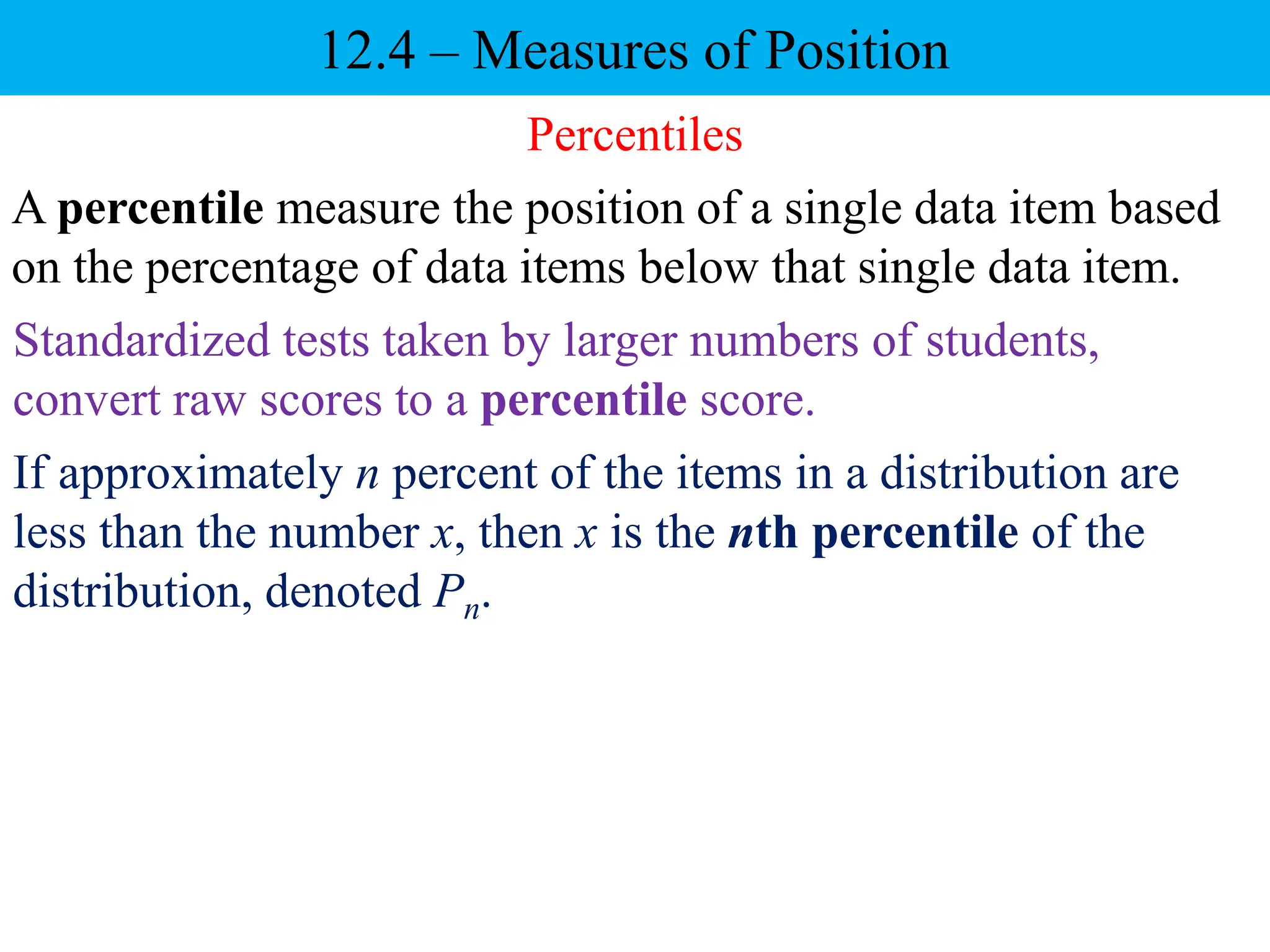
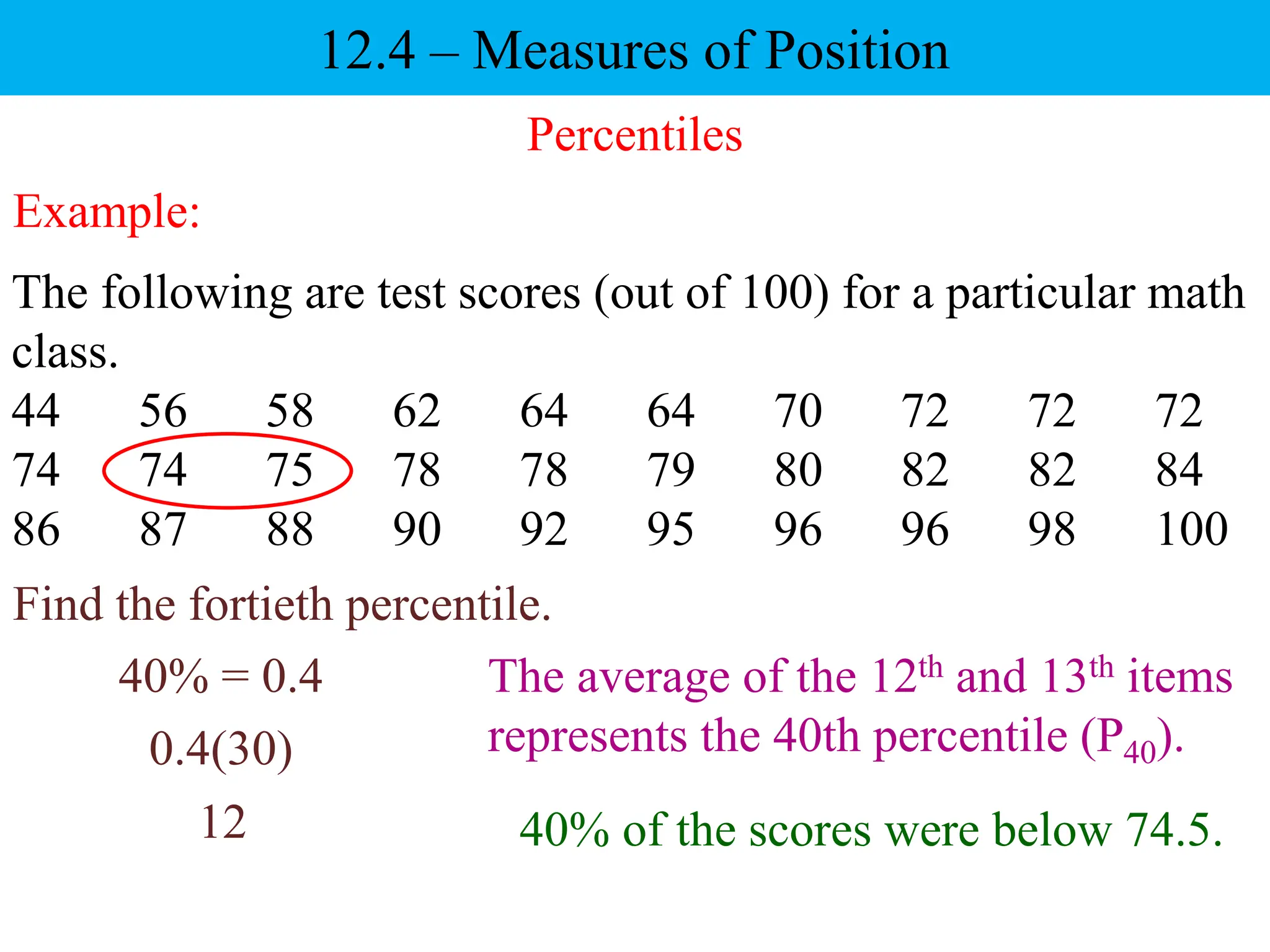
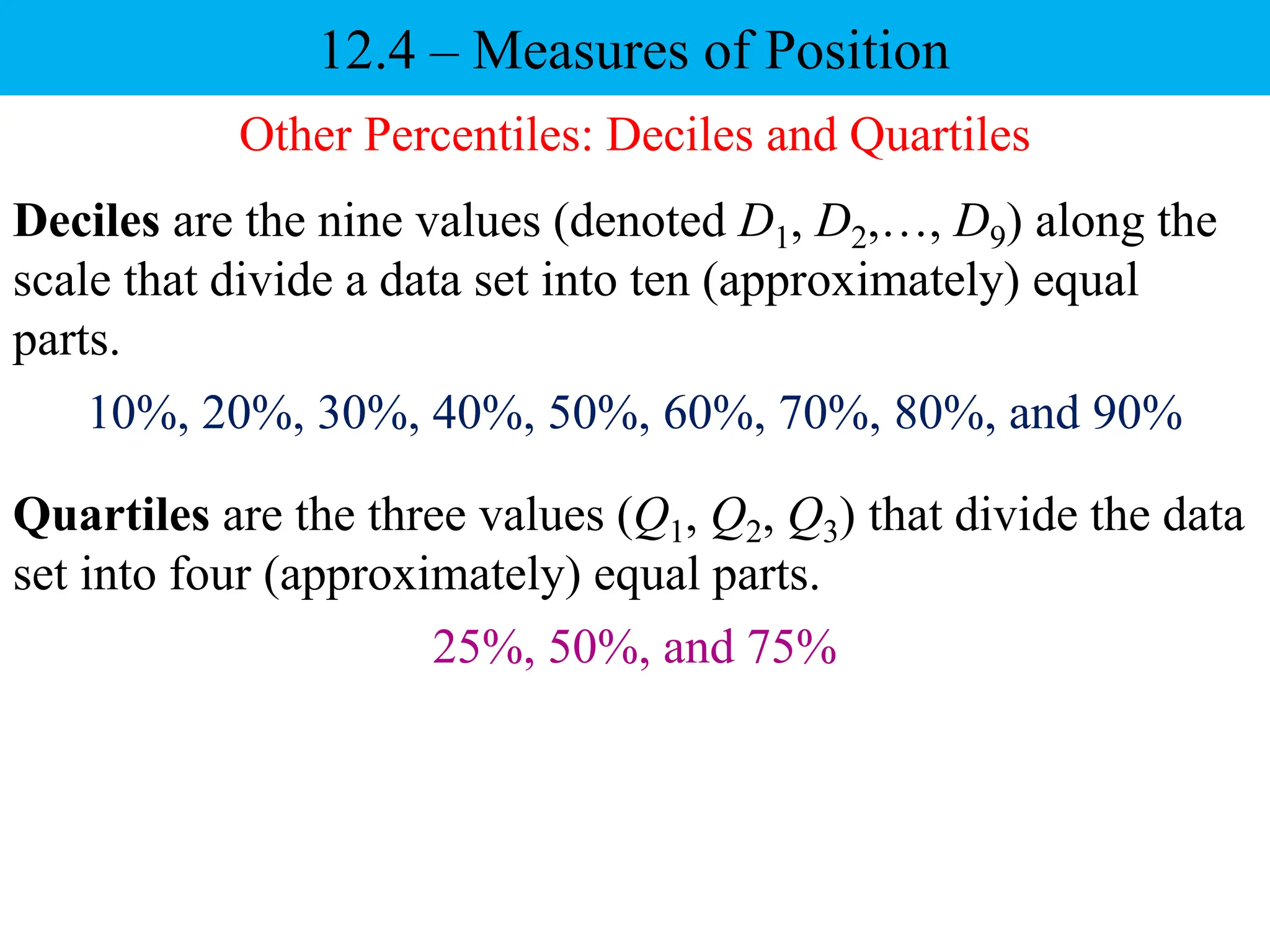
