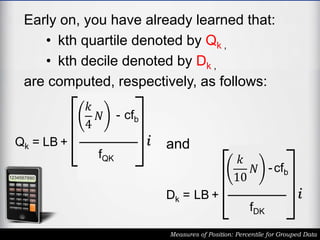
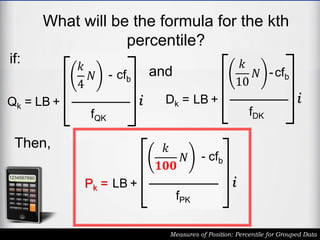
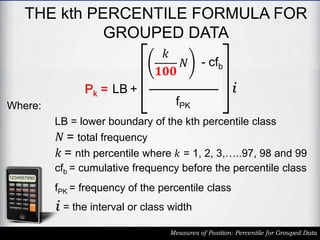
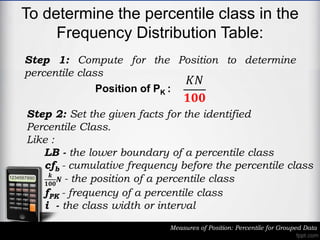
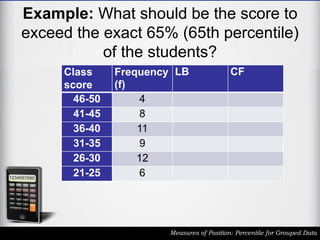
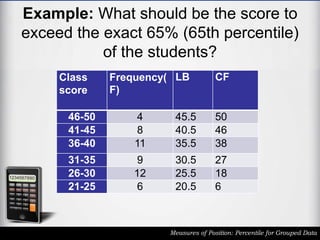
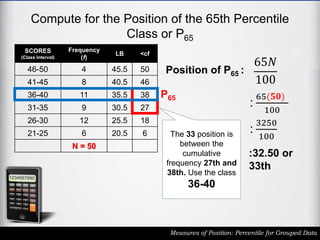
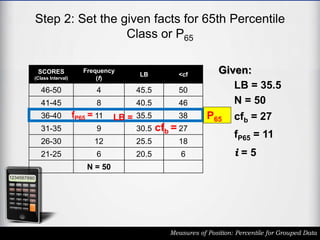
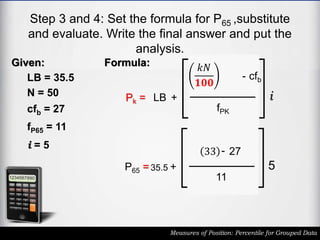
The document outlines the definition and calculation of percentiles for grouped data, explaining the necessary formulas and steps to derive the kth percentile. It provides detailed instructions for determining the class of a given percentile and includes examples to illustrate the calculation process. Additionally, it emphasizes classroom rules that encourage respect and engagement in learning.