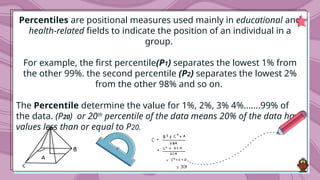
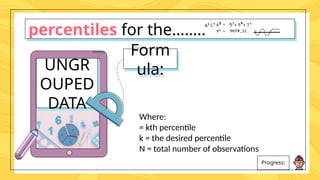
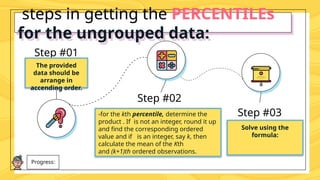
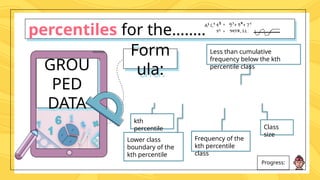
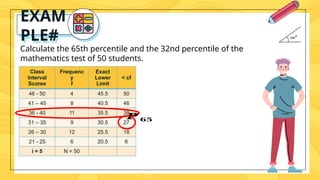
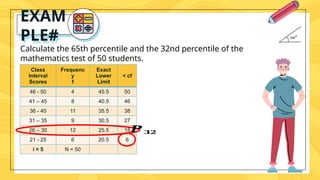
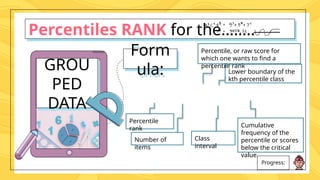
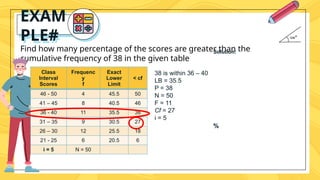
Percentiles are values that divide a data distribution into 100 equal parts, helping to characterize individual positions relative to a group, particularly in educational and health contexts. The document outlines how to calculate percentiles for both ungrouped and grouped data, providing examples for clarity. Additionally, it explains the concept of percentile rank, which indicates the proportion of scores that fall below or equal to a specific score.