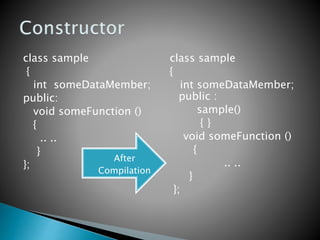
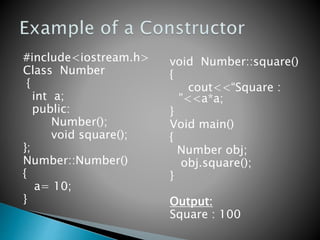
A constructor is a special member function that initializes the objects of a class. It has the same name as the class and is invoked automatically whenever a new object is created. Constructors ensure that objects are properly initialized. For example, a constructor for class add that initializes data members m and n to 0 would be automatically called when an add object is declared, initializing m and n without any other code.