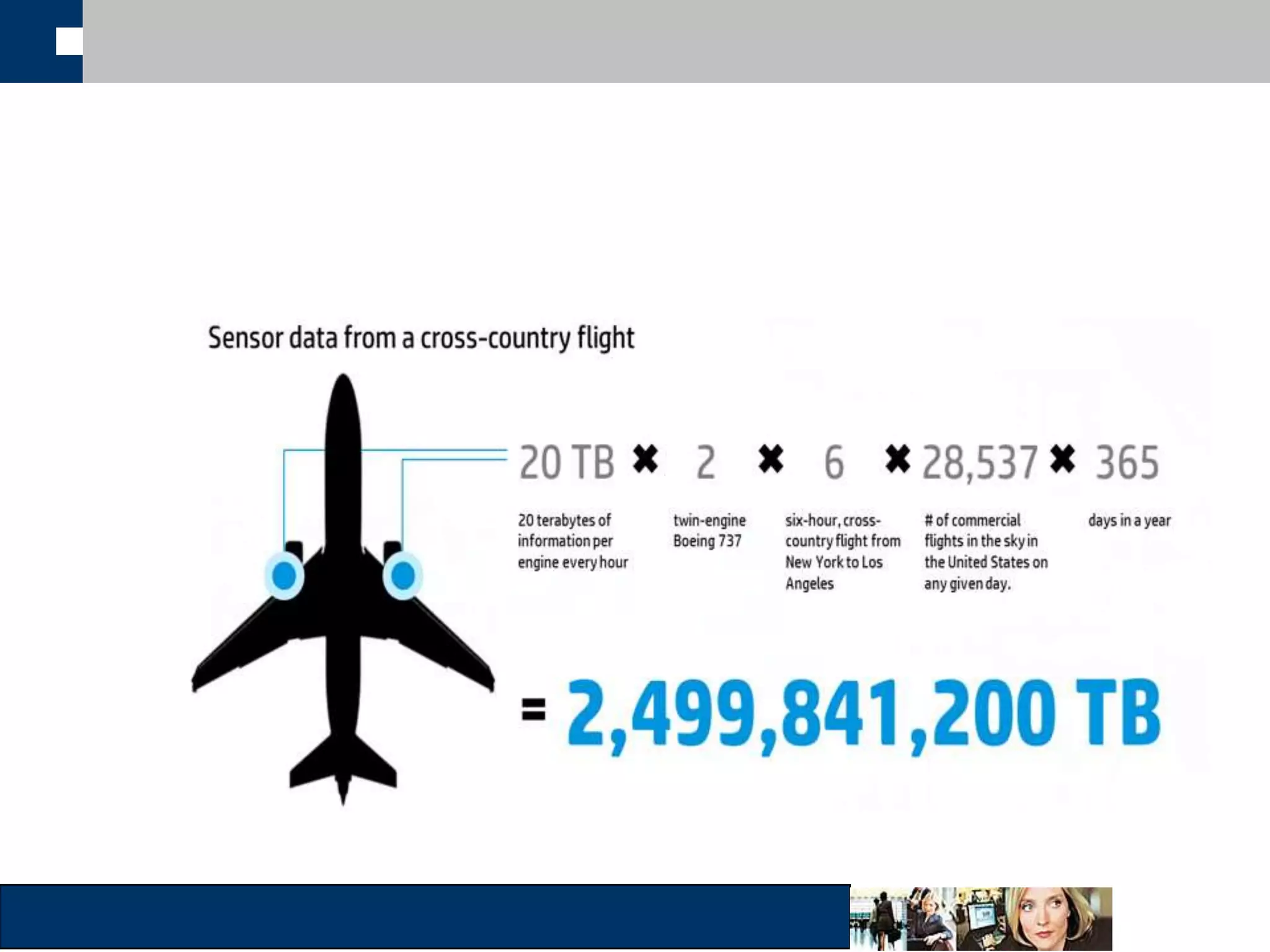
This document discusses big data and how organizations can get the most value from it. It defines big data as large data sets that are difficult to process using traditional data management tools due to their size and complexity. The document outlines the characteristics of big data, including volume, velocity, and variety. It also discusses different sources of big data, challenges of big data, and how organizations can analyze big data to gain insights, make predictions, and gain competitive advantages. The document advocates for measuring the success and value of big data initiatives.