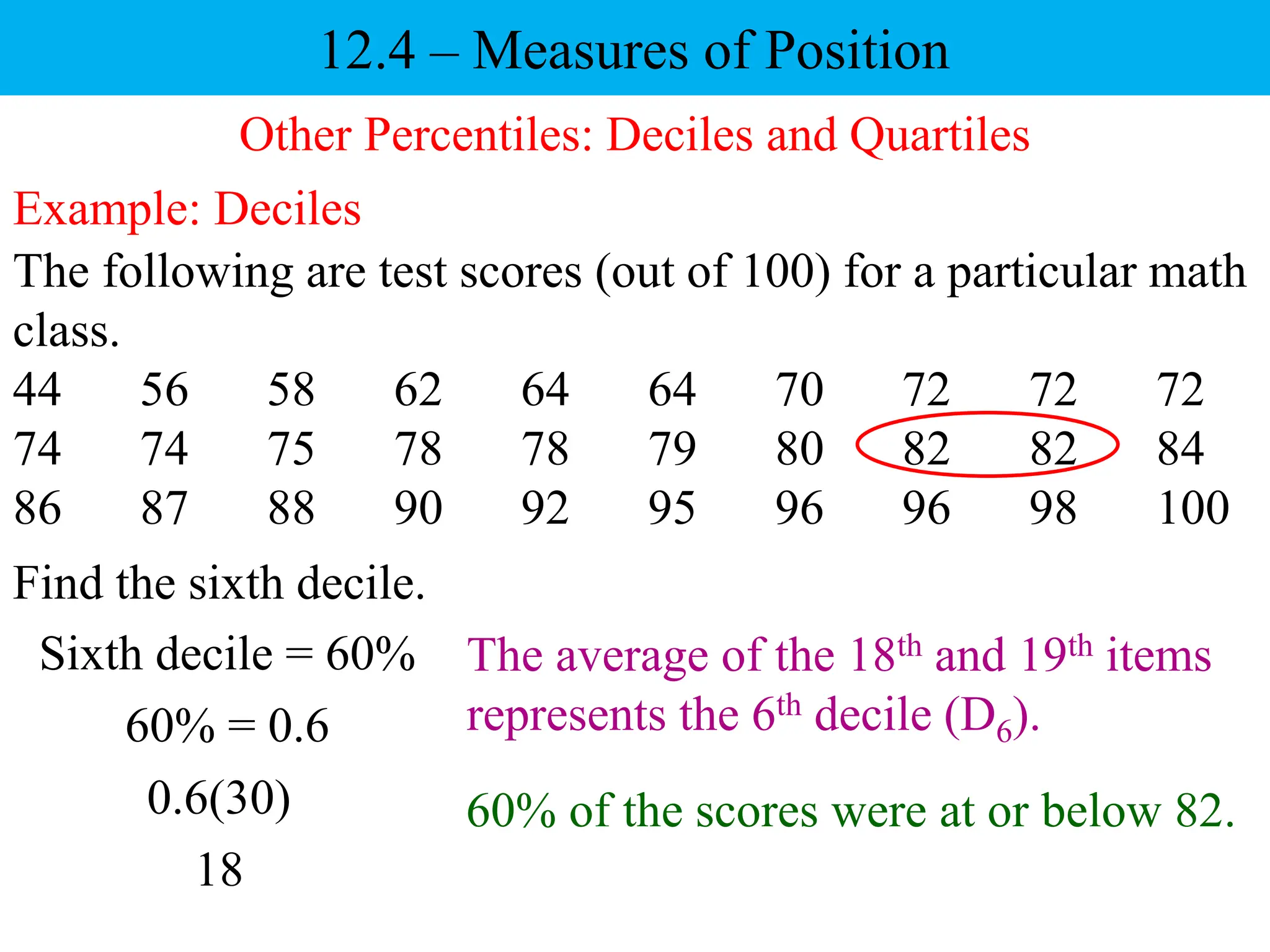
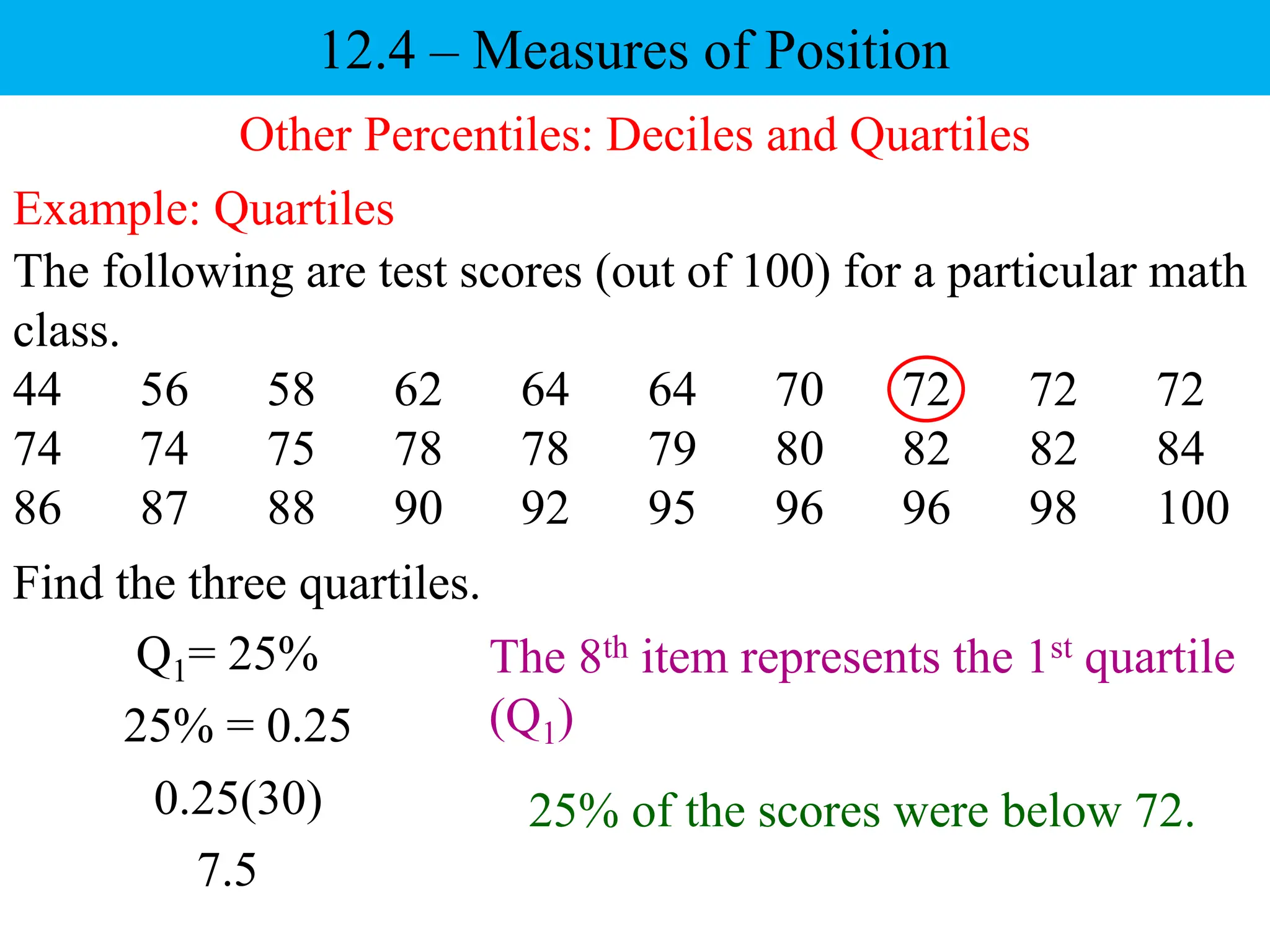
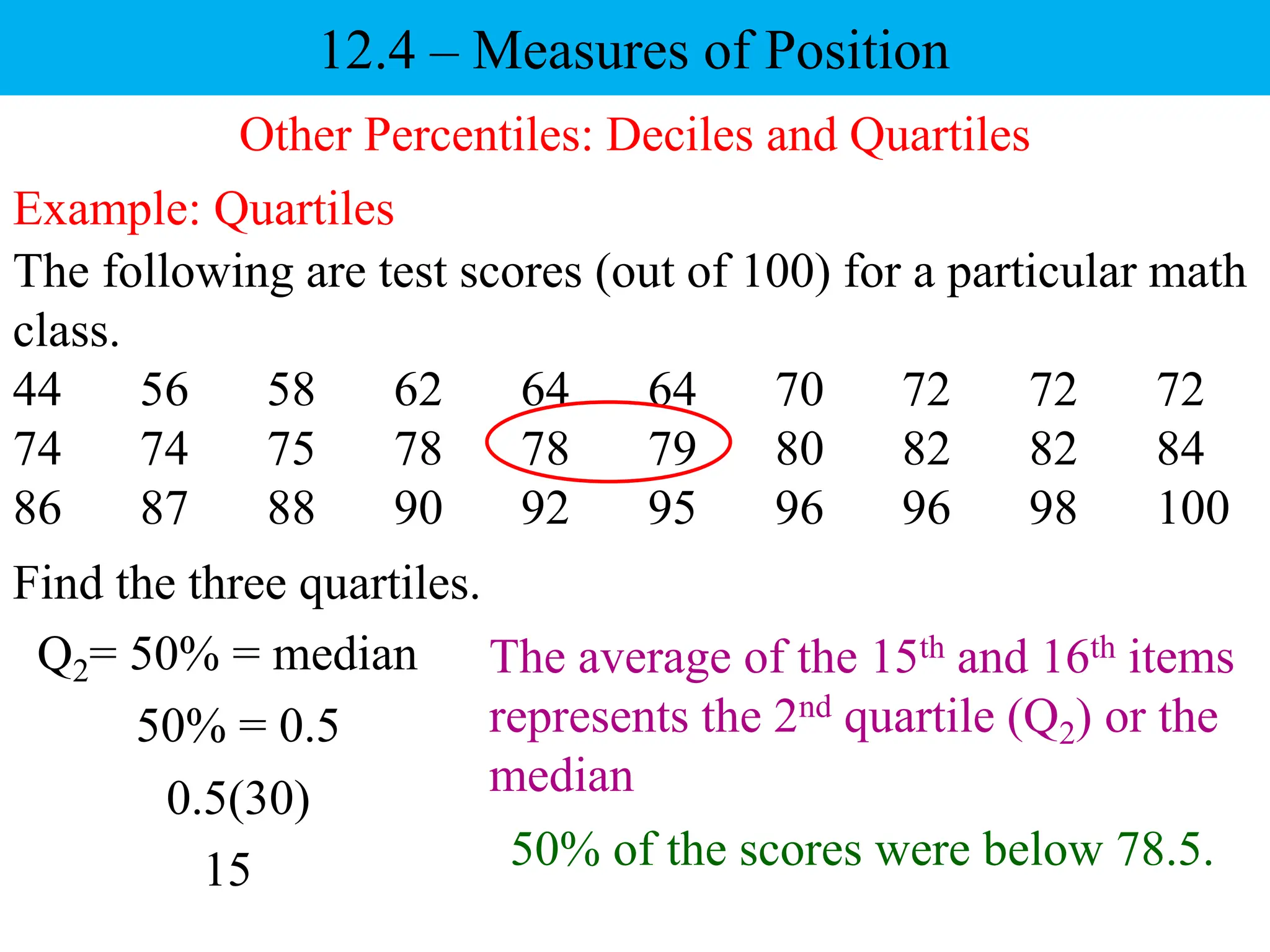
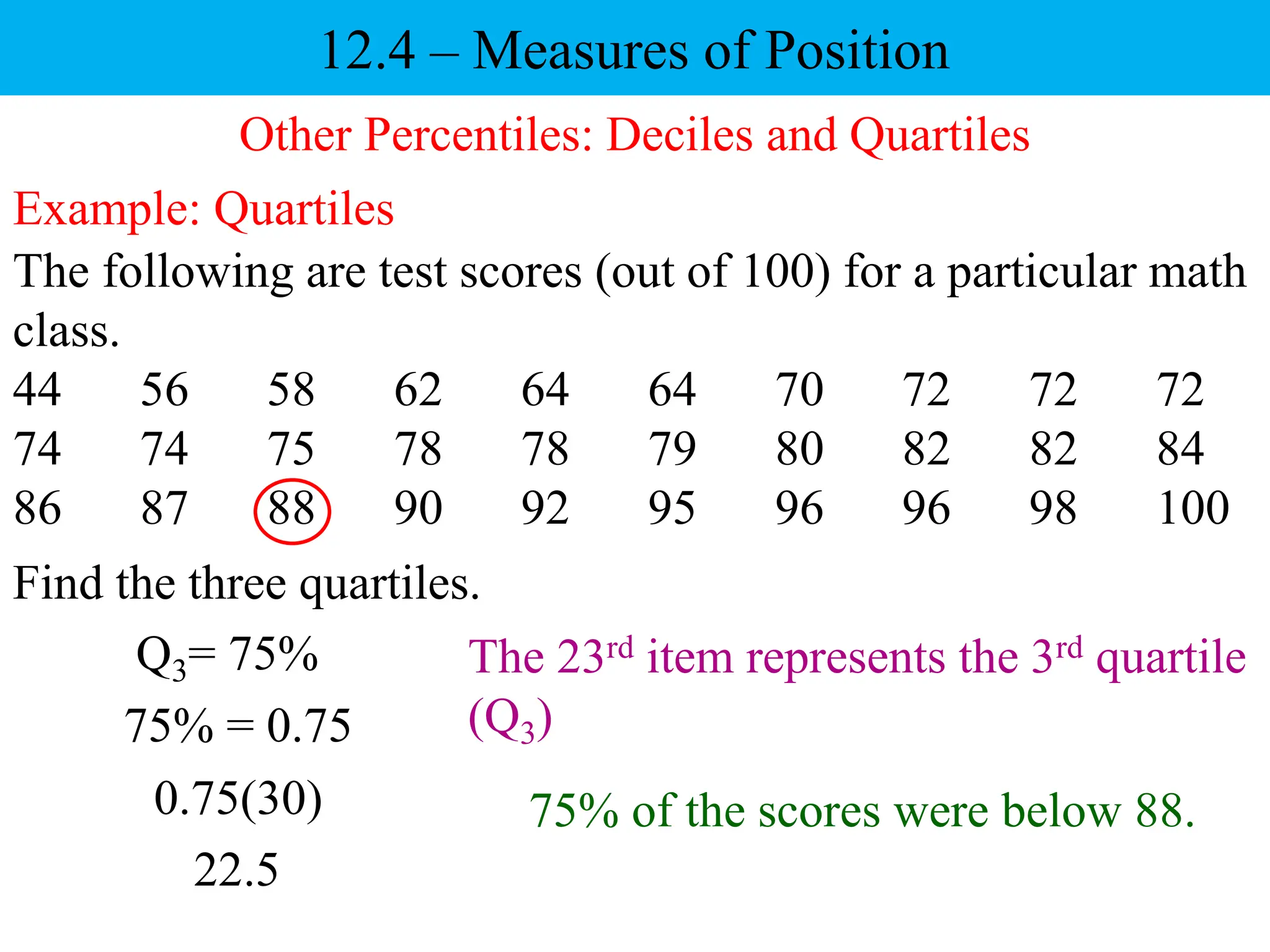
This document discusses different measures of position that can be used to compare individual data items or compare data sets. It defines percentiles, deciles, and quartiles. Percentiles indicate the percentage of values in a data set that are below a given value. Deciles and quartiles divide a data set into ten or four equal parts, respectively. Examples are provided to demonstrate how to calculate the 40th percentile, 6th decile, and the three quartiles for a data set of test scores.